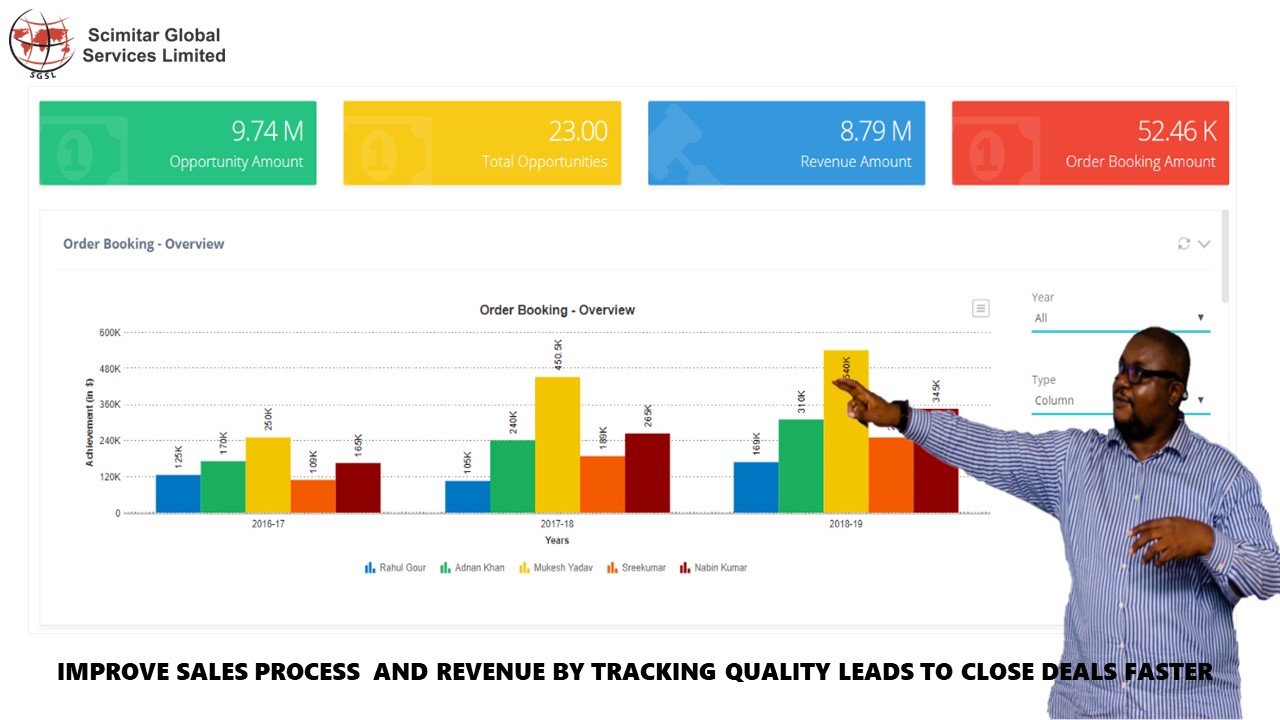
Customer relationship management (CRM) applications are rapidly transforming how businesses interact with their customers. From streamlining sales processes to enhancing customer service, CRM systems offer a powerful toolkit for improving overall business performance. This guide delves into the intricacies of CRM applications, examining their evolution, benefits, selection, implementation, and the impact of emerging technologies.
This guide explores the core functionalities of CRM applications, highlighting the different types, key features, and how they can benefit businesses of all sizes. We’ll analyze how these applications drive customer satisfaction, boost sales, and contribute to customer retention.
Introduction to Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Applications
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) applications are software systems designed to streamline and manage interactions with customers throughout the entire customer lifecycle. They provide a centralized platform for businesses to store, track, and analyze customer data, leading to improved customer satisfaction, enhanced sales processes, and increased profitability. Effective CRM implementation fosters stronger customer relationships, ultimately driving business growth.CRM applications have evolved significantly over the years.
