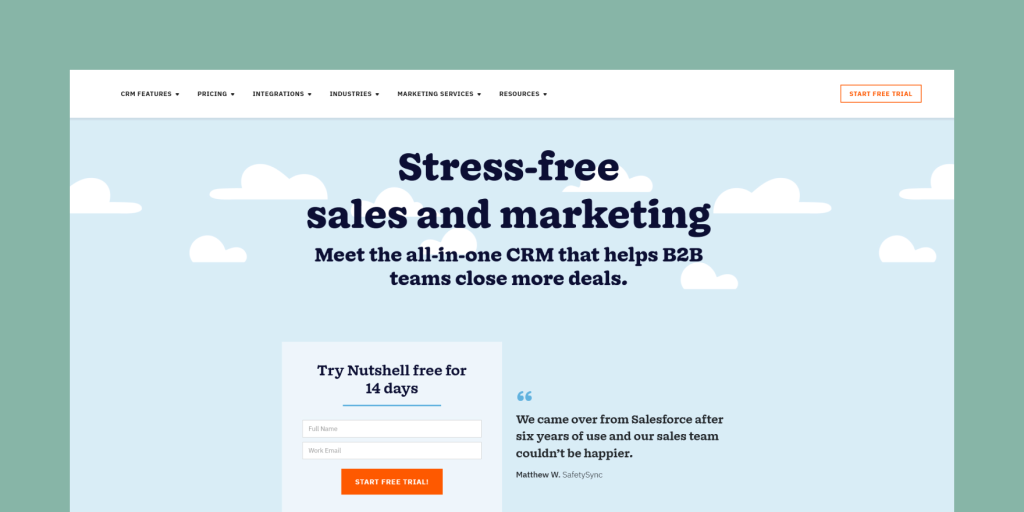
Finding the right sales software can be a game-changer for small businesses. It’s not just about tracking sales; it’s about streamlining operations, boosting efficiency, and ultimately, driving revenue. This guide dives deep into the world of sales software, exploring various options, key features, and practical implementation strategies.
From basic CRM tools to sophisticated marketing automation platforms, we’ll examine the different types of software available, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. We’ll also explore the common challenges small businesses face when choosing software and equip you with the knowledge to navigate the selection process confidently.
Introduction to Sales Software for Small Businesses
Sales software solutions are becoming increasingly crucial for small businesses aiming to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and ultimately, increase revenue. These tools provide a centralized platform for managing customer interactions, tracking sales progress, and automating various tasks, freeing up valuable time for business owners and their teams to focus on growth and strategic initiatives. By leveraging the power of these systems, small businesses can achieve greater control over their sales process and gain valuable insights into customer behavior and market trends.Utilizing sales software equips small businesses with essential tools for effective customer relationship management, marketing automation, and sales forecasting.
This empowers them to make data-driven decisions, optimize their sales strategies, and scale their operations effectively. By automating repetitive tasks and providing real-time data analysis, sales software fosters efficiency and profitability.
Overview of Sales Software Solutions
Sales software solutions encompass a wide array of tools designed to enhance various aspects of the sales process. These tools can be broadly categorized into CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems, marketing automation platforms, and sales forecasting and analytics tools. Each category offers specific functionalities tailored to address different business needs.
Key Benefits of Using Sales Software
Implementing sales software provides numerous advantages for small businesses. Improved efficiency and productivity are prominent benefits, stemming from automated tasks and streamlined workflows. Data-driven decision-making becomes possible through insightful reporting and analysis. Enhanced customer relationship management allows for personalized interactions and increased customer loyalty. Furthermore, sales software facilitates better sales forecasting, allowing businesses to anticipate future demands and adjust strategies accordingly.
Types of Sales Software
Sales software comes in various forms, each designed to cater to specific business requirements. Common types include CRM systems, marketing automation tools, and sales forecasting/analytics platforms. CRM systems are focused on managing customer interactions and relationships, while marketing automation platforms concentrate on streamlining marketing efforts. Sales forecasting and analytics tools provide insights into sales performance, enabling data-driven decisions.
Challenges in Choosing Sales Software
Small businesses often face challenges when selecting the right sales software. Budget constraints, the complexity of various software options, and the need for compatibility with existing systems are common hurdles. Finding software that aligns with specific business needs and growth goals is also critical. The time commitment to implementation and training can be a concern, requiring careful consideration of resource allocation.
