IT CRM systems are revolutionizing how businesses manage customer interactions and data. From streamlining support tickets to boosting sales, these powerful tools offer a multitude of advantages. This guide delves into the intricacies of IT CRM, exploring its implementation, integration, and ongoing management.
This comprehensive overview examines the core functionalities of an IT CRM, including customer relationship management, service ticket tracking, and data analysis. We will explore best practices for successful implementation, integration with other business systems, and user adoption. Furthermore, the guide emphasizes the importance of performance measurement and reporting, security measures, and the ongoing adaptation to future technological trends. We’ll also look at examples of different IT CRM systems available in the market and their key features.
Introduction to IT CRM
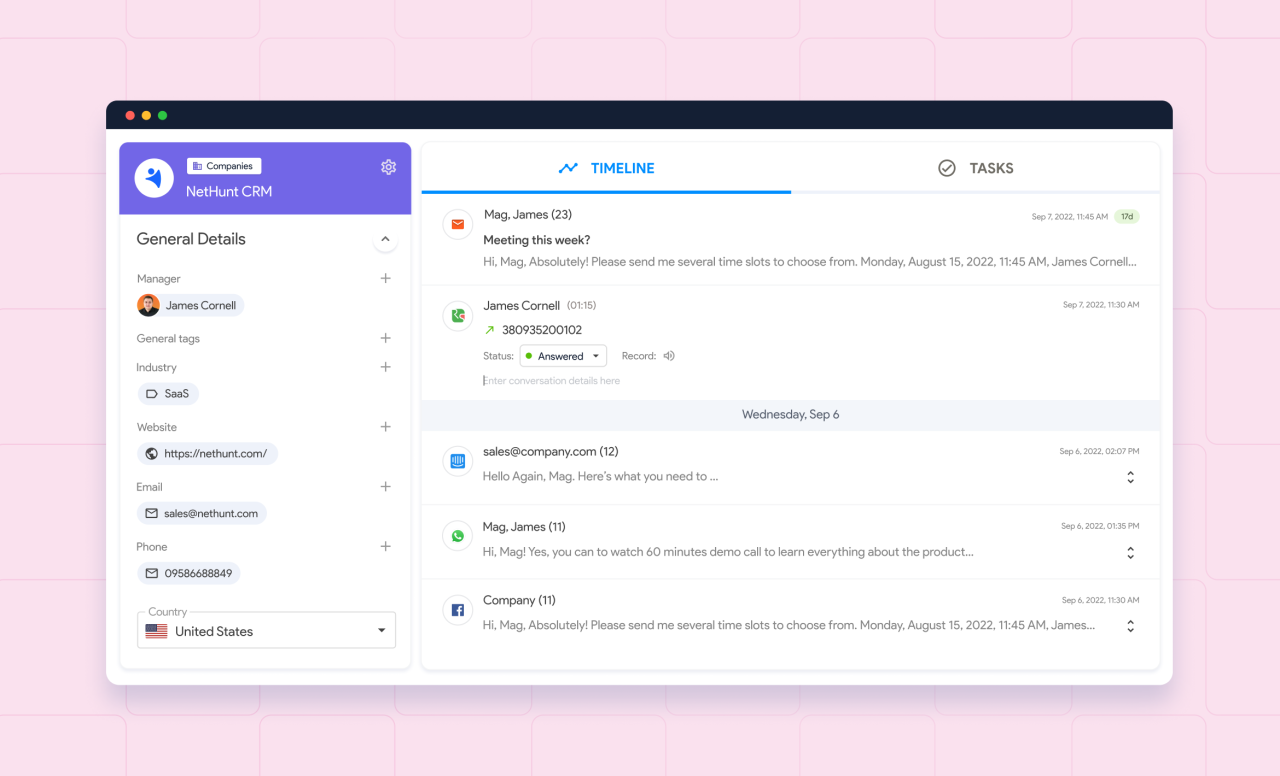
An IT CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a specialized software application designed to manage and streamline interactions with customers in the information technology sector. This includes everything from initial inquiries to ongoing support and future sales opportunities. Effective IT CRM systems provide a centralized platform for storing customer data, tracking interactions, and automating key processes.IT CRM systems are crucial for organizations in the tech industry to foster strong customer relationships, enhance service delivery, and drive revenue growth.
