Client CRM systems are no longer just a software tool; they’re a strategic investment for businesses of all sizes. They streamline client interactions, automate tasks, and ultimately, drive growth. This overview explores the multifaceted world of client CRM, from its core functionalities to the latest trends shaping its future.
This document delves into the intricacies of client relationship management (CRM) systems, examining their benefits, implementation strategies, and the vital role they play in modern business operations. We’ll explore the various types of CRMs, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses, and how they can be tailored to meet the unique needs of different industries.
Client CRM Overview
A Client Relationship Management (CRM) system is a software application designed to manage and improve interactions with clients. It serves as a centralized hub for storing and accessing client data, enabling businesses to track their relationships, improve customer service, and ultimately, boost sales and profitability. CRMs streamline communication, automate tasks, and provide valuable insights into customer behavior.CRM systems offer a comprehensive view of client interactions, from initial contact to ongoing support.
This data-driven approach enables businesses to tailor their offerings to individual client needs and preferences, fostering stronger and more profitable relationships. Effective CRM implementation can significantly enhance customer retention and loyalty.
Key Functionalities of a Typical CRM
A typical CRM system encompasses a suite of functionalities crucial for managing client relationships effectively. These include contact management, sales tracking, marketing automation, customer service management, and reporting & analytics. Contact management features allow for comprehensive data storage and organization of client information, including contact details, communication history, and relevant notes. Sales tracking provides insights into sales pipelines, allowing for efficient lead management and forecasting.
Marketing automation tools help in segmenting and targeting specific customer groups, improving campaign effectiveness and return on investment. Effective customer service management facilitates efficient issue resolution and enhances client satisfaction. Comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities offer valuable insights into customer behavior, allowing businesses to identify trends and make data-driven decisions.
Different Types of Client CRMs
Client Relationship Management (CRM) systems come in various forms to cater to diverse business needs and budgets. Cloud-based CRMs, hosted on external servers, offer accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, requiring minimal upfront investment in hardware. On-premises CRMs, installed and maintained on company servers, offer greater control and customization, but come with higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance responsibilities.
Open-source CRMs, available under open licenses, allow for extensive customization but may require in-house expertise for implementation and maintenance.
Examples of Successful CRM Implementations
Numerous businesses across various sectors have successfully leveraged CRM systems to enhance their operations. For example, a small retail store using a cloud-based CRM to track customer interactions and personalize offers saw a 25% increase in sales within the first year. A medium-sized enterprise employing an on-premises CRM for streamlined sales processes reported a 15% reduction in sales cycle time.
A large multinational corporation using a sophisticated CRM system for managing global client relationships noted significant improvements in customer retention rates.
Comparison of CRM Types
| CRM Type | Features | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-Based | Accessibility from anywhere, scalability, automatic updates, lower upfront costs. | Flexibility, cost-effectiveness, rapid deployment, reduced IT infrastructure needs. | Dependence on internet connectivity, potential security concerns, limited customization. |
| On-Premises | Greater control, customization, potential for integration with existing systems, data security. | Full control over data, customization options, often tailored to specific needs. | Higher upfront costs, maintenance responsibilities, limited scalability, dependence on IT infrastructure. |
| Open-Source | Extensive customization options, potentially lower costs, community support. | Highly customizable solutions, cost-effective, strong community support. | Requires technical expertise for implementation and maintenance, limited vendor support, potential security vulnerabilities. |
Client CRM Benefits and Use Cases
Client Relationship Management (CRM) systems are becoming increasingly crucial for businesses seeking to enhance client interactions and achieve sustainable growth. A well-implemented CRM provides a centralized platform for managing client data, fostering communication, and enabling informed decision-making. This facilitates improved client relations, streamlined processes, and ultimately, increased profitability.Effective CRM systems offer significant advantages for businesses of all sizes. By consolidating client information and automating tasks, CRMs free up valuable time and resources, enabling teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
This efficiency translates directly into improved client satisfaction and loyalty, leading to stronger long-term partnerships.