Comparison of Sales Software Types
| Software Type | Key Features | Pricing | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRM | Customer relationship management, contact management, sales pipeline tracking, reporting and analytics. Examples include Salesforce, Zoho CRM. | Variable, ranging from free tiers to premium enterprise plans. | Businesses with a large customer base, complex sales processes, and a need for comprehensive customer interaction management. |
| Marketing Automation | Email marketing, social media management, lead nurturing, and campaign tracking. Examples include Mailchimp, HubSpot. | Variable, often with tiered pricing based on features and volume. | Businesses focused on digital marketing, lead generation, and nurturing customer relationships through automated campaigns. |
| Sales Forecasting/Analytics | Predictive modeling, sales trend analysis, sales pipeline forecasting, and data visualization. Examples include Tableau, Power BI. | Variable, often dependent on the level of sophistication and customization required. | Businesses requiring advanced insights into sales performance and future projections, including those with established sales teams and data-driven strategies. |
Essential Features of Effective Sales Software
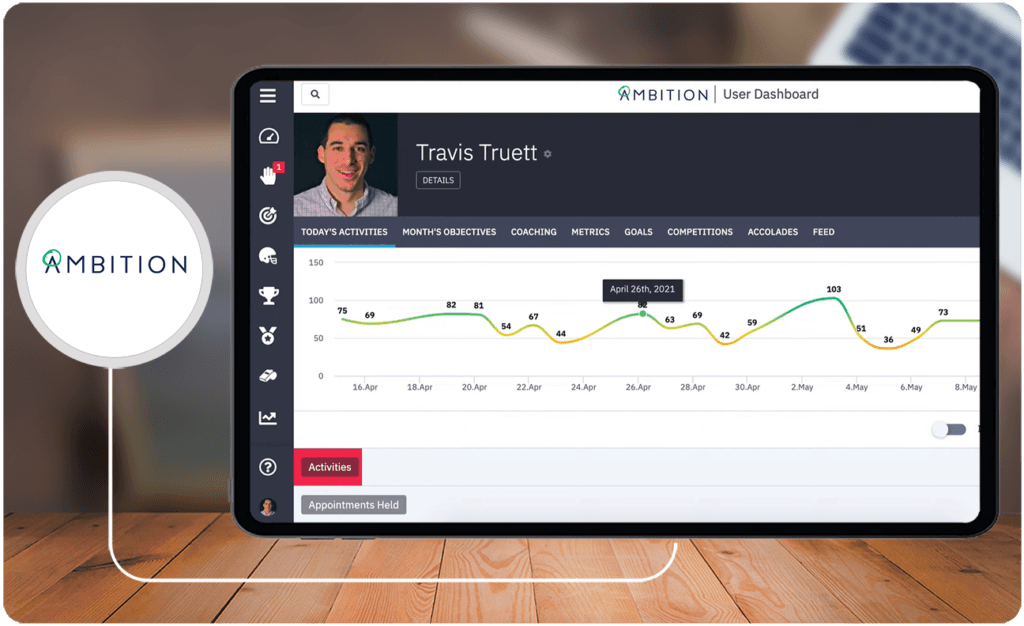
Small businesses often rely on robust sales software to streamline operations, improve customer engagement, and ultimately boost revenue. Effective sales software goes beyond simple record-keeping, providing a comprehensive suite of tools to manage the entire sales lifecycle. This detailed look at essential features highlights the critical components that transform sales processes for small businesses.Sales software today isn’t just about tracking deals; it’s about fostering relationships and understanding customer needs.
By automating tasks, providing valuable insights, and streamlining communication, sales software empowers businesses to excel in today’s competitive market.
Top 5 Must-Have Features
Small businesses need software that caters to their specific needs. The top 5 features for effective sales software are crucial for optimizing processes and achieving growth. These features provide a foundation for successful sales strategies.
