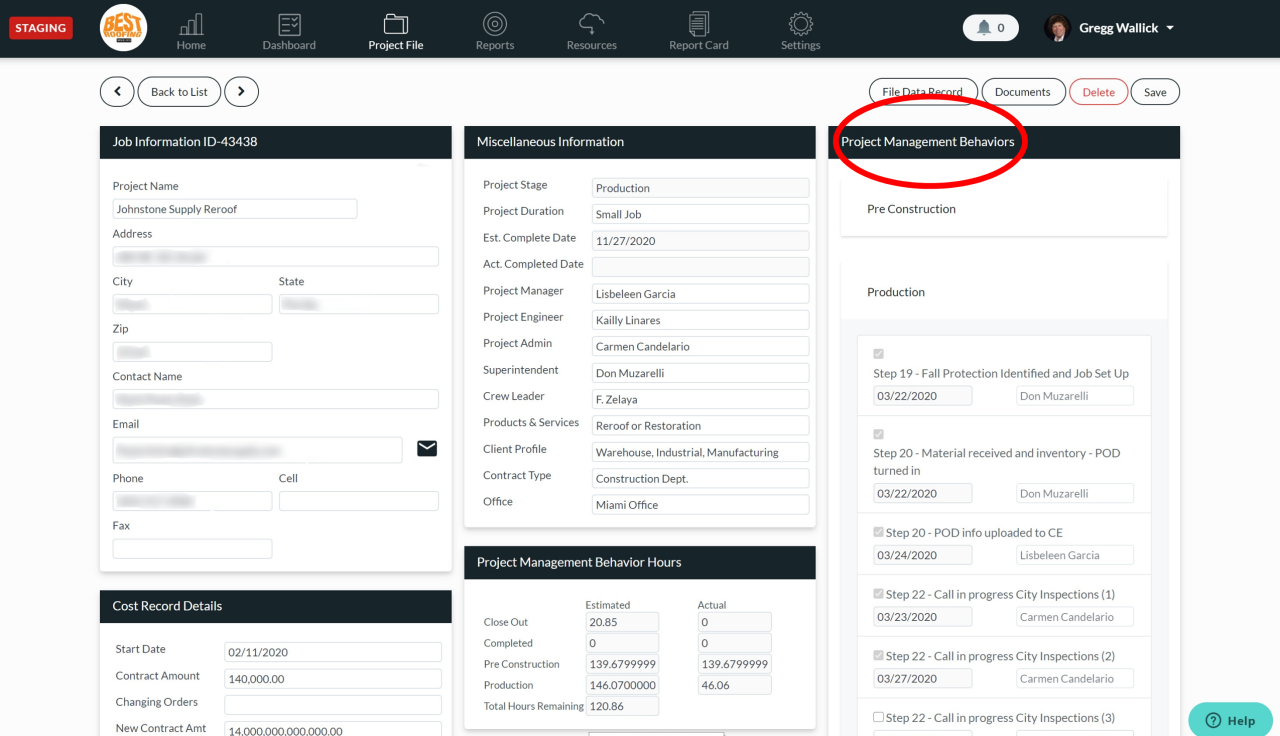
Follow-up CRM systems are essential for modern businesses seeking to optimize their sales and customer relationship management. They provide a structured approach to nurturing leads and maintaining contact with clients, automating crucial tasks and streamlining communication.
This guide delves into the intricacies of follow-up CRM systems, exploring their functionalities, benefits, implementation strategies, best practices, potential challenges, and future trends. We’ll cover everything from defining different types of systems to setting up automated follow-up sequences, ensuring a thorough understanding for anyone looking to leverage this technology.
Defining Follow-up CRM Systems
A follow-up CRM system is a specialized Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tool designed to streamline and optimize the follow-up process for sales leads, customer service interactions, and other business activities. It focuses on nurturing relationships, maintaining contact, and ultimately driving conversions. Unlike general CRM systems that manage a broad range of customer data, follow-up CRMs are specifically geared towards the action of maintaining contact and prompting engagement.These systems automate tasks, track interactions, and provide insights to improve the effectiveness of follow-up efforts.
They’re critical for businesses aiming to enhance customer engagement and achieve higher conversion rates. A well-implemented follow-up CRM system can significantly improve the efficiency of sales and customer service teams.