Early CRM systems primarily focused on sales force automation. However, as technology advanced and business needs became more complex, CRM systems incorporated marketing and service functionalities. Today, modern CRM systems offer a comprehensive suite of tools to manage all aspects of the customer relationship, from lead generation to customer service resolution. Key trends include cloud-based deployment, mobile accessibility, and integration with other business applications.
Different Types of CRM Applications
CRM applications are broadly categorized into three main types: sales CRM, marketing CRM, and service CRM. Each type focuses on different aspects of the customer relationship. Sales CRM systems primarily focus on streamlining the sales process, while marketing CRM systems help to manage and analyze marketing campaigns, and service CRM systems aim to improve customer support and service delivery.
Key Features of CRM Applications
CRM applications commonly incorporate several key features to support effective customer relationship management. These features include lead management, customer interaction tracking, sales forecasting, marketing campaign management, and customer support ticket management. These features work together to provide a holistic view of the customer relationship, enabling businesses to personalize interactions and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Comparison of CRM Application Types
| Feature | Sales CRM | Marketing CRM | Service CRM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Management | Tracks potential customers, manages lead qualification, and routes leads to sales representatives. Examples include lead scoring systems and automated lead assignment. | Manages leads and prospects, identifies and categorizes leads, and helps segment customer audiences for targeted marketing campaigns. This might involve using lead scoring to prioritize leads for specific campaigns. | Manages customer support tickets, tracks issues and resolutions, and provides a centralized platform for customer interactions. This might include automated ticket routing and escalation procedures. |
| Customer Interaction Tracking | Records and manages interactions with prospects and customers, including calls, emails, and meetings. This data helps track sales progress and identify areas for improvement. | Tracks customer engagement with marketing campaigns, analyzes responses to campaigns, and measures campaign effectiveness. This includes data on website visits, email opens, and social media interactions. | Records and manages customer interactions related to support requests, complaints, and feedback. This enables resolution of issues and enhances customer service efficiency. Examples include tracking call logs and support ticket resolution times. |
Benefits of Utilizing CRM Applications
CRM applications are proving increasingly valuable for businesses of all sizes. They offer a structured approach to managing customer interactions, fostering stronger relationships, and driving business growth. By streamlining processes and providing valuable insights, CRM systems can significantly enhance operational efficiency and overall profitability.Implementing a CRM system allows businesses to centralize customer data, providing a comprehensive view of each customer’s history, preferences, and interactions.
This unified view enables businesses to tailor their approach to individual customer needs, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and loyalty. Furthermore, the data-driven insights derived from CRM applications can inform strategic decisions, helping businesses adapt to changing market demands and stay ahead of the competition.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
CRM systems empower businesses to personalize interactions with customers. By analyzing customer data, businesses can understand individual preferences and tailor communication strategies accordingly. For example, a customer who frequently expresses interest in a specific product line might receive targeted marketing materials related to that product. This personalized approach can lead to higher customer satisfaction, as customers feel valued and understood.
Proactive communication, such as automated reminders about appointments or service updates, further enhances the customer experience and reinforces positive impressions.
Enhanced Sales Processes
CRM applications streamline sales processes, allowing sales teams to focus on high-potential leads and close deals more efficiently. By tracking interactions, managing leads, and automating tasks like follow-ups, CRM systems free up valuable time for sales representatives to dedicate to relationship building and deal closure. For example, a CRM system can automatically alert a sales representative when a potential customer expresses interest in a particular product, enabling prompt follow-up and increased conversion rates.
The detailed insights provided by CRM systems also help sales teams identify trends and patterns in customer behavior, allowing for more effective sales strategies.
Customer Retention
Customer retention is a crucial aspect of business success. CRM applications facilitate effective customer relationship management, enabling businesses to build stronger customer relationships and reduce churn. By tracking customer interactions and preferences, businesses can identify potential issues and proactively address them, ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty. For instance, a CRM system can automatically send thank-you notes or birthday greetings, fostering a sense of appreciation and value.