- Lead Management: This feature allows businesses to capture, track, and nurture potential customers effectively. Lead management tools enable businesses to qualify leads, assign them to sales representatives, and schedule follow-up actions. This targeted approach increases the likelihood of converting prospects into paying customers. A robust lead management system automates tasks, ensuring potential customers are followed up with in a timely and consistent manner, significantly boosting sales.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): A powerful CRM system enables businesses to maintain comprehensive customer records, track interactions, and manage customer relationships. This data-driven approach fosters deeper customer understanding, allowing businesses to tailor their sales strategies to individual customer needs. Detailed customer history and preferences are crucial for targeted marketing and personalized service, resulting in increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Sales Forecasting: Sales forecasting enables businesses to predict future sales trends based on historical data and market insights. This allows businesses to plan their inventory, staffing, and marketing activities more effectively, leading to improved resource allocation and optimized sales performance. By anticipating demand, businesses can avoid costly overstocking or understocking issues.
- Reporting and Analytics: These features provide valuable insights into sales performance, allowing businesses to identify trends, measure key metrics, and make data-driven decisions. Analyzing sales data helps understand what works and what doesn’t, enabling businesses to adjust strategies and optimize their sales process. The ability to visualize sales data through charts and graphs is critical for quick comprehension and strategic decision-making.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with other business tools, such as accounting software or email marketing platforms, is essential for a streamlined workflow. This feature enhances efficiency by automating data transfer between systems, minimizing manual data entry, and improving overall productivity.
Customer Relationship Management Enhancement
Effective CRM features are vital for building strong customer relationships. CRM systems help businesses track customer interactions, preferences, and purchase history, enabling personalized service and targeted marketing campaigns. By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can improve customer satisfaction and retention.
- Customizable dashboards: A CRM system should provide customizable dashboards for sales representatives, allowing them to track key metrics and manage customer interactions effectively. This personalized view ensures that sales representatives have quick access to the data they need.
- Automated follow-ups: Automated email sequences and reminders for follow-ups ensure that potential customers are engaged effectively, increasing the likelihood of conversions.
- Personalized communication: Sales software should allow for personalized communication, addressing customers by name and referencing past interactions to create a more human and engaging experience. This fosters stronger customer relationships.
Significance of Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics features are critical for understanding sales trends and making data-driven decisions. Sales data, when properly analyzed, provides valuable insights into sales performance, allowing businesses to identify areas for improvement.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): The software should provide clear visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as conversion rates, average deal size, and customer lifetime value. Tracking these metrics allows for consistent evaluation of sales effectiveness.
- Sales funnel analysis: Analyzing the sales funnel helps identify bottlenecks and areas where improvements can be made to enhance conversions.
- Sales trend forecasting: Data-driven forecasting allows businesses to predict future sales and adapt their strategies accordingly. This enables better resource allocation.
Organizing and Accessing Customer Data
Effective sales software should offer diverse ways to organize and access customer data, ensuring that information is readily available to sales teams.
- Customizable fields: The ability to create custom fields for storing specific customer information, such as preferred communication methods or past purchase history, enables personalized engagement and targeted marketing campaigns.
- Customer segmentation: Segmenting customers based on various criteria, such as demographics, purchase history, or engagement level, allows for targeted marketing efforts and personalized communication.
- Secure data storage: Security features are paramount to protect sensitive customer data and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Intuitive User Interfaces
User-friendly interfaces are critical for ensuring that sales representatives can easily navigate and utilize the software. A well-designed interface streamlines tasks, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Clean and organized layouts: A clean and well-organized layout ensures that sales representatives can quickly find the information they need without confusion.
- Clear navigation: Easy navigation through different modules and features allows representatives to perform tasks efficiently without getting lost in the software.
- Intuitive design: Intuitive design elements, such as clear icons and simple language, enhance the user experience and reduce the learning curve for new users.