Key Functionalities of a Follow-up CRM System
Follow-up CRM systems offer a range of functionalities that empower businesses to manage and track their interactions with potential and existing customers. These systems typically integrate various tools to ensure a comprehensive approach to follow-up. Core functionalities include automated reminders, scheduling, and tracking of follow-up actions.
- Automated Reminders: The system automatically sends reminders to sales representatives or customer service agents about upcoming follow-up actions, such as scheduled calls, emails, or meetings. This ensures that no important interactions are missed.
- Scheduling and Tracking: Follow-up CRM systems allow users to schedule and track appointments, meetings, and other interactions with customers. This feature enables better organization and ensures timely follow-up.
- Interaction Logging: Detailed records of all interactions with customers are maintained, including emails, calls, and notes. This centralized repository ensures all relevant information is accessible.
- Lead Scoring and Prioritization: The system can analyze customer data and assign scores to leads, prioritizing those most likely to convert. This allows sales teams to focus on the most promising leads.
- Reporting and Analytics: Crucially, follow-up CRM systems provide comprehensive reports and analytics on follow-up activities. These reports help businesses identify areas for improvement and track the effectiveness of their follow-up strategies.
Types of Follow-up CRM Systems
Various types of follow-up CRM systems cater to different business needs and preferences. Their functionalities can vary significantly, impacting their overall utility. Some systems are specifically designed for sales teams, while others are geared towards customer service.
- Sales-focused Follow-up CRM Systems: These systems are primarily designed to manage and track sales leads, nurture relationships, and schedule follow-up activities to convert leads into customers.
- Customer Service-focused Follow-up CRM Systems: These systems focus on managing customer interactions, resolving issues, and tracking follow-up actions to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Hybrid Systems: These systems combine elements of both sales and customer service functionalities, offering a comprehensive approach to managing both lead nurturing and customer support interactions.
Comparison of Different Follow-up CRM Systems
Different follow-up CRM systems offer varying levels of customization, integration capabilities, and reporting features. The choice of a particular system often depends on the specific needs and requirements of the business. Consider factors like pricing, scalability, and ease of use.
- Customization Options: The level of customization offered by different systems varies. Some allow for extensive customization to match specific business processes, while others provide more limited options.
- Integration Capabilities: The ability to integrate with other business tools, such as email marketing platforms or marketing automation software, is critical. This seamless integration can significantly improve workflow efficiency.
- Reporting and Analytics Features: The depth and breadth of reporting and analytics features can significantly impact decision-making. Businesses need to carefully evaluate the types of reports available and their usefulness in identifying trends and improving performance.
Features of Prominent Follow-up CRM Systems
The following table illustrates the key features of three prominent follow-up CRM systems:
| Feature | System A | System B | System C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Management | Robust lead scoring, categorization, and nurturing tools | Comprehensive lead tracking and pipeline management | Advanced lead qualification and prioritization |
| Email Automation | Extensive email templates and automated sequences | Integration with popular email marketing platforms | Personalized email campaigns and triggered responses |
| Reporting & Analytics | Detailed dashboards and customizable reports | Intuitive visualization of key metrics | Predictive analytics for lead conversion |
Implementing Follow-up CRM Systems
Implementing a follow-up CRM system is a crucial step for optimizing sales processes and enhancing customer relationships. A well-implemented system can streamline communication, automate tasks, and provide valuable insights into customer interactions. This process requires careful planning, meticulous execution, and a commitment to ongoing optimization.
Step-by-Step Implementation Procedure
A structured approach is vital for a successful CRM implementation. This involves a series of steps, starting with a comprehensive assessment of current processes and ending with ongoing monitoring and refinement. This structured procedure ensures the system is tailored to specific business needs and integrates seamlessly with existing workflows.
- Needs Assessment: Thoroughly analyze current processes, identify pain points, and define specific requirements for the new system. This analysis should involve key stakeholders from various departments to ensure buy-in and alignment with organizational goals. Examples include identifying current customer communication channels, tracking sales pipelines, and managing follow-up activities.
- System Selection: Research and evaluate various CRM options, considering features, pricing, scalability, and integration capabilities. Factor in user-friendliness and the potential for future growth. Consider the specific needs of your sales team, marketing team, and customer support team when making your selection.
