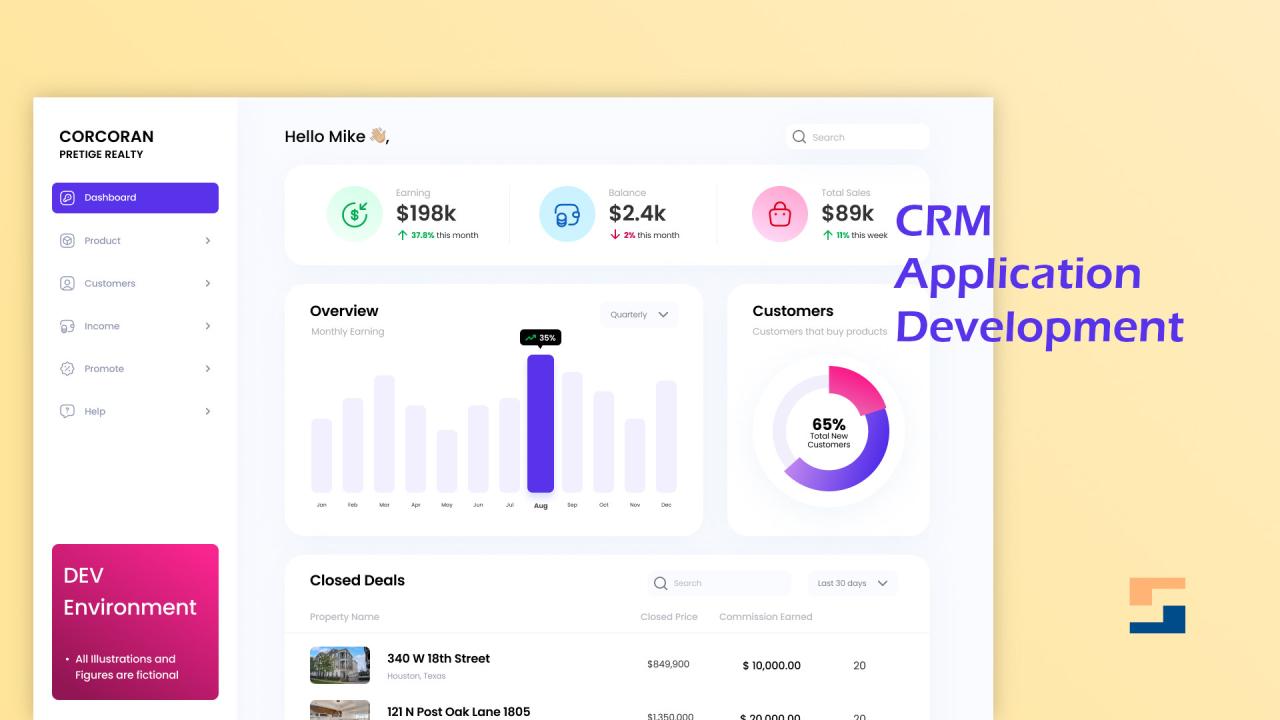
CRM applications are transforming how businesses interact with customers. They’re not just software; they’re strategic tools that streamline processes, enhance customer relationships, and drive business growth. This guide delves into the core functionalities, benefits, and future trends of CRM systems, offering insights into choosing the right solution for your needs.
From operational CRM systems that manage customer interactions to analytical CRM systems that extract insights from customer data, this guide covers a broad spectrum of applications. We’ll explore how these systems can improve efficiency, boost revenue, and ultimately, foster stronger customer relationships across various business sizes.
Introduction to CRM Applications

Customer Relationship Management (CRM) applications are software systems designed to manage and optimize interactions with customers. They provide a centralized platform for storing and accessing customer data, streamlining sales processes, and enhancing customer service. This allows businesses to better understand their customers, personalize interactions, and ultimately drive growth.CRM systems are crucial for businesses of all sizes and across diverse industries, from small startups to multinational corporations.
They provide a structured approach to managing customer relationships, which is vital for businesses looking to build strong, lasting customer relationships.