Comparing Popular Sales Software Options
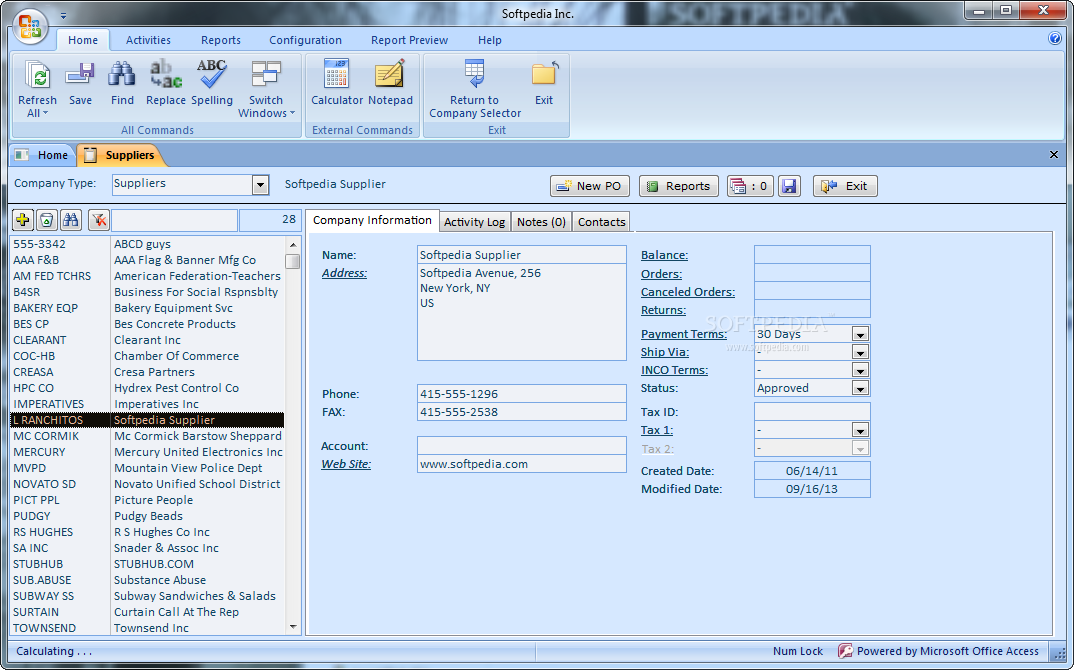
Choosing the right sales software can significantly impact a small business’s efficiency and profitability. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different options is crucial for making an informed decision. This section delves into comparisons of popular sales software, examining their features, pricing, and potential drawbacks to help you navigate the market.
Sales Software Solutions Comparison
Different sales software solutions cater to various needs and budgets. A comprehensive comparison necessitates examining several key aspects, including ease of use, reporting capabilities, customer support, and pricing models. This comparative analysis will focus on these critical factors to help you evaluate potential solutions.
| Software Name | Key Strengths | Potential Weaknesses | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce Sales Cloud | Robust CRM features, extensive customization options, strong reporting and analytics. Excellent for businesses with complex sales processes and significant data needs. | Steep learning curve, high initial setup costs, potentially overwhelming for smaller teams with simpler sales cycles. | Tiered pricing based on user volume and features. |
| HubSpot Sales Hub | Free tier available, user-friendly interface, excellent marketing automation integrations, and robust reporting. A good all-around option for businesses looking for comprehensive sales and marketing tools. | Limited customization options compared to Salesforce, potential for data silos with other HubSpot products. | Free plan available, tiered pricing for more features. |
| Zoho CRM | Affordable pricing, comprehensive features, easy-to-use interface, and mobile accessibility. Well-suited for small and medium-sized businesses looking for a reliable and feature-rich CRM. | Limited customization options compared to Salesforce, potential issues with integrations depending on the specific business needs. | Tiered pricing models based on user volume. |
| Freshsales | Focus on sales efficiency, intuitive interface, good customer support, and effective lead nurturing features. Suitable for businesses that prioritize straightforward sales management. | Limited reporting and analytics capabilities compared to other options, might not be the best fit for businesses with complex data needs. | Tiered pricing based on features and user volume. |
| Insightly | Easy-to-use interface, ideal for small businesses, great for project management integration, and robust customer relationship management. | Limited marketing automation features, may not be the best choice for businesses with large volumes of leads or a heavy marketing focus. | Monthly subscription fees, with different plans based on user needs. |
Pricing Models for Sales Software
Understanding the pricing models of different sales software solutions is essential for budgeting. Different pricing models exist, and they significantly affect the overall cost. For example, monthly subscriptions are common, offering flexibility but requiring ongoing payment. Some providers offer tiered pricing, where different plans offer varying feature sets, allowing businesses to choose the level of functionality they need.
Per-user pricing is another model, where the cost is determined by the number of users accessing the software.
Examples of Sales Software Interfaces
The user interface (UI) of sales software greatly impacts the user experience. A well-designed interface is intuitive and efficient, enabling users to easily navigate and manage data. Salesforce Sales Cloud’s interface is known for its robust customization capabilities, allowing users to tailor the experience to specific business needs. HubSpot Sales Hub, on the other hand, emphasizes a user-friendly approach with a straightforward layout for ease of use.