- Data Migration: Plan and execute the transfer of existing customer data to the new CRM system. This involves data cleansing, validation, and transformation to ensure data integrity and accuracy. Develop a detailed migration plan, including data mapping and testing procedures.
- System Configuration: Customize the CRM settings to match specific business processes and workflows. Define user roles, permissions, and access levels. This step ensures that the CRM aligns with your business’s operational structure and promotes efficient collaboration.
- Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training to all users on the new CRM system, including system navigation, features, and best practices. Establish a support system to address user queries and issues. Training materials should include practical examples, interactive exercises, and opportunities for hands-on practice.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the system to ensure it functions as expected and addresses the identified needs. Incorporate feedback from users and refine the system based on the testing results. This includes user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure the system meets the requirements.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Implement the system across the organization and monitor its performance to ensure it aligns with the expected outcomes. This includes continuous performance monitoring and making adjustments as needed.
Data Migration Process
Data migration is a critical phase in CRM implementation. A well-executed migration ensures a smooth transition and maintains data integrity. A robust plan is essential for a successful data migration.
- Data Inventory and Assessment: Identify all data sources, formats, and volume. Evaluate data quality, identify inconsistencies, and develop a plan to address any issues. This step helps to prepare the data for migration.
- Data Cleansing and Transformation: Cleanse and transform data to ensure consistency and accuracy. This involves standardizing formats, correcting errors, and resolving inconsistencies in data. Implement a robust data validation process.
- Data Mapping and Validation: Map existing data fields to corresponding fields in the new CRM system. Validate the mapped data to ensure accuracy and completeness. A detailed mapping document is crucial.
- Migration Execution: Execute the data migration plan. Monitor progress and address any issues that arise during the process. Choose a method for migration, either batch or real-time, and implement a backup strategy.
- Post-Migration Validation: Verify the accuracy and completeness of the migrated data in the new system. This ensures a seamless transition and minimizes data loss.
Training Requirements
Adequate training is crucial for successful CRM adoption. This ensures that employees can effectively use the system and maximize its benefits. Comprehensive training materials are essential for this step.
- Identify Training Needs: Assess the skills and knowledge of users and tailor training accordingly. Identify specific tasks and workflows that require training. Consider roles and responsibilities to ensure tailored training.
- Develop Training Materials: Create comprehensive training materials, including manuals, tutorials, videos, and interactive exercises. Use real-world examples to illustrate concepts and make the training more engaging.
- Deliver Training Sessions: Conduct hands-on training sessions to provide users with practical experience using the CRM. Encourage questions and address concerns promptly. Create a structured schedule for training.
- Post-Training Support: Provide ongoing support and resources after the initial training. Establish a help desk or FAQ section for continued access to information.
CRM Integration
Integration with existing tools is essential for seamless workflow. This includes ensuring compatibility and efficiency. A well-defined integration strategy is essential for success.
- Identify Integration Points: Identify all existing tools that need integration with the CRM system. Examples include email marketing platforms, marketing automation software, and sales reporting tools. This involves a detailed analysis of current workflow and identifying gaps.
- Choose Integration Methods: Evaluate various integration methods, such as APIs, middleware, or custom scripts. Consider factors like cost, complexity, and scalability. This includes choosing the right tools and strategies for integration.
- Configure Integrations: Configure the integrations to ensure data flows correctly between systems. This involves mapping data fields and defining triggers for data transfer. Ensure all systems are compatible.
Automated Follow-up Sequences
Automating follow-up sequences is a significant benefit of a CRM system. This streamlines communication and increases efficiency. Defining sequences is a key element.
- Define Follow-up Goals: Clearly define the objectives of each follow-up sequence. Examples include nurturing leads, scheduling appointments, or providing customer support. Consider your goals for each sequence.
- Create Sequence Steps: Design a series of automated steps within the sequence, including email messages, phone calls, or other actions. Ensure these steps are aligned with your goals.
- Schedule Trigger Points: Establish specific trigger points to initiate each step in the sequence, such as a lead submission or a missed call. Establish clear trigger points and conditions.
- Monitor and Optimize: Monitor the performance of automated sequences and adjust them as needed. This includes analyzing the effectiveness of each step and making improvements.