By efficiently managing customer information and interactions, IT CRMs facilitate improved communication, faster issue resolution, and ultimately, greater customer satisfaction.
Core Functionalities of an IT CRM System
IT CRM systems offer a wide array of functionalities to manage various aspects of the customer relationship. These functionalities often include:
- Contact Management: This involves storing and organizing detailed information about customers, including contact details, purchase history, support tickets, and preferences. Efficient contact management ensures quick access to crucial customer data, improving response times and service quality.
- Lead Management: IT CRMs aid in tracking potential customers (leads) throughout the sales funnel. This includes managing lead qualification, nurturing leads, and converting them into paying customers. This feature is vital for maximizing conversion rates and optimizing sales efforts.
- Support Ticket Management: IT CRMs streamline the process of managing customer support inquiries. This includes tracking tickets, assigning them to appropriate agents, and monitoring resolution times. Efficient support ticket management contributes to higher customer satisfaction and a positive brand image.
- Sales Force Automation: IT CRMs help automate various sales tasks, such as lead generation, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting. Automation improves efficiency and enables sales teams to focus on building relationships and closing deals.
- Reporting and Analytics: CRM systems generate valuable reports and insights on customer behavior, sales trends, and support performance. These insights help organizations make data-driven decisions, optimize strategies, and improve overall business performance.
Key Benefits of Implementing an IT CRM System
Implementing an IT CRM system offers a multitude of benefits to organizations in the tech industry. These benefits include:
- Improved Customer Relationships: IT CRMs provide a centralized platform to manage customer interactions, fostering better communication and understanding of customer needs. This leads to stronger customer relationships and increased loyalty.
- Enhanced Customer Service: By automating support tasks and providing access to customer data, IT CRMs improve the speed and quality of customer service responses. This results in happier customers and a positive brand image.
- Increased Sales Efficiency: Automating sales processes and tracking leads effectively improves the efficiency of sales teams, leading to increased sales opportunities and revenue generation.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: IT CRMs provide valuable data and insights that enable organizations to make informed decisions regarding marketing, sales, and customer service strategies. This data-driven approach leads to optimized resource allocation and improved ROI.
Examples of IT CRM Systems
Several IT CRM systems are available in the market, catering to diverse needs and budgets. Some prominent examples include Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, and Freshsales. Each platform offers a range of features and functionalities, tailored to different organizations and their specific requirements.
Comparison of IT CRM Systems
The table below provides a comparative overview of different IT CRM systems based on key features.
| CRM System | Pricing | User Interface | Scalability | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce | Typically starts in the thousands of dollars per user per year, with additional costs for custom features and support. | Modern and intuitive, but can be complex for users new to CRM systems. | Highly scalable, capable of handling large volumes of data and users. | Robust features across sales, marketing, and customer service. Known for extensive customization options. |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Pricing varies based on the specific features and functionalities selected. | Familiar and user-friendly for users accustomed to Microsoft products. | Highly scalable, offering options for both cloud-based and on-premises deployments. | Integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products, providing a comprehensive solution for businesses. |
| HubSpot | Offers various pricing tiers, ranging from free to enterprise-level plans. | User-friendly and intuitive, with a strong focus on ease of use. | Scalable, suitable for businesses of varying sizes. | Strong marketing automation capabilities, alongside sales and customer service tools. |
| Zoho CRM | Provides a range of pricing options, from free to premium tiers. | Intuitive and easy to navigate, with a focus on simplicity. | Scalable, capable of supporting growing businesses. | Comprehensive set of features, including sales automation, marketing automation, and customer support tools. |
| Freshsales | Offers various pricing options, focusing on affordable solutions for smaller and mid-sized businesses. | User-friendly and straightforward interface. | Scalable to accommodate growth. | Good for sales teams looking for efficient sales automation features. |
IT CRM Implementation Strategies
Implementing an IT CRM system is a significant undertaking requiring careful planning and execution. A well-defined strategy is crucial for success, ensuring the system aligns with business needs and provides a positive return on investment. A robust implementation process will streamline workflows, improve customer interactions, and ultimately drive business growth.A successful IT CRM implementation involves a phased approach, focusing on meticulous planning, careful execution, and ongoing monitoring.