Advantages of Using a Client CRM System
Client CRMs offer a comprehensive suite of features that improve client relationships. These features streamline communication, enabling businesses to respond promptly and efficiently to client inquiries. This proactive approach builds trust and strengthens the client-business bond. Furthermore, CRMs facilitate personalized interactions by allowing access to client history and preferences, leading to more relevant and satisfying engagements. This personalized approach fosters client loyalty and reduces churn.
Streamlining Communication Processes with Clients
Client CRMs automate and streamline various communication channels. This includes email marketing, social media engagement, and phone call scheduling. Automating these tasks allows businesses to respond quickly to client needs, improving response times and enhancing the overall client experience. The ability to track communication history within the CRM provides a comprehensive record of interactions, facilitating efficient problem-solving and proactive relationship management.
Data-Driven Decision Making Regarding Client Interactions
Client CRMs offer detailed insights into client behavior and preferences. Data analysis capabilities within these systems provide valuable information for improving marketing strategies, identifying potential issues, and predicting future client needs. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions, tailoring their services and offerings to optimize client satisfaction and retention. Detailed reports and dashboards provide clear visualizations of client interactions, facilitating a deeper understanding of client behavior.
Specific Use Cases for a Client CRM
Client CRMs provide numerous benefits across diverse business functions. They are particularly valuable for lead management, sales tracking, and customer support. By centralizing lead information, CRMs allow businesses to track the progress of potential clients through the sales funnel. This facilitates targeted outreach and personalized nurturing, maximizing conversion rates. Sales tracking capabilities within CRMs provide valuable insights into sales performance, identifying areas for improvement and optimizing sales strategies.
Furthermore, CRMs empower customer support teams by providing instant access to client history and preferences. This allows for faster resolution of issues, enhancing client satisfaction.
CRM Use Cases Across Industries
| Industry | Use Case | CRM Features Used | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Managing customer loyalty programs | Customer segmentation, personalized offers, reward tracking | Increased customer lifetime value, improved customer retention, boosted sales through targeted promotions. |
| Healthcare | Scheduling appointments and managing patient records | Appointment scheduling, patient communication, medical history tracking | Improved appointment efficiency, reduced administrative overhead, enhanced patient experience, improved data security. |
| Financial Services | Tracking client interactions and managing portfolios | Client communication, account management, investment tracking | Improved client service, increased portfolio management efficiency, enhanced compliance, reduced errors, and improved client relationships. |
| Real Estate | Managing leads and tracking property sales | Lead management, property listings, sales pipeline tracking | Increased lead conversion rates, improved sales forecasting, efficient resource allocation, streamlined sales processes. |
Key Features and Modules
A robust client CRM system goes beyond basic contact management. It’s a powerful tool for streamlining business processes, fostering stronger client relationships, and ultimately, driving revenue growth. Understanding the key features and how different modules work together is crucial for maximizing its potential.A well-designed CRM system integrates various functionalities, automating tasks and providing comprehensive insights into client interactions.
This allows businesses to personalize client experiences, anticipate needs, and proactively address issues, leading to increased client satisfaction and loyalty.
Essential CRM Features
A comprehensive CRM system should encompass essential features that facilitate efficient client management and sales processes. These include contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, and reporting & analytics capabilities. The seamless integration of these features is critical for a holistic view of client interactions and the effective tracking of progress.
Contact Management
This fundamental module serves as the foundation of any CRM system. It allows for the organization and management of client data, including contact details, communication history, and relevant notes. A robust contact management system enables quick access to vital client information, fostering personalized interactions and a deeper understanding of individual needs. This can significantly enhance client satisfaction by showcasing a commitment to understanding their specific requirements.
Sales Automation
A well-implemented sales automation module streamlines sales processes, from lead qualification to closing deals. It automates tasks like scheduling appointments, sending follow-up emails, and tracking sales progress. This automation frees up sales teams to focus on building relationships and closing deals, ultimately improving sales efficiency and revenue generation.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation modules empower businesses to personalize and streamline marketing campaigns. This involves automating tasks such as email marketing, social media scheduling, and lead nurturing. By automating these tasks, businesses can reach a wider audience, segment their campaigns, and measure the effectiveness of different approaches.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics capabilities are essential for evaluating CRM performance and identifying areas for improvement. This includes generating reports on sales performance, client interactions, and marketing campaign effectiveness. The insights gleaned from these reports can inform strategic decision-making, enabling data-driven improvements in business operations and strategies. Effective reporting also helps identify trends and patterns in client behavior, allowing businesses to adapt their strategies accordingly.