Core Functionalities of CRM Systems
CRM systems offer a wide array of functionalities, enabling businesses to manage various aspects of their customer interactions. Key functions encompass sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service management, and analytics. Sales force automation tools help manage leads, track sales opportunities, and close deals efficiently. Marketing automation features streamline marketing campaigns, enabling targeted messaging and improved customer segmentation. Customer service management allows businesses to track and resolve customer issues promptly and effectively.
Comprehensive analytical tools provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Types of CRM Applications
CRM applications can be broadly categorized into three primary types: operational, analytical, and collaborative. Each type serves a distinct purpose in managing customer relationships.
- Operational CRM: This type of CRM focuses on automating and streamlining business processes related to customer interactions. Examples include automating sales processes, managing marketing campaigns, and handling customer service requests. Operational CRM systems are vital for enhancing efficiency and productivity in customer-facing departments.
- Analytical CRM: This type of CRM centers around using data analysis to gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior and preferences. By analyzing customer data, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and insights to improve marketing strategies, personalize offerings, and enhance customer experience. Data mining and reporting tools are key components of analytical CRM.
- Collaborative CRM: This type of CRM facilitates communication and collaboration among different departments within an organization, as well as with external partners. It enhances teamwork by providing a platform for sharing information, coordinating activities, and improving customer service response times. Examples include customer support portals and shared communication platforms.
Common Use Cases Across Industries
CRM applications are widely adopted across diverse industries, enabling businesses to improve customer engagement and drive profitability. Examples include:
- Retail: Retailers can use CRM to track customer preferences, personalize recommendations, and manage loyalty programs. This can lead to increased sales and customer retention.
- Finance: Financial institutions can use CRM to manage customer accounts, track interactions, and personalize financial products. This can result in improved customer satisfaction and increased profitability.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers can use CRM to manage patient records, track interactions, and improve communication with patients. This can lead to better patient care and improved operational efficiency.
Key Features of CRM Application Types
| Feature | Operational CRM | Analytical CRM | Collaborative CRM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Customer interactions | Customer data analysis | Teamwork and communication |
| Examples | Sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service management | Market trend analysis, customer segmentation, predictive modeling | Customer support portals, shared communication platforms, knowledge bases |
Benefits and Advantages of CRM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are proving invaluable for businesses of all sizes. They offer a structured approach to managing interactions with customers, fostering stronger relationships, and ultimately driving revenue growth. This structured approach enhances efficiency and productivity, leading to significant improvements in customer service and satisfaction.CRM systems offer a centralized platform for storing and accessing customer data.
This centralized data repository enables businesses to understand their customers better, anticipate their needs, and tailor their offerings to specific customer segments. This deep understanding translates into improved marketing campaigns, personalized customer experiences, and ultimately, higher customer lifetime value.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
CRM systems streamline various business processes, leading to significant gains in efficiency and productivity. Automated tasks, such as appointment scheduling and follow-up reminders, free up valuable time for employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. Improved communication and collaboration tools within the CRM platform also facilitate teamwork and information sharing, resulting in a more cohesive and productive work environment.
For example, sales teams can access a comprehensive customer history, allowing them to personalize interactions and close deals faster.
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management
CRM systems enable businesses to cultivate stronger and more meaningful customer relationships. By providing a unified view of each customer, businesses can personalize communications and offer tailored support. This personalized approach builds trust and loyalty, leading to increased customer retention and advocacy. For instance, a business can track a customer’s purchase history and offer relevant product recommendations or promotions, enhancing the customer experience.
Increased Revenue and Customer Satisfaction
CRM systems play a pivotal role in boosting revenue and customer satisfaction. By tracking sales activities and analyzing customer data, businesses can identify trends and opportunities for growth. Targeted marketing campaigns based on customer insights can significantly increase conversions and sales. Moreover, improved customer service through personalized interactions and faster response times contribute to higher customer satisfaction levels, ultimately driving repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
A notable example is a company using CRM to segment its customers by purchasing behavior and tailor marketing messages, resulting in a 20% increase in conversion rates.