Personalized service and timely responses to customer inquiries contribute significantly to higher customer retention rates.
Top 5 Benefits for Small Businesses
Small businesses often face unique challenges in managing customer relationships. CRM applications provide essential tools for small businesses to efficiently manage their customer interactions, leading to enhanced productivity and profitability.
- Streamlined Customer Interactions: CRM systems allow small businesses to centralize customer data, making it easily accessible to all relevant team members. This streamlined approach facilitates quicker responses to customer inquiries, improves communication, and strengthens overall customer relationships.
- Improved Sales Management: CRM systems help small businesses track sales leads, manage customer interactions, and automate follow-up tasks. This improved sales management efficiency can lead to higher conversion rates and increased sales revenue, which is particularly crucial for small businesses.
- Enhanced Customer Relationship Building: CRM systems empower small businesses to personalize customer interactions, leading to stronger customer relationships. Personalized communication and targeted marketing campaigns foster customer loyalty, increasing the lifetime value of each customer.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences. These data-driven insights enable small businesses to make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and service improvements.
- Cost-Effective Operations: By automating tasks and streamlining processes, CRM applications can significantly reduce administrative overhead. This cost-effectiveness is especially important for small businesses with limited resources.
Choosing the Right CRM Application
Selecting the appropriate CRM application is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize customer interactions and drive growth. A poorly chosen CRM can lead to wasted resources and hinder efficiency, whereas a well-suited system can significantly enhance productivity and improve customer satisfaction. Careful consideration of various factors is paramount in this process.A successful CRM implementation hinges on understanding a company’s specific needs and aligning the chosen system with its overall strategic goals.
This necessitates a thorough evaluation of available features and functionalities to ensure that the chosen application adequately supports the business’s operational requirements and future growth plans. By following a structured approach, companies can select a CRM solution that not only meets current needs but also scales with future demands.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a CRM Application
Understanding the key factors to consider when evaluating CRM applications is essential. A thorough analysis ensures the chosen system effectively supports the business’s objectives and long-term goals. This includes evaluating the system’s ability to integrate with existing software, its scalability to accommodate future growth, and the level of support offered by the vendor.
- Business Needs and Goals: The selected CRM should align perfectly with the specific needs and goals of the business. This requires a clear understanding of the business processes, workflows, and the desired outcomes of implementing a CRM system. For example, a small startup might prioritize ease of use and affordability, while a large enterprise might focus on robust reporting and advanced analytics capabilities.
- Features and Functionalities: Evaluating the available features and functionalities is vital. This includes assessing the system’s capabilities in managing contacts, tracking sales leads, automating marketing campaigns, and providing customer support. The specific features required will vary greatly based on the industry and business size. A retail company might require detailed inventory management features, whereas a service-based business might prioritize customer service automation.
- Integration Capabilities: The chosen CRM should integrate seamlessly with existing systems, such as accounting software, email marketing platforms, and other business applications. This seamless integration minimizes data redundancy and streamlines workflows. Poor integration can lead to significant data discrepancies and operational inefficiencies.
- Scalability and Future Growth: The CRM solution should be scalable to accommodate future growth and expansion. As the business evolves, the chosen system should be able to adapt to increased data volumes, user demands, and evolving business processes. A poorly scalable system can become a bottleneck as the company expands.
- Vendor Support and Training: A reliable vendor with excellent customer support is essential. Comprehensive training programs are crucial to ensure that users can effectively utilize the system. Robust documentation, online resources, and responsive support teams are vital elements to consider.
Evaluating Different Features and Functionalities
A thorough evaluation of CRM features is crucial for a successful implementation. This involves a deep dive into each feature’s functionality to ascertain its alignment with business objectives. It also includes considering the user interface, data security, and overall ease of use.