Personalized Client Experiences
A robust CRM system facilitates personalized client experiences by providing a 360-degree view of each client. This holistic view allows businesses to understand client preferences, needs, and past interactions. This knowledge allows for tailored communication, targeted recommendations, and proactive service offerings. This personalized approach fosters stronger client relationships, driving loyalty and repeat business.
CRM Modules Overview
This table Artikels various CRM modules, their descriptions, key features, and associated benefits.
| Module Name | Description | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Organizes and manages client data | Contact details, communication history, notes | Improved client understanding, personalized interactions, efficient data access |
| Sales Automation | Streamlines sales processes | Appointment scheduling, email follow-ups, sales progress tracking | Increased sales efficiency, improved revenue generation, reduced administrative burden |
| Marketing Automation | Personalizes and streamlines marketing campaigns | Email marketing, social media scheduling, lead nurturing | Wider reach, targeted campaigns, improved marketing ROI |
| Reporting & Analytics | Evaluates CRM performance | Sales performance reports, client interaction reports, marketing campaign effectiveness reports | Data-driven decision-making, identification of improvement areas, better business strategies |
Implementation and Integration
Implementing a Client CRM system is a crucial step in streamlining business operations and maximizing customer relationship management. A well-executed implementation ensures that the CRM system effectively integrates with existing processes, facilitating data flow and minimizing disruptions. This phase requires careful planning, meticulous execution, and consistent monitoring.
Steps Involved in Implementation
The implementation process typically involves several key stages. Initial setup involves configuring the CRM system according to specific business needs. Data migration and integration are vital to transferring existing client data seamlessly. Training staff on the new system is crucial for efficient usage. Testing the system thoroughly ensures its functionality aligns with expectations.
Finally, the system goes live and ongoing support ensures the system remains efficient.
Data Migration and Integration
Data migration is a critical component of CRM implementation. It involves transferring existing client data from legacy systems to the new CRM. Effective data migration strategies minimize data loss and ensure data accuracy. Integration with existing systems is equally important, enabling seamless data exchange and avoiding data silos. This often includes APIs, custom integrations, or third-party tools.
Proper planning and careful execution are key to successful data migration and integration.
Staff Training
Comprehensive staff training is essential for effective CRM usage. Training programs should cover the key features and functionalities of the CRM system, focusing on practical application rather than just theoretical knowledge. Interactive workshops, hands-on exercises, and access to online resources are valuable training tools. Regular follow-up sessions and ongoing support are crucial for sustaining user proficiency.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Updates
Regular maintenance and updates are crucial for a CRM system’s continued effectiveness. System maintenance involves routine checks, addressing bugs, and optimizing performance. Updating the system with new features and security patches is equally important. Continuous monitoring ensures system stability and user satisfaction. Regular data cleansing and validation prevent data inconsistencies.