Comparison of CRM Benefits Across Business Sizes
| Benefit | Small Business | Medium Business | Large Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved Sales | Increased lead conversion rates, faster sales cycles | Enhanced sales forecasting, improved pipeline management | Streamlined sales processes, optimized sales territories |
| Enhanced Customer Service | Improved response times, more efficient ticket management | Personalized customer support, proactive issue resolution | Centralized customer support, improved knowledge base access |
| Marketing Efficiency | Targeted marketing campaigns, improved ROI | Segmented marketing campaigns, enhanced campaign performance tracking | Data-driven marketing strategies, sophisticated campaign optimization |
The table above demonstrates how CRM benefits vary based on the size and complexity of the business. Smaller businesses benefit from increased lead conversion and streamlined processes, while larger enterprises gain from sophisticated sales processes and optimized marketing campaigns. Medium-sized businesses experience the benefits in between these extremes, leveraging the platform to refine sales forecasting and customer service.
Key Features and Functionality
Robust CRM applications are designed to streamline business operations by centralizing customer interactions and data. These systems offer a wide array of features that empower businesses to enhance customer relationships, automate processes, and gain valuable insights into customer behavior. A well-implemented CRM system is a critical component for modern businesses seeking to optimize their performance.
Essential Features of Robust CRM Applications
Modern CRM systems are built upon a foundation of essential features that enable businesses to manage customer interactions effectively. These features often include contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, customer service, and advanced reporting and analytics. Effective CRM implementation ensures a comprehensive view of customer data, leading to improved decision-making and enhanced customer experiences.
Contact Management
Contact management is a fundamental component of CRM systems. It allows businesses to store, organize, and access detailed information about their contacts. This includes names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, purchase history, communication preferences, and any other relevant data. Well-organized contact information facilitates personalized communication and targeted marketing efforts. Access to complete contact details empowers sales representatives to tailor their approach to individual customer needs, leading to improved conversion rates and stronger customer relationships.
Sales Automation
CRM systems automate many aspects of the sales process. This automation can include lead qualification, sales pipeline management, opportunity tracking, and automated follow-up. Sales automation streamlines workflows, reducing manual tasks and improving efficiency. Automated email campaigns and personalized communication tailored to individual customer needs can lead to a substantial improvement in conversion rates.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation capabilities within CRM systems allow businesses to manage and automate their marketing campaigns. This includes tasks like email marketing, social media marketing, and targeted advertising. Marketing automation empowers businesses to deliver targeted and personalized messages to specific customer segments, optimizing marketing spend and maximizing return on investment. Integration with email marketing tools and social media platforms enables consistent communication and enhances brand visibility.
Customer Service and Support
CRM systems play a critical role in managing customer service and support interactions. Features like ticketing systems, knowledge bases, and automated responses streamline customer inquiries and provide efficient resolution. This enables businesses to effectively manage customer issues and ensure timely responses, fostering positive customer experiences. Access to a central repository of customer data allows customer service representatives to quickly access relevant information, improving resolution times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Advanced Features: Reporting and Analytics
Advanced CRM systems offer comprehensive reporting and analytics tools. These tools provide valuable insights into sales performance, marketing effectiveness, and customer behavior. Reporting and analytics help businesses identify trends, measure key performance indicators (KPIs), and make data-driven decisions. For example, sales reports can highlight top-performing sales representatives, identify areas for improvement, and track overall sales performance. Business intelligence dashboards allow for easy monitoring of key performance indicators and identification of areas for optimization.