Zoho CRM presents a clean and organized interface, facilitating quick access to essential information. Each platform offers unique interfaces reflecting their specific features and target audience.
Practical Implementation and Integration
Choosing the right sales software and seamlessly integrating it into your existing business processes is crucial for success. A poorly implemented system can lead to wasted resources and decreased efficiency. Careful planning and a well-defined implementation strategy are key to realizing the full potential of your new sales software.A successful implementation involves more than just purchasing the software.
It necessitates a thorough understanding of your business needs, careful selection of the appropriate software, a structured setup process, effective data migration, and comprehensive employee training. The process must be tailored to your specific circumstances to ensure optimal outcomes.
Selecting the Right Sales Software for Your Business
Understanding your business’s unique needs is paramount. Consider factors like the size of your sales team, the complexity of your sales processes, the volume of data you manage, and your existing infrastructure. Analyzing these factors will help you narrow down the choices and identify software that aligns with your specific requirements. For example, a small startup might benefit from a cloud-based solution with affordable pricing, while a large enterprise might need a more robust system with advanced reporting and CRM capabilities.
Thorough research and evaluation of potential software options are essential to avoid costly mistakes.
Setting Up and Integrating with Existing Systems
The setup process should be meticulously planned, involving a dedicated team and clear communication channels. Careful consideration of existing systems and workflows is critical to avoid disruption. Integration with accounting software, CRM systems, or other crucial applications needs to be seamless and well-documented. Testing is vital to ensure the software functions as expected and integrates effectively with existing platforms.
Data Migration Strategies
Data migration is a crucial aspect of implementation. A well-defined plan is essential to ensure a smooth transition. This includes creating a detailed inventory of data to be migrated, mapping fields between the old and new systems, and validating the accuracy of the transferred data. A phased approach is often beneficial, allowing for thorough testing and verification at each stage.
For instance, migrating a portion of data first, followed by a full transfer, allows for more controlled and manageable data migration.
Employee Training and Adoption
Effective training programs are vital for employee adoption of new software. Training should cover the software’s features, functionalities, and practical applications within their daily tasks. Tailoring training to different roles within the sales team ensures that employees understand how to use the software effectively in their respective contexts. Regular follow-up sessions and hands-on practice can reinforce the training and address any arising questions.
Incentivizing employee participation and demonstrating the value proposition of the software to the team are also critical for success.
Successful Implementation Strategies
Successful implementation often involves adopting a phased approach, starting with a pilot group to identify and address potential issues before a full rollout. Close collaboration with the software vendor throughout the implementation process is essential. Regular communication and feedback mechanisms are crucial to ensure everyone is on the same page. For example, setting up clear milestones and timelines for different phases of implementation can help maintain momentum and track progress effectively.
Flowchart of Sales Software Selection and Implementation
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify Business Needs |
| 2 | Research and Evaluate Software Options |
| 3 | Select Suitable Software |
| 4 | Plan and Budget for Implementation |
| 5 | Configure and Integrate with Existing Systems |
| 6 | Migrate Data |
| 7 | Implement Employee Training |
| 8 | Monitor and Evaluate Performance |
| 9 | Iterate and Improve |
Success Stories and Case Studies
Seeing firsthand how sales software has transformed small businesses is incredibly insightful. Real-world examples illustrate the tangible benefits and demonstrate how these tools can significantly impact revenue, efficiency, and overall performance. These case studies provide a practical understanding of the software’s potential and demonstrate its effectiveness in a variety of contexts.
Small Business Sales Performance Improvements
Sales software empowers small businesses by streamlining operations and improving data management. This leads to better decision-making and ultimately, higher sales figures. The tools enable businesses to track leads, manage customer interactions, and automate tasks, which collectively reduces administrative overhead and allows sales teams to focus on closing deals. Examples include a reduction in time spent on manual tasks, improved lead conversion rates, and an increase in average deal size.
Streamlined Sales Processes
A key aspect of successful sales software is its ability to automate and streamline sales processes. By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can free up valuable time for their sales teams. This often translates to a faster sales cycle, improved customer satisfaction, and ultimately, increased revenue. For instance, automated email sequences and follow-up reminders can significantly improve the efficiency of sales outreach.
Lead nurturing and qualification are simplified through the use of software, allowing sales representatives to prioritize high-potential leads.