CRM Implementation Strategies
Different approaches can be employed during CRM implementation. Choosing the right strategy depends on various factors. This section details various implementation strategies.
| Strategy | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phased Implementation | Implementing the CRM system in stages, focusing on specific departments or functions. | Reduces risk, allows for gradual adaptation, and provides opportunities for feedback. | Can be slower, may require more resources for ongoing maintenance. |
| Big Bang Implementation | Implementing the entire CRM system simultaneously across the entire organization. | Faster implementation, potential for significant cost savings, allows for complete system adoption. | Higher risk of disruption, more challenging to adapt, potentially overwhelming for users. |
Best Practices for Effective Follow-up
Leveraging a CRM system for follow-up interactions significantly enhances customer engagement and conversion rates. This section details best practices for maximizing the effectiveness of your follow-up strategies, focusing on personalized sequences and tailored messaging for various customer segments.Effective follow-up isn’t just about sending emails; it’s about understanding your audience and crafting messages that resonate with their specific needs and preferences.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can nurture leads, maintain customer relationships, and drive sales.
Utilizing Follow-up CRM Systems
Implementing a structured follow-up system within a CRM empowers businesses to automate and personalize communications. A well-designed CRM system allows for the segmentation of customers based on various criteria, enabling targeted messaging and optimized follow-up sequences. By leveraging automation, businesses can ensure timely follow-ups, minimizing delays and maximizing engagement.
Creating Personalized Follow-up Sequences
Personalized follow-up sequences go beyond generic messages. Understanding customer behavior and preferences is key to crafting effective sequences. This involves analyzing customer interactions, purchase history, and demographics to tailor messages that address specific needs and desires. Consider incorporating interactive elements like polls or surveys to gauge customer feedback and adapt your follow-up strategy accordingly.
Tailoring Follow-up Messages to Different Customer Segments
Different customer segments require tailored follow-up messages. Analyzing customer demographics, purchase history, and engagement levels allows for the creation of distinct follow-up sequences. For example, a new customer segment might benefit from a series of introductory emails outlining product features and benefits, while returning customers might receive promotional offers or updates on new releases. Understanding customer journey stages is critical to crafting relevant and engaging messages.
Examples of Successful Follow-up Sequences
A successful follow-up sequence should be carefully planned and executed. For example, a company selling software might send an initial email outlining the product’s key features, followed by a second email highlighting specific benefits tailored to the recipient’s industry. A third email could offer a trial period or a discounted introductory price. This structured approach fosters engagement and increases the likelihood of conversion.
Comparing Email Follow-up Approaches
| Approach | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Follow-up | A straightforward approach that immediately follows up with a customer. | Can be effective for urgent or time-sensitive matters. | Can feel impersonal if not tailored to the customer. May not be suitable for nurturing long-term relationships. |
| Personalized Follow-up | Tailored messages that address specific customer needs and preferences. | High engagement potential, fosters stronger customer relationships. | Requires more effort and data analysis to personalize effectively. |
| Segmented Follow-up | Tailored messages based on customer demographics, behavior, and engagement. | Increases the relevance of the message and maximizes engagement potential. | Requires detailed customer data and segmentation strategies. |
Challenges and Solutions for Follow-up CRM
Implementing a follow-up CRM system, while offering significant benefits, can present various challenges. Understanding these potential hurdles and developing effective solutions is crucial for successful adoption and optimization. This section delves into common difficulties, offering practical strategies for overcoming them.Implementing a new system, even a well-designed one, requires a shift in workflow and potentially a change in employee habits.
Resistance to adopting new tools is a common obstacle, but it can be effectively mitigated by demonstrating the system’s value and offering comprehensive training.
Potential Implementation Challenges
Effective follow-up CRM implementation hinges on careful planning and consideration of potential roadblocks. Common challenges include resistance to change, inadequate training, data migration issues, and insufficient system customization. Addressing these issues proactively can significantly improve the chances of a successful rollout.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to adopt a new CRM system, fearing disruption to their established workflows. This resistance can stem from a lack of understanding of the system’s benefits or concerns about increased workload. Overcoming this requires clear communication, emphasizing the system’s potential for improved efficiency and productivity, and providing adequate training to ensure a smooth transition.
