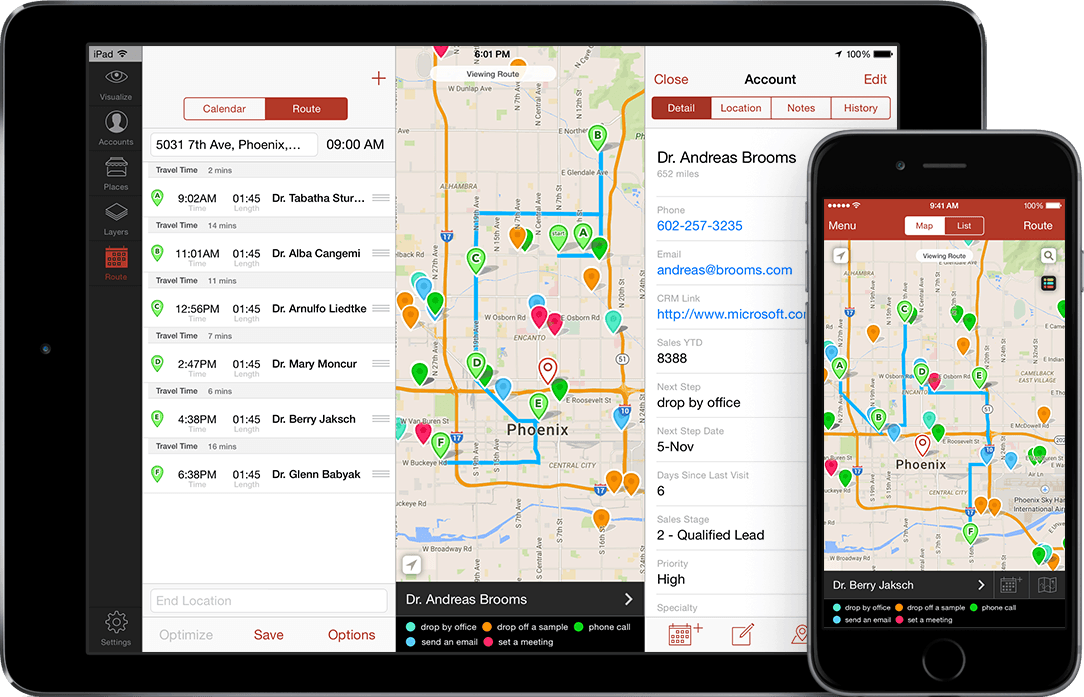
CRM mapping is crucial for modern businesses. It’s not just about organizing customer data; it’s about understanding how your entire operation interacts with customers. This process allows you to optimize workflows and identify bottlenecks, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and business efficiency.
This guide will delve into the core aspects of CRM mapping, from defining it and collecting data to identifying customer interactions, process optimization, and technology integration. We’ll also discuss how to measure and evaluate your CRM mapping’s effectiveness and look ahead to future trends.
Defining CRM Mapping
CRM mapping is a critical process in modern business operations, facilitating the alignment of customer relationship management (CRM) systems with existing business processes and data structures. This alignment ensures that CRM data is utilized effectively, leading to enhanced customer understanding and improved business performance. It goes beyond simple data transfer; it involves a strategic restructuring of how information flows and is utilized within the organization.Effective CRM mapping involves a deep understanding of both the CRM system’s capabilities and the specific needs of the business.
This process requires careful consideration of the different departments and their interactions with customers, enabling streamlined communication and efficient data utilization across the entire organization. By understanding how different systems interact, CRM mapping helps organizations optimize their workflows and gain a holistic view of customer interactions.
CRM Mapping Methodologies
Different methodologies exist for CRM mapping, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of methodology depends heavily on the specific business context and goals. Understanding the various approaches allows for a tailored approach to CRM mapping.
- Functional Mapping: This method focuses on aligning CRM functionalities with specific business processes. It involves mapping CRM modules to tasks performed by different departments, ensuring that the system supports their workflows effectively. This approach is particularly useful for streamlining sales, marketing, and customer service processes.
- Data Mapping: This approach emphasizes the structure and content of the data within the CRM system. It involves defining how data from existing systems will be transferred and integrated into the CRM. Thorough data mapping is crucial for avoiding data inconsistencies and ensuring data integrity.
- Process Mapping: This methodology focuses on the flow of customer interactions and business processes. It analyzes how customers interact with the organization and maps these interactions to the relevant CRM processes, highlighting opportunities for improvement and automation.