CRM Implementation Stages
| Stage | Activities | Key Considerations | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | Defining system requirements, selecting the CRM, creating a budget, developing a timeline | Alignment with business goals, scalability of the system, budget constraints, stakeholder buy-in | Clear project scope, realistic timeline, system selection, budget approval |
| Data Migration | Transferring data from existing systems, cleaning and validating data, integrating with other systems | Data accuracy, data volume, potential data loss, system compatibility | Accurate and complete data transfer, smooth data integration, data integrity |
| Customization and Configuration | Tailoring the CRM to specific business processes, setting up user roles and permissions, configuring workflows | Customization limitations, impact on existing processes, user experience | Optimized CRM functionality, efficient workflow processes, streamlined user access |
| Testing and Training | Thorough testing of all functionalities, developing training materials, conducting training sessions | System performance, user feedback, training effectiveness, testing coverage | High system performance, proficient users, successful user adoption |
| Go-Live and Support | Deploying the system, providing ongoing support, monitoring performance, collecting feedback | System stability, user adoption, data security, support availability | System uptime, user satisfaction, efficient operations, ongoing support |
Client CRM Trends and Future
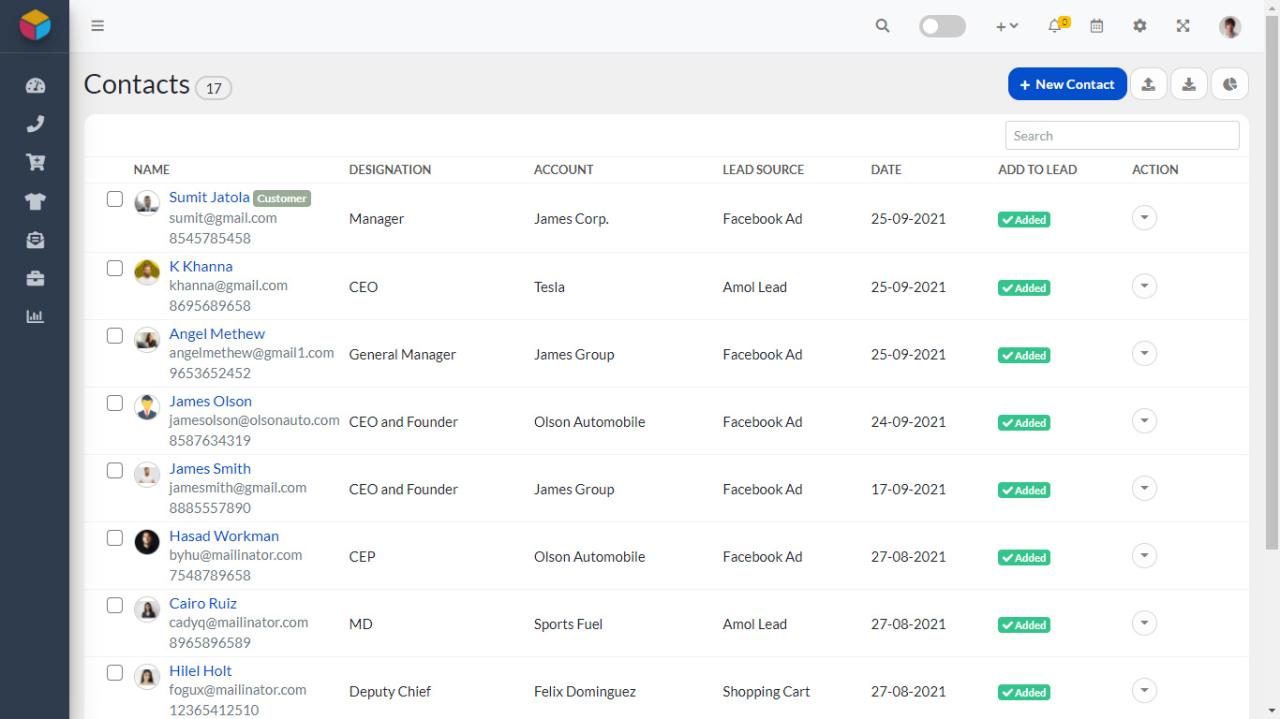
Client Relationship Management (CRM) systems are constantly evolving, adapting to changing business needs and technological advancements. This dynamic environment necessitates a proactive understanding of current trends and future implications for successful CRM implementation and maintenance. A forward-thinking approach to CRM is crucial for staying competitive and maximizing ROI.The future of client CRM is intricately linked with the ever-increasing importance of data-driven insights and personalized experiences.
Organizations are increasingly leveraging CRM systems to gain deeper understandings of their customer base, enabling more targeted marketing campaigns and improved customer service.