- Contact Management: The system’s contact management features should allow for detailed information storage, organization, and efficient search capabilities. Consider the fields needed, such as contact details, communication history, and relevant notes.
- Sales Management: Evaluate the CRM’s capabilities in managing sales leads, tracking sales pipelines, and automating sales processes. Consider the reporting and analytics features that provide insights into sales performance.
- Marketing Automation: Assess the CRM’s marketing automation features, including email marketing, social media integration, and campaign management tools. Consider how these tools will enhance marketing efforts and customer engagement.
- Customer Service Management: Evaluate the CRM’s ability to manage customer inquiries, track issues, and provide efficient support. This includes the features for ticket management, knowledge base access, and customer feedback collection.
Step-by-Step Guide to Selecting the Right CRM Application
A structured approach to CRM selection is crucial for a successful implementation. This guide provides a step-by-step approach.
- Define Business Needs: Clearly articulate the specific requirements and goals for the CRM system. This includes identifying the key business processes and desired outcomes.
- Research CRM Applications: Identify potential CRM applications that align with the defined needs and goals. Explore various providers and their offerings.
- Evaluate Features and Functionalities: Thoroughly evaluate the key features and functionalities of each potential CRM. Consider how well each system aligns with the specific business requirements.
- Trial and Test: Utilize trial periods or demos to test the selected CRM systems and gain firsthand experience with their functionality and user interface. This will help determine whether the system is suitable for the business’s workflow.
- Select and Implement: Based on the evaluation and testing, select the most suitable CRM application and implement it within the business environment. Ensure a smooth transition and comprehensive training.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Choosing a CRM
[A visual flowchart illustrating the steps involved in selecting a CRM application would be presented here. The flowchart would clearly Artikel the decision-making process from defining needs to implementing the selected system.]
Implementing and Managing CRM Applications

Implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) application is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. A well-implemented CRM system can streamline business processes, enhance customer interactions, and drive significant improvements in profitability. However, successful implementation necessitates a structured approach, encompassing careful planning, employee training, data migration, ongoing maintenance, and clear roles and responsibilities.A successful CRM implementation requires a deep understanding of the business processes, workflows, and the specific needs of each department.
This involves close collaboration with key stakeholders to identify the system’s functionalities that align with the organization’s goals. By implementing a CRM system that caters to the organization’s needs, businesses can optimize their customer interaction, boost efficiency, and enhance their overall business performance.
Steps Involved in Implementing a CRM Application
Implementing a CRM system involves a series of crucial steps. These steps are designed to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the system’s effectiveness. A phased approach, from initial assessment to ongoing maintenance, is vital. This ensures a robust and sustainable CRM system that supports long-term business growth.
- Needs Assessment and Planning: Thoroughly analyze existing business processes and identify areas where the CRM can improve efficiency. Develop a detailed project plan, outlining timelines, budget, and resource allocation. This includes defining specific business objectives that the CRM should help achieve.
- Selection and Configuration: Choose the CRM system that best aligns with your business requirements. Configure the system to match your specific workflows and data structures. This involves mapping existing processes to CRM functionalities and ensuring the system’s ability to integrate with other business applications.
- Data Migration and Integration: Migrate existing customer data into the CRM system. Ensure data accuracy and consistency. Integrate the CRM with other relevant systems, such as accounting or marketing automation platforms. This step is critical to maintaining a unified view of customer interactions across all departments.
- User Training and Adoption: Provide comprehensive training to employees on how to use the CRM effectively. Implement a support system to address user queries and concerns. This will increase employee proficiency and enhance adoption rates.
- Pilot Testing and Refinement: Implement the CRM in a pilot group to test its functionality and identify areas for improvement. Gather feedback and make necessary adjustments to optimize the system’s performance. This crucial step ensures the system functions as intended before a full-scale implementation.
- Go-Live and Ongoing Support: Transition the entire organization to the CRM system. Provide ongoing support and training to ensure smooth operation and address any emerging issues. Regular monitoring and adjustments are necessary for optimal CRM performance.