This meticulous process will yield a smooth transition and efficient utilization of the system. This meticulous planning and execution are vital to maximize the CRM’s value and minimize potential disruptions.
Implementation Steps
A structured approach to implementation is essential for a successful IT CRM deployment. The process typically involves several key steps, each contributing to a seamless transition. These steps are crucial to ensure the system aligns with business goals and user expectations.
- Needs Assessment and Planning: Thoroughly analyze existing processes and identify areas where the CRM can improve efficiency and customer satisfaction. This crucial initial step includes defining clear goals, identifying key stakeholders, and mapping out the system’s integration with existing IT infrastructure.
- System Selection and Configuration: Choosing the right CRM system is vital. This step includes evaluating different options based on business requirements, budget constraints, and scalability needs. Configuration involves customizing the system to meet specific business processes and workflows, ensuring a tailored solution.
- Data Migration: Data migration is a critical step, involving the transfer of existing customer data into the new CRM system. This process requires careful planning and execution to ensure data accuracy and completeness. Proper data validation and cleansing procedures are paramount to ensure the system’s integrity.
- Training and User Adoption: Comprehensive training programs are essential to ensure users effectively utilize the new CRM system. This includes hands-on workshops, online tutorials, and dedicated support resources to facilitate user adoption and maximize system utilization.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support: The go-live phase marks the transition to the new system. Post-implementation support includes ongoing monitoring, feedback collection, and system adjustments to ensure optimal performance and address user concerns.
Implementation Approaches
Different implementation approaches exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these approaches is crucial for choosing the best fit for the organization’s specific circumstances.
- Phased Rollout: This approach involves implementing the CRM system in phases, typically starting with a pilot group or a specific department. This allows for iterative testing and refinement before full implementation, reducing risk and allowing for adjustments based on real-world experience. Phased rollouts are particularly useful for organizations with complex systems or a large number of users.
- Big Bang Implementation: This approach involves deploying the CRM system to all users simultaneously. While potentially faster, it carries higher risk due to potential disruptions and resistance from users. It’s best suited for organizations with a smaller number of users and a well-defined process.
Data Migration Importance
Data migration is crucial in IT CRM implementation, as it ensures a seamless transition from the old system to the new. Accurate and complete data transfer is paramount for the CRM system to function effectively and provide meaningful insights.
Accurate data migration is critical for a successful CRM implementation. Inaccurate data leads to unreliable insights and poor decision-making.
Potential Challenges
Several challenges can arise during IT CRM implementation. Recognizing and proactively addressing these issues is key to a successful project.
- User Resistance: Resistance to change can hinder user adoption and impact system effectiveness. Effective communication and training strategies are crucial to overcome this obstacle.
- Data Integrity Issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to unreliable reports and flawed decision-making. Rigorous data validation and cleansing procedures are essential.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the CRM with existing systems can be complex. Careful planning and a thorough understanding of the integration process are vital.
- Budget Constraints: Implementing a CRM can be expensive. Careful planning and cost management are essential to stay within budget.
Mitigation Strategies
Effective strategies can mitigate potential challenges and ensure a smooth implementation.
- Addressing User Resistance: Develop a communication plan that addresses user concerns and emphasizes the benefits of the new system. Provide comprehensive training to build confidence and proficiency.
- Maintaining Data Integrity: Establish rigorous data validation and cleansing procedures to ensure data accuracy and completeness. Utilize data quality tools to maintain data integrity.
- Managing Integration Complexity: Thoroughly analyze and plan the integration process, including testing and troubleshooting potential issues. Seek expert advice if necessary.
- Controlling Budget: Develop a detailed budget and stick to it. Identify cost-effective solutions and seek out potential funding opportunities.