Example: “Tech Solutions”
“Tech Solutions,” a small software development company, initially struggled with managing multiple sales leads and follow-ups manually. Their sales team spent significant time on administrative tasks, hindering their ability to nurture leads effectively. After implementing sales software, “Tech Solutions” witnessed a notable improvement in their sales performance. The software automated lead qualification, nurturing, and follow-up emails, freeing up the sales team to focus on building relationships with potential clients.
The result was a 25% increase in conversion rates and a 15% rise in overall revenue within the first six months of implementation. The software also allowed for detailed reporting, enabling “Tech Solutions” to identify key sales trends and optimize their strategies. This led to more targeted marketing campaigns and a more efficient allocation of resources. The ability to track and analyze sales data in real-time was crucial for “Tech Solutions” to identify areas needing improvement and to make data-driven decisions.
Future Trends in Sales Software
The sales landscape for small businesses is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer expectations. Adapting to these shifts is crucial for staying competitive and ensuring sustainable growth. Sales software is at the forefront of this evolution, with emerging trends shaping the way businesses operate and interact with their customers.The future of sales software for small businesses will be characterized by an increasing focus on automation, integration, and mobile accessibility.
This shift empowers businesses to streamline operations, improve customer engagement, and ultimately boost sales performance. These trends are not just theoretical predictions; they’re already impacting businesses across various industries, from retail to services.
Mobile Accessibility and Cloud-Based Solutions
Mobile accessibility and cloud-based solutions are becoming paramount for sales teams. This allows for real-time data access and flexibility, crucial for today’s on-the-go professionals. Sales representatives can access customer information, track progress, and manage deals from anywhere with an internet connection. The shift towards cloud-based platforms ensures data security and accessibility for remote teams.
Integration with Other Business Systems
Sales software is no longer an isolated system. The need for seamless integration with other business applications, such as CRM, accounting software, and inventory management systems, is a significant trend. This integrated approach allows for a holistic view of the business, eliminating data silos and providing a complete picture of customer interactions and business performance. Such integration streamlines workflows and automates tasks, boosting efficiency and reducing manual data entry.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming sales software by automating tasks, providing insights, and personalizing customer interactions. Predictive analytics, powered by AI, can help sales teams identify potential leads, personalize outreach, and forecast future sales. Chatbots and automated email responses can handle routine inquiries, freeing up sales representatives to focus on high-value interactions. For instance, companies can use AI to analyze customer data and predict which customers are most likely to convert, leading to targeted marketing campaigns and optimized sales strategies.
Emphasis on Customer Experience (CX)
Modern sales software prioritizes improving the customer experience (CX). Features such as personalized recommendations, automated follow-ups, and seamless communication channels contribute to enhanced customer satisfaction. This trend recognizes that a positive customer experience directly correlates with increased sales and customer loyalty. Companies are now implementing sales software that allows them to tailor their interactions with customers based on individual preferences and needs.
Data Visualization and Reporting
Data visualization and reporting tools within sales software are becoming more sophisticated. Clear and actionable dashboards help sales teams track key metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. This ability to visualize data allows for a deeper understanding of sales performance and facilitates proactive adjustments to strategies. These tools enable sales managers to monitor team performance, pinpoint areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
Last Word
In conclusion, selecting the best sales software is a crucial step in scaling your small business. By carefully considering your specific needs, comparing different solutions, and understanding the implementation process, you can equip your team with the tools necessary to thrive. Remember, successful implementation goes beyond the software itself; it’s about empowering your team and fostering a culture of efficiency and customer focus.
Top FAQs
What are the most common challenges small businesses face when choosing sales software?
Budget constraints, the need for user-friendly interfaces, integration with existing systems, and finding software that aligns with the specific needs of the business are some common hurdles.
How can I determine the right pricing model for my sales software?
Pricing models vary widely, from subscription-based options to per-user costs. Consider your expected usage, the number of employees who will need access, and the features you require to choose the best option for your budget.
What are some tips for integrating new sales software with existing systems?
Thorough planning, clear data migration strategies, and training for employees are essential to ensure a smooth transition. Consider using APIs for seamless integration where possible.
What are some key considerations when choosing sales software for a specific industry?
The industry’s unique needs and sales processes should be a key factor. For example, a software tailored to the retail industry may offer different features compared to one designed for a service-based company.