Current Trends in Client CRM Technology
Client CRM systems are undergoing a transformation, driven by advancements in cloud computing, mobile technology, and data analytics. These developments are enabling organizations to build more sophisticated and responsive customer relationships. Cloud-based CRM solutions are gaining significant traction due to their accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Mobile CRM apps allow for real-time data access and support, boosting productivity and flexibility.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Client CRM Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming increasingly prevalent in client CRM systems. AI-powered chatbots can automate customer service interactions, freeing up human agents for more complex issues. ML algorithms can analyze customer data to predict future behavior, enabling proactive outreach and personalized recommendations. This integration enhances customer satisfaction and streamlines operational efficiency.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Client CRM Systems
Several emerging technologies are impacting client CRM systems, shaping their capabilities and functionalities. These include the Internet of Things (IoT), which allows for the integration of customer interactions across various devices and channels. Blockchain technology offers enhanced security and transparency in managing customer data. These innovative technologies are transforming the landscape of client CRM, driving greater efficiency and security.
Innovative CRM Applications in Various Sectors
Numerous innovative CRM applications are emerging in various sectors. In the retail sector, CRM systems are used to track customer preferences and personalize product recommendations, leading to increased sales and customer loyalty. In the healthcare sector, CRM systems facilitate patient communication and streamline administrative tasks. The financial sector leverages CRM for managing customer relationships and ensuring compliance.
These examples highlight the adaptability and versatility of modern CRM systems across diverse industries.
Evolution of CRM Systems Over Time
| Time Period | Key Features | Technology | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-1990s | Manual processes, limited data storage, basic contact management. | Spreadsheets, paper-based systems. | Limited customer insights, inefficient processes, and difficult data analysis. |
| 1990s – 2000s | Emergence of early CRM software, improved data management, basic reporting. | Dedicated CRM software, relational databases. | Enhanced data organization, improved sales tracking, better customer segmentation. |
| 2010s – Present | Cloud-based CRM, mobile access, AI integration, predictive analytics, personalized experiences. | Cloud computing, mobile devices, AI algorithms. | Real-time data access, enhanced customer engagement, improved efficiency and scalability. |
| Future | Integration of IoT, blockchain, augmented reality, and advanced analytics for hyper-personalized interactions. | IoT, blockchain, augmented reality, advanced data analytics. | Predictive insights, hyper-personalized customer journeys, enhanced security, and data transparency. |
Security and Privacy Considerations
Protecting client data is paramount in a client CRM. Robust security measures and adherence to privacy regulations are crucial for maintaining trust and avoiding reputational damage. Failure to prioritize these aspects can lead to significant financial losses and erosion of client relationships.
Importance of Data Security
Data security in a client CRM is essential for several reasons. Compromised client data can result in identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational harm for both the client and the organization using the CRM. The sensitive nature of client information, including contact details, financial data, and personal preferences, demands robust security protocols. Furthermore, regulatory compliance mandates stringent data protection measures.
Organizations that fail to safeguard client data may face hefty fines and legal repercussions.
Safeguarding Client Data from Unauthorized Access
Implementing strong security measures is critical to prevent unauthorized access to client data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, requiring multiple verification steps before granting access. Regular security audits help identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the system. Implementing robust encryption protocols ensures that sensitive data is unreadable to unauthorized individuals even if intercepted.
Restricting access privileges based on roles and responsibilities further limits the potential for misuse of information. Regular password updates and the use of strong, unique passwords are also essential.
Complying with Data Privacy Regulations
Adherence to data privacy regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is mandatory. Organizations must clearly Artikel their data collection and usage policies, obtaining explicit consent from clients before collecting and processing their personal information. Providing clients with clear and accessible information about their rights, including the right to access, rectify, and erase their data, is vital.
Implementing procedures to ensure data minimization and data retention within specified timeframes is also necessary.
Implications of Data Breaches on Client Relationships
Data breaches can have devastating consequences for client relationships. Loss of trust and confidence can lead to a decline in client loyalty and a significant loss of business. Clients may seek legal recourse if their data is compromised. The financial implications of a breach, including fines, legal costs, and lost revenue, can be substantial. Reputation damage can take years to repair, impacting the organization’s credibility and future business prospects.