Resource Allocation
A clear understanding of the resources required at each stage is vital. This includes personnel, budget, and time.
| Phase | Personnel | Budget | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Needs Assessment & Planning | Project Manager, Business Analysts | Project Initiation Costs | 2-4 weeks |
| System Selection & Configuration | IT Staff, Consultants | Software Licensing Fees | 4-6 weeks |
| Data Migration | Data Migration Specialists | Data Migration Costs | 4-8 weeks |
| Training & User Adoption | Training Specialists | Training Materials | 2-4 weeks |
| Go-Live & Post-Implementation Support | Support Staff, Project Manager | Ongoing Maintenance Costs | Ongoing |
IT CRM Integration with Other Systems
Integrating an IT Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system with other business applications is crucial for a streamlined and efficient workflow. This integration fosters a unified view of customer interactions, enabling better decision-making and improved overall operational performance. A well-integrated system allows for a seamless flow of data, reducing redundancies and improving data accuracy.
Importance of Integration
Effective integration between IT CRM and other business systems, such as accounting and project management, is paramount for several reasons. A unified system provides a holistic view of customer interactions, encompassing sales, support, and financial data. This holistic perspective allows for more informed decisions about customer relationships and business strategies. Integration also improves data accuracy by eliminating manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors.
This, in turn, leads to more reliable reporting and analysis.
Integration Methods
Several methods facilitate the integration of IT CRM with other systems. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are a common method, providing a structured way for different applications to communicate and exchange data. Middleware acts as an intermediary between different systems, translating data formats and ensuring seamless communication. Choosing the right integration method depends on the specific requirements of the IT CRM system and the other business systems being integrated.
Benefits of Integrating IT CRM with Specific Systems
| System Integrated | Benefits ||—|—|| Accounting System | Improved accuracy in revenue recognition, streamlined billing processes, automated invoice generation, and enhanced financial reporting. || Project Management System | Enhanced visibility into project timelines and customer interactions, enabling more efficient project management and improved customer satisfaction. || Inventory Management System | Real-time inventory tracking, optimized stock levels, improved order fulfillment, and reduced stock-outs, thus increasing efficiency and minimizing costs.
|| Marketing Automation System | Improved customer segmentation and targeted marketing campaigns, automated email marketing, lead nurturing, and enhanced customer lifetime value (CLTV). |
Security Concerns
Security is a critical concern when integrating IT CRM with other systems. Protecting sensitive customer data and ensuring the integrity of data exchange is paramount. Robust security protocols, including encryption and access controls, are essential to mitigate risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.
Data Synchronization
A crucial aspect of integration is data synchronization. This process ensures that data is consistently updated across all integrated systems. Real-time synchronization is ideal, but near-real-time updates are also effective. The method of synchronization needs to be carefully chosen to ensure data integrity and minimize disruptions to business operations. For instance, a two-way synchronization method allows for updates to be reflected in both CRM and the other system.
IT CRM User Adoption and Training
User adoption is critical to the success of any IT CRM system. A poorly adopted system, no matter how sophisticated, will not deliver the expected ROI. Successful implementation hinges on a robust training program and clear communication channels that address user needs and concerns.Effective training and ongoing support are crucial to ensure that users understand and utilize the system’s capabilities, maximizing its potential benefits.
This, in turn, fosters a positive user experience and encourages continued system use. A well-structured training program, combined with ongoing support, is paramount to achieving high user adoption rates.
Significance of User Adoption
User adoption is paramount for a successful IT CRM implementation. High adoption rates translate to increased efficiency, improved data accuracy, and better decision-making across the organization. Conversely, low adoption rates lead to wasted resources, frustrated users, and ultimately, a system that fails to deliver its intended value. Companies that prioritize user adoption see significant gains in productivity and operational effectiveness.
Comprehensive Training Program
A comprehensive training program is a cornerstone of user adoption. The program should be tailored to the specific needs of different user groups within the organization. For example, sales representatives may require training focused on lead management and opportunity tracking, while customer service representatives might need training on handling customer inquiries and resolving issues effectively. This targeted approach ensures that users acquire the necessary skills to maximize the system’s value for their roles.