CRM Features and Functionality
| Feature | Functionality | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Management | Capture, track, and qualify leads, enabling prioritization and follow-up. | Lead scoring, automated follow-up emails, lead nurturing campaigns. |
| Sales Automation | Streamline sales processes, from lead qualification to closing deals. | Automated email campaigns, sales pipeline management, opportunity tracking. |
| Customer Service | Manage customer interactions efficiently through ticketing systems, knowledge bases, and automated responses. | Ticketing systems, knowledge bases, automated email responses, chatbots. |
CRM Implementation and Integration
Implementing a CRM system is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. A successful implementation hinges on a thorough understanding of the business needs, careful selection of the appropriate solution, seamless integration with existing systems, and effective training for personnel. This section delves into the critical aspects of CRM implementation and integration.Effective CRM implementation ensures that the system aligns with the business’s strategic objectives, ultimately driving improved efficiency and profitability.
A well-integrated CRM solution provides a unified view of customer interactions, facilitating informed decision-making and targeted strategies.
CRM System Implementation Process
Implementing a CRM system involves a phased approach, encompassing various stages from initial assessment to ongoing maintenance. A structured implementation plan is crucial for success, ensuring that the system is effectively utilized and integrated into existing workflows. This process typically includes a series of steps.
- Needs Assessment: Identifying specific business needs and defining clear objectives is paramount. This includes understanding existing workflows, identifying pain points, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
- Solution Selection: Evaluating different CRM solutions based on specific business requirements is crucial. This involves a comprehensive evaluation process, considering factors like pricing, features, scalability, and vendor support.
- System Configuration: Customizing the CRM system to align with specific business processes and workflows is a critical step. This often involves configuring various modules, setting up user roles, and defining access permissions.
- Data Migration: Transferring existing customer data into the new CRM system accurately and efficiently is essential. This step often involves data cleansing, validation, and mapping to ensure data integrity. A well-executed data migration process minimizes errors and disruptions.
- User Training: Providing comprehensive training to users on how to effectively utilize the CRM system is critical for adoption and successful implementation. Training programs should cover various aspects, from basic navigation to advanced functionalities.
- System Testing and Validation: Thoroughly testing the CRM system to identify potential issues and ensure it meets business requirements before full implementation. This step includes testing workflows, data entry, and reporting capabilities.
- Deployment and Go-Live: Launching the CRM system and transitioning users to the new platform. A smooth go-live process minimizes disruption to business operations.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance: Providing ongoing support, updates, and maintenance to ensure the CRM system remains effective and aligns with evolving business needs.
Choosing the Right CRM Solution
Selecting the right CRM solution is critical for achieving desired outcomes. A thorough evaluation process is essential, considering factors like scalability, functionality, and budget constraints.
- Defining Requirements: Clearly outlining specific business needs, desired functionalities, and budget constraints is essential. This step ensures the selected solution meets the unique needs of the organization.
- Vendor Evaluation: Conducting thorough research and comparing different CRM vendors based on their capabilities, customer support, pricing models, and scalability. This involves reviewing vendor websites, case studies, and testimonials to make an informed decision.
- Trial and Demo: Utilizing trial periods and demonstrations to test the CRM system’s functionalities, usability, and integration capabilities. Hands-on experience provides valuable insights.
- Integration Considerations: Assessing the CRM’s compatibility with existing systems and the potential for seamless integration to avoid conflicts and data inconsistencies.
- Long-Term Strategy: Evaluating the long-term scalability and adaptability of the chosen CRM solution to accommodate future growth and evolving business needs.
CRM System Integration
Integrating CRM with other business applications is vital for a unified view of customer interactions. This integration ensures that data flows seamlessly between systems.
- Data Migration Strategy: A carefully planned strategy for transferring data between systems, ensuring data accuracy and consistency. This is crucial for avoiding data silos and maintaining data integrity.
- API Integration: Utilizing Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for seamless data exchange between systems. APIs facilitate the exchange of data between CRM and other applications.
- Data Mapping: Mapping fields and data points between different systems to ensure accurate data transfer and avoid data loss or misinterpretation. This is crucial for accurate data integration.
- System Configuration: Configuring the CRM and other systems to facilitate data exchange and integration.
Data Migration and Training
Proper data migration and training are essential for successful CRM implementation. Data migration ensures a smooth transition and accurate data transfer, while training equips personnel to effectively utilize the system.