- Inadequate Training: Lack of proper training on the CRM system can lead to user confusion and frustration. A well-structured training program, encompassing hands-on exercises and practical examples, is essential to maximize user adoption and efficiency. Training should cover both the technical aspects of the system and the practical application of its features.
- Data Migration Issues: Migrating existing data to the new CRM system can be complex, requiring careful planning and execution. Inaccurate or incomplete data migration can lead to inconsistencies and errors in the system, impacting its effectiveness. Robust data validation and migration processes, coupled with meticulous testing, are crucial to ensure accurate data transfer.
- Insufficient System Customization: A CRM system that doesn’t align with specific business processes or workflows will likely prove inefficient. The system needs to be customized to fit the company’s unique requirements. This might involve tailoring the reporting tools or developing custom workflows to match specific business processes. Careful analysis of workflow and data needs will ensure the CRM is optimized for the company’s operations.
Common User Problems
Users may encounter various issues when utilizing a follow-up CRM system. These problems, if left unaddressed, can hinder productivity and create dissatisfaction.
- Difficulty Navigating the System: A complex or poorly designed interface can make the CRM system cumbersome to use. Intuitive navigation, clear labeling, and helpful user guides are essential for user satisfaction. Simple and easy to use interfaces with clear labeling will significantly reduce the user learning curve.
- Data Entry Errors: Inaccurate data entry can lead to flawed reports and decisions. Implementing data validation rules, automated data entry features, and clear data entry guidelines can minimize these errors. Robust data validation tools can identify and flag inaccurate data entry, preventing issues further down the line.
- Lack of Reporting Capabilities: If the CRM system lacks the ability to generate relevant reports, users might struggle to analyze their progress and identify areas for improvement. Comprehensive reporting features, tailored to specific needs, can provide valuable insights. Customizable reporting dashboards provide a streamlined view of key performance indicators.
Solutions to Address User Problems
Several solutions can address the problems users face when utilizing a follow-up CRM system. Addressing these issues proactively can lead to higher user satisfaction and increased system utilization.
- Improving User Interface: A user-friendly interface, with clear navigation and intuitive design, can significantly improve the user experience. Intuitive design, clear visual cues, and simplified navigation will enhance user experience and adoption.
- Implementing Data Validation: Robust data validation rules and automated data entry features can reduce errors and ensure data accuracy. Implementing automatic data entry tools and strict data validation checks can minimize errors in the system.
- Enhancing Reporting Features: Customizable reporting tools, tailored to specific business needs, can provide valuable insights into performance and progress. Customizable reporting options will provide greater insight and improved decision-making.
Overcoming Resistance to Adoption
Resistance to adopting a new CRM system can stem from various factors, but addressing these concerns proactively can lead to a smooth transition.
- Communicate the Value Proposition: Highlight the benefits of the CRM system, emphasizing how it will improve productivity, streamline workflows, and enhance decision-making. Demonstrating the value proposition and highlighting tangible benefits of the system will help overcome resistance.
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Offer hands-on training sessions, user guides, and online resources to equip users with the necessary skills to effectively use the CRM system. Thorough training programs will ensure user confidence and competence in using the system.
- Encourage Feedback and Iteration: Create a feedback loop to gather user input and suggestions for improvement. Allowing users to shape the system will increase engagement and adoption.
Troubleshooting CRM Errors
A well-defined troubleshooting process can help address CRM system errors quickly and effectively.
- Identify the Error: Carefully examine the error message or the symptoms of the problem. Precise error identification is the first step in troubleshooting.
- Check System Logs: Review system logs to determine the source and nature of the error. System logs can provide valuable clues for identifying and resolving errors.
- Consult Documentation: Refer to the CRM system’s documentation for troubleshooting steps and solutions. System documentation will contain the most accurate troubleshooting information.
- Contact Support: If the problem persists, contact the CRM vendor’s support team for assistance. Vendor support can provide expert assistance in resolving complex issues.
“The key to successful CRM implementation lies in a combination of meticulous planning, user-centric design, and continuous feedback. The system should not be imposed, but rather integrated into the existing workflow, making it an essential part of the daily operations.”