Clear Communication and Support
Clear communication and ongoing support are essential for successful user adoption. Regular updates, clear documentation, and readily available help resources should be provided to address user questions and concerns. This includes easily accessible FAQs, online tutorials, and dedicated support channels. Prompt and helpful support reduces user frustration and ensures users feel empowered to utilize the system effectively.
Potential User Resistance
User resistance to new systems is a common phenomenon. Users may be hesitant to adopt new technologies due to concerns about learning new processes, unfamiliar interfaces, or fear of losing control over their workflow. Understanding these concerns is critical to addressing them effectively.
Assessment of User Satisfaction
A systematic approach to assessing user satisfaction is crucial to identifying areas for improvement. Regular feedback mechanisms, such as surveys, focus groups, and one-on-one interviews, should be implemented to gauge user satisfaction with the system. Gathering this feedback allows for the identification of areas where the training or support could be improved, fostering a more positive user experience.
Key metrics such as system usage frequency and user satisfaction scores should be monitored to assess the effectiveness of the implementation.
Effective User Training Materials
Various training materials can be utilized to enhance user understanding and proficiency with the IT CRM system. These materials include comprehensive user manuals, step-by-step video tutorials, interactive webinars, and role-playing exercises. These materials should be designed to be accessible, engaging, and easy to understand.
Example of Effective Training Materials
User Manuals
Detailed, well-organized manuals with clear instructions, screenshots, and examples of how to perform various tasks within the system. These should be available in both print and digital formats.* Video Tutorials: Short, concise videos demonstrating specific tasks or functionalities of the IT CRM system. These should be easily accessible on a dedicated training portal.* Webinars: Interactive webinars conducted by IT experts, allowing users to ask questions and receive real-time assistance.
These should cover specific modules and functions, such as lead management or opportunity tracking.* Role-Playing Exercises: Interactive sessions where users practice using the system in realistic scenarios. This practical approach can help users develop confidence and proficiency.
IT CRM Performance Measurement and Reporting
Effective IT CRM implementation hinges on consistent monitoring and evaluation. A robust performance measurement framework provides valuable insights into the system’s impact on business processes, identifying areas of success and highlighting opportunities for improvement. This ensures the CRM investment yields maximum return on investment (ROI).A well-structured reporting system, coupled with accurate data analysis, allows for proactive adjustments to CRM strategies.
This data-driven approach facilitates informed decision-making, optimizing resource allocation, and maximizing the CRM’s contribution to organizational goals.
Methods for Measuring IT CRM Effectiveness
Several methods contribute to assessing the effectiveness of an IT CRM implementation. These include tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), analyzing user feedback, and comparing pre- and post-implementation data. Quantitative and qualitative data sources provide a holistic perspective on CRM performance. For instance, comparing sales figures before and after implementation offers a measurable benchmark.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for IT CRM
A comprehensive set of KPIs is essential for evaluating IT CRM performance. These indicators should align with business objectives and provide a clear picture of the system’s contribution. Examples include sales conversion rates, customer retention rates, and average customer lifetime value.
Framework for Generating IT CRM Performance Reports
A structured framework for generating reports is crucial. This involves defining specific reporting periods, establishing clear reporting formats, and ensuring consistent data collection. Reports should be easily accessible and understandable by relevant stakeholders. This includes executives, sales teams, and customer service representatives.
Tracking and Analyzing IT CRM Use Data
Tracking and analyzing data related to IT CRM usage is paramount for understanding user behavior and system performance. Tools that provide detailed activity logs, access reports, and usage trends are vital for identifying areas of system inefficiency. Data analysis reveals patterns and insights for targeted improvements.
Importance of Regular Performance Reviews
Regular performance reviews are critical for continuous improvement. Reviews enable organizations to identify and address issues proactively, adapt strategies, and maintain alignment with evolving business needs. This ongoing feedback loop allows for system optimization and ensures the CRM remains a valuable asset.