- Data Cleansing and Validation: Identifying and correcting inaccuracies or inconsistencies in existing data to ensure data integrity and prevent issues during migration.
- Data Mapping and Transformation: Mapping existing data fields to new CRM fields to facilitate the transfer of information and ensure data consistency. Data transformation processes can adapt data formats to align with CRM requirements.
- Training Program Development: Creating a comprehensive training program for users, encompassing both basic and advanced functionalities, to maximize system adoption and utilization.
Step-by-Step CRM System Integration Procedure
A well-defined integration procedure minimizes disruptions and maximizes efficiency.
- Assessment of Existing Systems: Identifying all relevant systems and applications that need integration.
- Data Mapping and Validation: Mapping fields and validating data for accurate transfer.
- API Integration Setup: Configuring API connections and testing data exchange.
- System Testing and Validation: Rigorously testing integration to ensure data integrity.
- Data Migration Execution: Implementing the data migration plan to transfer data.
- User Training and Support: Providing training and ongoing support to users.
- Post-Implementation Review: Evaluating system performance and making necessary adjustments.
CRM Trends and Future Developments
CRM systems are constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses and their customers. Emerging trends in technology, particularly artificial intelligence and cloud computing, are significantly impacting the way CRM solutions are designed and utilized. These advancements promise to enhance customer experiences, streamline business operations, and drive overall growth.
Emerging Trends in CRM Technology
CRM technology is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in areas like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing. These trends are leading to more sophisticated and effective CRM solutions. Businesses are increasingly adopting AI-powered tools for automation, personalization, and predictive analysis. Cloud-based CRM solutions are expanding their functionalities, offering enhanced scalability and accessibility.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in CRM
AI and machine learning are transforming CRM by enabling automation and personalization at scale. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to address complex issues. Machine learning algorithms analyze customer data to predict future needs and preferences, enabling proactive support and targeted marketing campaigns. For example, a retail company could use AI to personalize product recommendations based on individual customer browsing history and purchase patterns.
Innovative CRM Features and Functionalities
New CRM features are continuously emerging, reflecting the ongoing evolution of business needs. Predictive analytics is becoming increasingly important, allowing businesses to anticipate customer behavior and tailor their strategies accordingly. Improved integration with other business applications, such as marketing automation platforms, is streamlining workflows and improving overall efficiency. Enhanced security measures are also critical, given the increasing reliance on data-driven insights.
Evolution of Cloud-Based CRM Solutions
Cloud-based CRM solutions are becoming more sophisticated, offering greater scalability and accessibility. The shift towards mobile-first solutions is allowing businesses to manage their CRM data and interactions on any device, anytime. Enhanced security measures, such as data encryption and access controls, are becoming standard features in cloud-based CRM systems. Businesses can access and manage their CRM data remotely, regardless of location.
Predicted Future Developments in CRM
The future of CRM is shaped by ongoing technological advancements and evolving business needs. The integration of AI and machine learning will continue to enhance personalization, automation, and predictive capabilities. Cloud-based solutions will further expand their functionalities, offering seamless integration with other business applications. The table below Artikels predicted future developments in CRM:
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI-powered CRM | Utilizing AI for automation and personalized experiences, including predictive analytics and proactive support. | Improved customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and enhanced decision-making through data-driven insights. |
| Cloud-based CRM | Access to CRM solutions through the cloud, offering greater scalability, accessibility, and enhanced collaboration. | Increased flexibility and adaptability to changing business needs, improved data security, and reduced IT infrastructure costs. |
| Hyper-personalization | CRM systems will leverage AI to tailor interactions to individual customer preferences and behaviors. | Significant improvement in customer engagement and loyalty, leading to higher conversion rates and revenue growth. |
| Integration with other applications | CRM systems will integrate seamlessly with other business applications like marketing automation and e-commerce platforms. | Streamlined workflows, improved data visibility, and reduced manual data entry, enabling efficient and effective business processes. |
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
CRM systems are proving invaluable in diverse industries, helping companies achieve specific business objectives. Examining successful implementations provides insights into the effectiveness and adaptability of these technologies. This section details compelling case studies showcasing the transformative power of CRM solutions.