Security Measures and Privacy Protocols
| Measure | Description | Implementation | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification steps. | Implement MFA for all user accounts, including administrators and employees. Choose strong authentication methods like one-time passwords (OTPs) or biometric authentication. | Significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised. |
| Regular Security Audits | Systematically evaluate the security posture of the CRM to identify and address vulnerabilities. | Conduct regular security assessments, penetration testing, and vulnerability scans. Employ a dedicated security team or engage external security experts. | Early detection of potential weaknesses, proactive mitigation of threats, and maintenance of a secure system. |
| Data Encryption | Transform data into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access. | Implement end-to-end encryption for sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Utilize industry-standard encryption algorithms. | Protection of sensitive information even if data is intercepted or systems are compromised. |
| Access Control | Limit access to client data based on user roles and responsibilities. | Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to define specific permissions for each user role. Regularly review and update access permissions. | Minimizes the potential for data breaches and unauthorized access, as well as maintaining compliance with data privacy regulations. |
Client CRM Case Studies
Client Relationship Management (CRM) systems have demonstrably transformed businesses across various industries. Successful implementations often lead to increased efficiency, enhanced client satisfaction, and improved profitability. This section presents real-world examples of how CRM systems have positively impacted organizations.
Successful CRM Implementations
Several companies have successfully implemented CRM systems, achieving substantial improvements in their operations. These implementations often involve careful planning, meticulous execution, and a dedication to ongoing optimization. One notable example is a mid-sized retail company that implemented a cloud-based CRM. This decision was driven by the need for enhanced customer service and improved sales forecasting.
Improved Client Satisfaction
CRM systems can significantly enhance client satisfaction by providing a more personalized and responsive service experience. For instance, the retail company mentioned previously, by leveraging the CRM’s comprehensive client data, they could tailor marketing campaigns and offer targeted product recommendations. This personalized approach directly contributed to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementing a CRM system can present challenges, such as data migration, user training, and system integration. The retail company encountered difficulties with data migration, requiring significant effort to ensure data accuracy and consistency. They addressed this challenge by employing a phased approach to data migration, starting with a smaller subset of clients and gradually expanding the process. This approach minimized disruptions and ensured the integrity of the data.
Further, comprehensive user training programs were implemented to equip employees with the necessary skills to effectively utilize the CRM.
Enhanced Business Efficiency
CRMs can streamline workflows, automate tasks, and provide insightful data analysis. A manufacturing company using a CRM system saw a reduction in order processing time by 25%. This was achieved by automating tasks such as order entry and customer communication, thereby allowing sales representatives to focus on building relationships and closing deals.
Impact on Bottom Line and Growth
The impact of a CRM system on a company’s bottom line and growth can be substantial. The manufacturing company experienced a 15% increase in sales revenue within the first year of CRM implementation. This was attributed to improved customer retention, increased sales conversions, and optimized sales processes. The CRM system also facilitated better forecasting, allowing the company to adjust production schedules more effectively and reduce inventory costs.
Final Thoughts

In conclusion, a well-implemented client CRM system can significantly enhance client relationships, optimize communication, and drive data-driven decision-making. The future of client CRM is bright, with continuous innovation and advancements in AI and automation. By understanding the key features, trends, and implementation strategies, businesses can leverage client CRMs to achieve greater efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and ultimately, sustainable growth.
Expert Answers
What are some common CRM integration challenges?
Integrating a CRM with existing systems can be complex, often involving data migration and customization. Compatibility issues, lack of clear integration strategies, and insufficient staff training can all contribute to integration challenges.
How can I choose the right CRM for my business?
Consider your specific business needs, budget, and the size of your team. Evaluate the CRM’s features, scalability, and ease of use. Look for a CRM that integrates seamlessly with existing systems and provides adequate support.
What are the security best practices for client CRM systems?
Robust security measures are crucial. Implement strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and data encryption. Comply with relevant data privacy regulations and train staff on security protocols.
How does a CRM improve client satisfaction?
A well-structured CRM system enables personalized interactions and efficient communication, which ultimately improves client satisfaction. Data insights gleaned from the CRM can inform targeted communication and better meet client needs.