Table of KPIs and Tracking Methods
| KPI | Description | Tracking Method | Example Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Conversion Rate | Percentage of leads that convert into sales. | Track the number of leads converted to sales over a specific time period, and divide by the total number of leads. | 85% of leads converted to sales in Q3 2024. |
| Customer Retention Rate | Percentage of customers retained over a specific period. | Divide the number of customers retained by the total number of customers at the start of the period. | 92% customer retention rate in the last quarter. |
| Average Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | Total revenue generated from a customer throughout their relationship with the company. | Calculate the total revenue generated from each customer over their entire relationship and find the average. | Average CLTV of $5,000 per customer. |
| Customer Support Response Time | Average time taken to respond to customer support requests. | Track the time taken to respond to each support request and find the average. | Average response time of 24 hours. |
| System Uptime | Percentage of time the system is operational. | Monitor system logs and identify periods of downtime. | 99.9% system uptime in the last month. |
IT CRM Security and Compliance
Robust security measures are crucial for protecting sensitive customer data within an IT CRM system. A breach can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Implementing appropriate security protocols and adhering to data privacy regulations is paramount for maintaining trust and ensuring the long-term success of the CRM system.Protecting sensitive data in an IT CRM environment requires a multi-layered approach encompassing various security protocols.
This includes not only technical safeguards but also policies and procedures for user behavior and data handling. Understanding and complying with relevant data privacy regulations is equally critical to mitigating potential risks and ensuring legal compliance.
Security Measures to Protect Sensitive Data
Implementing strong access controls is essential to limit access to sensitive customer data. This involves establishing user roles with specific permissions, restricting access to data based on roles, and regularly reviewing and updating access rights. Employing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing the system. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is also a critical measure to protect data from unauthorized access.
Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system.
Data Privacy Regulations
Several data privacy regulations globally affect the management of customer data within an IT CRM system. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States are prominent examples. These regulations mandate organizations to implement measures to protect personal data, provide individuals with control over their data, and ensure transparency in data handling practices.
Understanding the specific requirements of each jurisdiction is crucial for ensuring compliance. For instance, GDPR mandates explicit consent for data collection, while CCPA grants consumers the right to access, delete, and correct their personal data. Adherence to these regulations is critical to avoiding hefty fines and potential legal challenges.
Best Practices for Maintaining Data Security
Maintaining a strong security posture requires a proactive approach. Regular software updates are essential to patch vulnerabilities and ensure the system is protected against emerging threats. Employee training on data security best practices is paramount, as human error often plays a significant role in security breaches. Implementing robust incident response plans allows organizations to effectively address security incidents and minimize the impact on operations.
Regular security awareness training for employees can help prevent phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics.
Potential Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
Common security risks include malware infections, phishing attacks, and insider threats. Malware can compromise the system and steal sensitive data, while phishing attacks attempt to trick users into revealing their credentials. Insider threats can arise from employees with malicious intent or those who inadvertently expose sensitive information. Vulnerabilities in the system’s architecture or software can also be exploited by attackers.
Regular security assessments and penetration testing help identify and mitigate these risks.
Ensuring Compliance with Relevant Regulations
Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations involves several steps. A comprehensive data privacy policy should be developed and communicated to all employees. Data mapping exercises can help identify all personal data held within the IT CRM system. Regular audits of the data privacy policy and procedures are necessary to identify any gaps and ensure ongoing compliance. Regularly reviewing and updating the system’s security controls is critical to address evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
Seeking legal counsel to ensure compliance with relevant regulations is also recommended.
Security Protocols and Importance
| Security Protocol | Importance |
|---|---|
| Multi-factor Authentication | Adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain access. |
| Data Encryption | Protects data in transit and at rest, preventing unauthorized access. |
| Regular Security Audits | Identifies vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system, allowing for proactive remediation. |
| Employee Training | Reduces the risk of human error and social engineering attacks. |
| Incident Response Plan | Enables organizations to effectively address security incidents and minimize their impact. |
Future Trends in IT CRM
IT CRM systems are constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. Emerging technologies are driving innovation, creating new opportunities, and reshaping how companies interact with their customers. This section explores the key future trends in IT CRM, focusing on emerging technologies, anticipated features, and the impact on overall usage.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly transforming IT CRM systems, enabling more intelligent and personalized customer interactions. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex issues. Machine learning algorithms analyze customer data to predict future behavior, allowing businesses to proactively address potential problems and tailor offers to individual preferences. For example, a retail company might use AI to identify customers likely to abandon their shopping carts and send targeted promotions.