Future Trends in Follow-up CRM
Follow-up CRM systems are rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer expectations. This evolution is poised to reshape how businesses interact with prospects and clients, demanding adaptability and innovation. The future of follow-up CRM will be characterized by intelligent automation, personalized experiences, and a greater emphasis on data-driven insights.The future of follow-up CRM is not merely about improved efficiency, but about achieving a deeper understanding of customer needs and preferences.
This will be achieved through advanced analytics and machine learning, enabling a more proactive and personalized approach to customer engagement. By anticipating customer needs and proactively offering solutions, businesses can strengthen relationships and foster loyalty.
Predicting Future Trends in the Follow-up CRM Market
The follow-up CRM market is experiencing a shift towards systems that are more intuitive, user-friendly, and deeply integrated with other business tools. Businesses are increasingly seeking solutions that provide a holistic view of customer interactions, streamlining the entire customer journey. This trend reflects a growing need for efficient and automated processes, particularly in high-volume sales environments.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Follow-up CRM Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a significant driver of innovation in follow-up CRM systems. AI-powered chatbots are becoming more sophisticated, capable of handling a wider range of customer inquiries and requests. This automation frees up human agents to focus on more complex issues, leading to increased efficiency and customer satisfaction. Machine learning algorithms are also being integrated into CRM systems to identify patterns and predict customer behavior, enabling businesses to personalize their interactions and proactively address potential issues.
Further, the integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies could revolutionize the way businesses conduct client training and demonstrations.
Potential Future Applications of AI in Follow-up CRM Systems
AI can enhance follow-up CRM systems in numerous ways. Predictive analytics powered by AI can identify high-potential leads and personalize follow-up strategies accordingly. AI can also analyze communication data to determine the most effective times and channels for contacting customers, optimizing the entire follow-up process. Furthermore, AI can identify and categorize customer sentiment, allowing businesses to adapt their follow-up strategies based on customer feedback.
Examples of Innovative Follow-up CRM Features
Several innovative features are emerging in follow-up CRM systems. These include AI-powered sentiment analysis to gauge customer response to communications, dynamic scheduling tools to automate appointment setting, and personalized email templates that adapt to individual customer needs and preferences. Additionally, predictive lead scoring features, powered by machine learning, are becoming increasingly common, helping sales teams prioritize high-potential leads.
How Cloud-Based CRM Systems are Evolving
Cloud-based CRM systems are becoming more integrated with other business applications, such as marketing automation platforms and customer support systems. This integration facilitates a seamless customer journey, providing a comprehensive view of customer interactions across all touchpoints. Furthermore, cloud-based CRM systems are becoming more mobile-friendly, allowing sales teams to access and manage customer data on the go.
Comparison of Current and Future CRM Technologies
| Feature | Current CRM | Future CRM |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Relational databases, on-premise servers | Cloud-based, distributed databases, potentially using blockchain for enhanced security and transparency |
| Analytics | Basic reporting, dashboards | Advanced predictive analytics, real-time insights, AI-powered insights and recommendations |
Last Recap
In conclusion, implementing a robust follow-up CRM system can significantly improve sales processes and customer relationships. By automating tasks, personalizing interactions, and analyzing data, businesses can maximize their return on investment. Understanding the benefits, implementation strategies, and potential challenges is crucial for successful adoption. Ultimately, a well-managed follow-up CRM system empowers businesses to stay ahead in today’s competitive market.
Q&A
What are the common challenges in implementing a follow-up CRM system?
Resistance to change from employees, data migration issues, and inadequate training can pose significant hurdles. Also, integrating with existing systems and ensuring data accuracy are crucial for successful implementation.
How can I choose the right follow-up CRM system for my business?
Consider your specific needs and budget. Evaluate the features offered by different systems, such as lead management, email automation, and reporting capabilities. Thorough research and vendor comparisons are essential.
What is the difference between a basic and advanced follow-up CRM system?
Basic systems typically focus on fundamental features like email automation and contact management, while advanced systems often incorporate AI-powered features, more sophisticated reporting tools, and complex automation capabilities.
How do I integrate my existing marketing tools with a new follow-up CRM system?
Careful planning and a structured approach to integration are essential. Assess the compatibility of your existing tools with the CRM and consider using APIs or other integration methods.