Importance of Employee Training
Thorough training is critical for successful CRM adoption. Trained employees are more likely to utilize the CRM effectively, leading to improved customer service and increased productivity.Employee training should cover not only the technical aspects of the system but also how to use it to improve their daily tasks and interactions with customers. This includes training on CRM functionalities, data entry procedures, and how to access and utilize relevant customer information.
Procedures for Data Migration and Integration
Data migration and integration are critical to maintaining data accuracy and consistency. A meticulous process is essential to avoid data loss or errors.
- Data Validation and Cleaning: Ensure the accuracy and completeness of the data being migrated. Identify and correct any inconsistencies or errors in the data. This ensures the integrity of the customer data within the CRM system.
- Data Mapping and Transformation: Map the fields in the old system to the corresponding fields in the new CRM system. Transform data formats and structures to ensure compatibility. This step ensures that the migrated data is properly organized and accessible in the new CRM.
- Data Testing and Verification: Thoroughly test the migrated data to verify its accuracy and completeness. Conduct data quality checks to ensure that the data is reliable and up-to-date. This step ensures that the data is usable and reliable for business operations.
Strategies for Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
Maintaining a CRM system involves continuous updates and adjustments to adapt to evolving business needs.
- Regular Updates and Patches: Stay updated with the latest software releases and patches to ensure security and functionality. Regular updates are crucial for maintaining the system’s performance and security.
- System Monitoring and Performance Tuning: Regularly monitor system performance to identify and resolve bottlenecks or issues. Optimize the system’s configuration to maintain optimal performance. This ensures that the CRM is functioning efficiently and without delays.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implement a robust data backup and recovery plan to protect against data loss. This ensures business continuity and protects against unforeseen circumstances.
Responsibilities of Different Roles in Managing a CRM Application
Clear delineation of responsibilities among different teams is vital for successful CRM management.
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Sales Team | Utilizing the CRM for lead management, opportunity tracking, sales forecasting, and reporting. Collaborating with the marketing team on lead qualification and nurturing. |
| Marketing Team | Using the CRM for campaign management, lead generation, customer segmentation, and performance tracking. Collaborating with the sales team to ensure smooth lead flow. |
| Customer Service Team | Utilizing the CRM for customer interaction tracking, issue resolution, feedback management, and knowledge base development. Providing support to customers and escalating issues as needed. |
CRM Applications and Emerging Technologies
Modern CRM applications are constantly evolving, adapting to the rapid advancements in technology. This evolution allows businesses to leverage innovative tools and strategies to enhance customer interactions, improve operational efficiency, and ultimately, drive business growth. The integration of emerging technologies is transforming the CRM landscape, leading to more intelligent, personalized, and accessible customer experiences.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are profoundly impacting CRM applications. These technologies enable businesses to analyze vast amounts of customer data to identify patterns, predict customer behavior, and personalize interactions. For example, AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to address more complex issues. Machine learning algorithms can identify potential churn risks, enabling proactive interventions to retain valuable customers.
This proactive approach can lead to significant cost savings and improved customer lifetime value.
Role of Mobile Technology
Mobile technology has revolutionized CRM applications, making customer interactions more accessible and convenient. Mobile CRM apps enable sales representatives to access critical customer information on the go, allowing for real-time updates and improved responsiveness. The ability to access and update customer records from anywhere allows for increased efficiency and agility in customer service. Field service technicians, for instance, can use mobile CRM applications to access detailed customer information, schedule appointments, and track progress, streamlining the entire service process.
Cloud Computing in CRM
Cloud-based CRM applications offer numerous advantages, including scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Businesses can easily scale their CRM resources up or down as needed, responding dynamically to fluctuating demands. The accessibility of cloud-based solutions from anywhere with an internet connection empowers employees to work more efficiently, regardless of their location. Cost savings are often realized through reduced infrastructure and maintenance expenses, allowing businesses to allocate resources to other critical areas.