Future Direction of IT CRM Systems
The future of IT CRM systems lies in their ability to provide comprehensive customer insights and facilitate seamless omnichannel interactions. Systems will increasingly integrate with other business applications, providing a unified view of the customer across all touchpoints. Predictive analytics will play a crucial role in anticipating customer needs and proactively addressing issues. Personalized experiences will be central, driven by AI and machine learning capabilities.
Innovative IT CRM Features
Several innovative features are anticipated in future IT CRM systems. These include:
- AI-powered chatbots: These chatbots can handle routine inquiries, providing instant support and reducing wait times.
- Predictive analytics: Using historical data and machine learning, CRM systems can predict customer behavior, enabling proactive interventions and personalized offers.
- Omnichannel integration: CRM systems will seamlessly integrate with other communication channels (e.g., email, social media, mobile apps), offering a unified view of the customer across all touchpoints.
- Personalized recommendations: AI algorithms will analyze customer data to provide highly tailored product recommendations, increasing customer satisfaction and sales.
Impact of Mobile Technologies
Mobile technology is transforming how businesses interact with customers. Mobile-first CRM systems are becoming increasingly common, allowing for real-time access to customer data and interactions from anywhere. Mobile apps provide employees with on-the-go access to customer information, enabling more efficient service and support. For instance, field service technicians can use mobile CRM apps to update customer records, schedule appointments, and track inventory in real-time.
Adapting to Future Business Needs
To meet the evolving needs of businesses, IT CRM systems must be adaptable and scalable. Cloud-based CRM solutions offer flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust resources based on their growth. Systems should also be designed with open APIs, enabling integration with other business applications and future technologies. Customizable dashboards and reporting tools are essential for providing relevant insights to stakeholders.
Potential Impact of Different Technologies
| Technology | Potential Impact on IT CRM Systems ||—|—|| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Enhanced personalization, predictive analytics, automation of tasks || Machine Learning (ML) | Improved customer segmentation, prediction of customer behavior, proactive support || Mobile Technology | Real-time access to customer data, improved customer service, omnichannel integration || Cloud Computing | Scalability, accessibility, cost-effectiveness || Internet of Things (IoT) | Enhanced customer insights, proactive service, personalized experiences |
Last Word
In conclusion, implementing and effectively utilizing an IT CRM system is a significant investment that can significantly enhance a business’s operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and profitability. By understanding the various facets discussed in this guide, businesses can make informed decisions and build strategies for long-term success. The future of IT CRM is bright, with emerging technologies promising even more advanced features and capabilities.
FAQ Explained
What are the common pitfalls in IT CRM implementation?
Resistance from users, inadequate training, poor data migration strategies, and insufficient resources are common pitfalls in IT CRM implementation. A robust implementation plan that addresses these potential challenges can significantly increase the chances of success.
How can I ensure data security in an IT CRM system?
Implementing strong access controls, regular security audits, and adhering to relevant data privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA are crucial steps to ensure data security in an IT CRM system. This involves encrypting sensitive data and having a robust disaster recovery plan in place.
What are some key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring IT CRM success?
Key performance indicators for IT CRM success include customer satisfaction scores, sales conversion rates, support ticket resolution times, and the return on investment (ROI) of the system. Tracking these KPIs helps businesses gauge the effectiveness of their IT CRM strategy.
What are the different types of IT CRM systems available?
The IT CRM market offers a range of solutions, from cloud-based platforms to on-premise systems. Factors like scalability, pricing models, and specific functionalities should be considered when selecting a suitable system for your business needs.