Successful CRM Implementations in Retail
Retailers often face challenges in managing customer interactions and sales processes. CRM systems can streamline these operations, leading to improved customer service and increased sales. For instance, a large clothing retailer implemented a CRM system that tracked customer purchase history, preferences, and feedback. This allowed them to personalize marketing campaigns, offering tailored recommendations and promotions. The result was a 15% increase in customer retention and a 10% boost in average order value.
CRM’s Impact on Customer Insights
CRM systems are powerful tools for gathering and analyzing customer data. This data-driven approach enables companies to develop a deeper understanding of customer needs and preferences, leading to more effective marketing strategies. A major telecommunications company used its CRM to analyze customer call logs, website activity, and service requests. This detailed analysis revealed customer pain points and opportunities for improvement, enabling them to refine their services and reduce customer churn.
Illustrative Examples Across Industries
CRM applications cater to various industries, each with its unique needs. The following examples highlight how different sectors utilize CRM for enhanced operations.
- Finance: A financial institution utilized a CRM system to manage customer interactions, track loan applications, and personalize financial advice. This resulted in improved customer satisfaction scores and a 12% increase in loan applications.
- Healthcare: A healthcare provider implemented a CRM to manage patient records, track appointments, and improve communication between patients and staff. This enhanced efficiency and improved patient experience, leading to a 10% decrease in appointment no-shows.
- Hospitality: A hotel chain implemented a CRM system to track guest preferences, manage reservations, and personalize guest experiences. This improved guest satisfaction and increased repeat bookings, resulting in a 15% increase in revenue.
Leveraging CRM for Better Customer Insights
“Data-driven insights are crucial for understanding customer behavior and preferences.”
CRM systems provide a centralized repository for customer data, facilitating the analysis of various interactions and behaviors. By analyzing this data, companies can gain a comprehensive understanding of their customer base. A prominent online retailer used its CRM to identify trends in customer purchasing behavior, leading to the development of targeted marketing campaigns and personalized product recommendations. This approach resulted in a 20% increase in conversion rates.
Examples of CRM System Benefits
A structured presentation of successful implementations is provided below, highlighting the positive impact of CRM on specific companies.
| Company | Industry | CRM Implementation Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Technology | Increased sales by 18% and reduced customer service response time by 10%. |
| Company B | Retail | Improved customer satisfaction by 15% and boosted marketing campaign ROI by 12%. |
| Company C | Finance | Reduced loan processing time by 8% and increased loan application volume by 10%. |
Epilogue
In conclusion, CRM applications are essential for modern businesses seeking to optimize customer interactions and achieve sustainable growth. By understanding the different types of CRM systems, their advantages, and future trends, businesses can make informed decisions about implementing and integrating these powerful tools. This guide provides a solid foundation for understanding the multifaceted world of CRM applications, enabling businesses to navigate the complexities and harness their full potential.
FAQ Guide
What are the different types of CRM applications?
CRM applications are broadly categorized into operational, analytical, and collaborative types. Operational CRM focuses on automating customer interactions, analytical CRM focuses on data analysis for insights, and collaborative CRM facilitates teamwork and communication.
How can CRM systems improve customer satisfaction?
CRM systems can improve customer satisfaction by providing a holistic view of customer interactions. By centralizing customer data, businesses can tailor interactions, anticipate needs, and resolve issues efficiently, ultimately leading to happier customers.
What are the key steps in implementing a CRM system?
Implementing a CRM system involves careful planning, choosing the right solution, data migration, and comprehensive training for staff. Careful consideration of your business needs and existing systems is crucial for a successful implementation.
How do CRM systems integrate with other business applications?
CRM systems often integrate with other business applications, such as accounting software or marketing automation tools. This integration streamlines workflows and allows for a more comprehensive view of the customer journey.