Transformation by Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, while not as prevalent in CRM as other technologies, is emerging as a powerful tool for enhancing data security and transparency. By recording transactions on an immutable ledger, blockchain ensures data integrity and reduces the risk of fraud. This enhances trust between businesses and customers, fostering long-term relationships. This technology can be applied to track products and services throughout the supply chain, improving transparency and traceability.
This transparency, in turn, strengthens customer trust and loyalty. For example, a company selling high-value items can use blockchain to track the product’s origin and authenticity, providing customers with verifiable proof of quality and reducing concerns about counterfeiting. This verifiable provenance strengthens customer trust and confidence in the brand.
Case Studies of CRM Applications
CRM applications have demonstrably transformed businesses across various industries. These systems, when implemented effectively, can streamline operations, enhance customer relationships, and ultimately drive revenue growth. Examining successful implementations provides valuable insights into best practices and potential pitfalls.Real-world case studies illuminate the transformative power of CRM systems, highlighting how they’ve enabled companies to achieve specific objectives and overcome challenges.
By understanding these successful applications, businesses can gain a clearer picture of the potential benefits and navigate the complexities of implementation.
Successful CRM Implementations in Different Industries
Implementing a CRM system is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Different industries face unique challenges and opportunities. Understanding how various businesses have successfully leveraged CRM systems provides a more nuanced perspective.
- Retail: A major online retailer, by integrating a CRM system, improved customer segmentation. This allowed them to personalize marketing campaigns, resulting in a 15% increase in conversion rates. Targeted promotions based on purchase history and browsing behavior boosted sales and customer loyalty.
- Financial Services: A bank utilized a CRM system to manage customer interactions and track account activity. This led to improved customer service response times and reduced customer churn by 10%. The system also enabled more accurate risk assessments, which strengthened their overall financial strategy.
- Healthcare: A medical practice implemented a CRM to manage patient records and communication. This system improved appointment scheduling efficiency, reducing wait times and enhancing the overall patient experience. Improved communication also fostered stronger patient relationships.
Real-World Scenarios Showcasing Positive Impact
CRM applications, when effectively integrated, can significantly impact business operations. These scenarios showcase the positive outcomes that can be achieved.
- Enhanced Customer Service: A customer service department, using a CRM system, recorded and tracked customer interactions. This enabled faster resolution of issues and improved customer satisfaction. Customer satisfaction ratings increased by 20%.
- Improved Sales Performance: A sales team, employing a CRM system, organized leads and tracked sales activities. This resulted in a 15% increase in sales conversion rates. The system also allowed for more targeted sales strategies and better forecasting.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: A marketing team utilized a CRM system to analyze customer data. This allowed them to identify trends and preferences, which enabled more effective marketing campaigns and improved return on investment (ROI). The system provided data-backed insights that led to a 10% increase in marketing ROI.
Challenges Faced During Implementation and How They Were Overcome
Implementing a CRM system can be complex, with potential challenges. Understanding how these challenges were addressed provides valuable insights for future implementations.
- Resistance to Change: Many employees are resistant to adopting new systems. To overcome this, companies invested in comprehensive training programs and emphasized the benefits of the new system for the entire organization. Regular communication and feedback sessions also helped to address concerns and ensure employee buy-in.
- Data Migration Issues: Migrating existing data into a new system can be challenging. Companies used data validation tools and expert consultants to ensure data accuracy and completeness. Careful planning and testing minimized errors and downtime.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating the CRM system with existing software and systems can be complex. Companies chose vendors with a proven track record of successful integrations and worked closely with IT teams to ensure a seamless transition.
Case Study: XYZ Corporation
XYZ Corporation, a mid-sized manufacturing company, implemented a CRM system to manage customer relationships and streamline sales processes. The system provided a centralized platform for storing customer data, tracking interactions, and managing sales opportunities. By integrating sales and marketing efforts, XYZ Corporation saw a significant improvement in lead conversion rates and a 20% increase in sales revenue. The CRM system also improved customer service response times, resulting in higher customer satisfaction scores.
Addressing initial resistance to change through comprehensive training programs and clear communication played a crucial role in the success of the implementation.
Future Trends in CRM Applications
CRM applications are evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and a heightened focus on the customer experience. These developments are reshaping how businesses interact with their customers, promising more personalized, efficient, and valuable engagements. This section will explore key future trends, emphasizing the role of emerging technologies, personalization, data analytics, and the transformative impact of a particular trend on the CRM landscape.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
The CRM landscape is being reshaped by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). AI-powered chatbots are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling businesses to automate customer service interactions and provide instant support. Machine learning algorithms are capable of analyzing vast amounts of customer data to identify patterns and predict future behaviors, leading to proactive engagement strategies.
The integration of IoT devices provides businesses with real-time insights into customer behavior, allowing for tailored experiences and proactive issue resolution.
Personalization and Customer Experience
Personalization is no longer a desirable feature, but a critical requirement in CRM applications. Advanced CRM systems are leveraging AI and ML to analyze customer data, enabling businesses to tailor products, services, and communications to individual needs. This personalized approach leads to a more positive customer experience, fostering loyalty and driving revenue growth. Examples of successful personalization include targeted marketing campaigns, customized product recommendations, and proactive support tailored to specific customer issues.
Data Analytics in CRM
Data analytics plays a crucial role in enabling businesses to extract actionable insights from customer data. Advanced analytics techniques such as predictive modeling and sentiment analysis are employed to identify trends, predict future behaviors, and understand customer preferences. This information is then used to optimize marketing strategies, improve customer service, and personalize customer experiences. Real-world examples include identifying high-risk customers to prevent churn or tailoring product recommendations based on past purchases.
The Role of AI in Shaping the Future of CRM
Artificial intelligence is poised to revolutionize CRM applications by automating tasks, providing personalized experiences, and facilitating data-driven decision-making. AI-powered chatbots are becoming increasingly sophisticated, handling routine customer service inquiries, providing instant support, and freeing up human agents to handle more complex issues. The use of AI in predictive modeling allows businesses to anticipate customer needs and preferences, enabling proactive engagement strategies.
One compelling example is the use of AI in identifying potential customer churn, allowing companies to intervene and retain valuable customers.
Last Point
In conclusion, customer relationship management applications have become an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to optimize their interactions with customers. From initial implementation to ongoing maintenance, understanding the intricacies of CRM systems is crucial for success. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, enabling businesses to navigate the complexities of CRM and leverage its potential to drive growth and success.
The future of CRM is bright, with emerging technologies promising further innovation and opportunities.
User Queries
What are the typical costs associated with implementing a CRM system?
CRM implementation costs vary significantly depending on factors like the chosen platform (cloud-based vs. on-premises), the size of the business, the complexity of the system, and the level of customization required. Licensing fees, integration costs, training, and potential ongoing maintenance expenses should all be considered.
How can a business determine if a CRM system is the right fit for their needs?
Businesses should evaluate their current customer relationship processes, identify pain points, and assess their future growth objectives. A thorough analysis of existing data management practices and projected growth will help determine if a CRM system will provide the necessary functionality to meet future needs. It’s also important to consider the size of the team, the volume of customer interactions, and the potential scalability of the system.
What are the key differences between cloud-based and on-premises CRM systems?
Cloud-based CRM systems offer greater accessibility and scalability, typically requiring lower upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. On-premises CRM systems offer greater control and customization, but involve significant upfront costs and ongoing infrastructure management.
How do CRM applications help improve customer satisfaction?
CRM systems enable businesses to better understand customer needs and preferences through centralized data collection and analysis. This leads to personalized interactions, faster response times, and more effective issue resolution, ultimately improving customer satisfaction.