Key Benefits and Drawbacks of CRM Mapping Strategies
Different CRM mapping strategies offer varying advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these implications is vital for making informed decisions.
- Functional Mapping Benefits: Improved workflow efficiency, reduced manual data entry, enhanced data accuracy, and better integration between departments. Drawbacks: Potential for over-reliance on the CRM system, difficulties in adapting to evolving business needs, and the potential for increased complexity if not carefully planned.
- Data Mapping Benefits: Improved data quality, reduced data redundancy, and enhanced data consistency. Drawbacks: Time-consuming process, potential for data loss during transfer, and the need for specialized expertise.
- Process Mapping Benefits: Enhanced customer experience, improved customer satisfaction, and identification of areas for process optimization. Drawbacks: Can be challenging to implement if existing processes are not well-defined, and the need for detailed process documentation.
Examples of Successful CRM Mapping Implementations
Successful CRM mapping implementations demonstrate the positive impact on business operations. These examples showcase the potential for improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Retail Industry: A major retailer mapped their existing customer service processes to their new CRM system, leading to a 15% reduction in customer service response time and a 10% increase in customer satisfaction. This illustrates the efficiency gains achieved by linking processes with CRM tools.
- Financial Services: A financial institution mapped their customer onboarding process to a CRM, allowing them to streamline the process and reduce the average onboarding time by 20%. This exemplifies the use of CRM to optimize critical business workflows.
Comparison of CRM Mapping Techniques
The table below summarizes the key differences between the discussed mapping methodologies.
| Technique | Focus | Application | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Functional Mapping | CRM functionalities and business processes | Streamlining sales, marketing, customer service | Improved workflow, reduced manual data entry | Potential over-reliance on CRM, adapting to change |
| Data Mapping | Data structure and content | Data migration, integration | Improved data quality, reduced redundancy | Time-consuming, potential data loss |
| Process Mapping | Customer interactions and business processes | Optimizing customer journey, automating tasks | Enhanced customer experience, process optimization | Requires detailed process documentation, adapting to change |
Data Collection and Preparation for Mapping
A crucial initial step in CRM mapping is the meticulous collection and preparation of relevant data. This phase lays the groundwork for accurate insights and effective mapping strategies. The quality of the data directly impacts the reliability and value of the resulting CRM map. Thorough data collection and cleansing are paramount to achieving the desired objectives.Data collection, cleansing, and validation are critical steps in the process of building an accurate CRM map.
Without meticulously prepared data, the resulting map will be unreliable and lack the insights necessary for strategic decision-making. This process involves identifying the necessary data points, sourcing them from various systems, and then ensuring the data is clean, consistent, and readily usable. The subsequent steps involve organizing the data into a usable format for analysis.
Collecting Relevant Data
Gathering the appropriate data for CRM mapping involves identifying the key data points required for analysis. This often involves exploring various customer touchpoints and interactions, such as sales interactions, marketing campaigns, and customer service records. Careful consideration of the specific goals of the CRM mapping exercise is crucial. If the goal is to identify customer segments, data about demographics, purchase history, and interaction patterns is essential.
Data Cleansing and Validation
Data cleansing and validation are indispensable for CRM mapping. Incomplete, inaccurate, or inconsistent data can lead to flawed insights and ineffective strategies. The process of data cleansing involves identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies, and missing values in the collected data. Validation ensures that the data conforms to the defined standards and meets the criteria for accurate analysis.
Data Sources for CRM Mapping
CRM mapping leverages a multitude of data sources. These include customer databases, sales records, marketing campaign data, customer service interactions, and website analytics. By combining data from various sources, a comprehensive view of customer interactions and preferences can be developed. Using a combination of data sources provides a holistic view of customer behaviour.
Organizing and Structuring Data
Data organization and structuring are essential for efficient analysis. This involves transforming raw data into a usable format, ensuring consistency across data points. Organizing the data in a structured format enables easier analysis and interpretation. This could involve creating tables, using standardized formats, and ensuring consistency in data entry.
Data Collection Tools
The selection of appropriate data collection tools is critical. The choice of tools should be guided by the specific needs and characteristics of the CRM mapping exercise. Different tools offer different functionalities, and understanding these functionalities is essential for effective data collection.
| Data Collection Tool | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software | Provides a centralized repository for customer data, facilitating data collection and management. Examples include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM. |
| Sales Force Automation (SFA) Tools | Tracks sales interactions and activities, providing insights into sales processes and customer engagement. Examples include Salesforce Sales Cloud, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales. |
| Marketing Automation Platforms | Captures data from marketing campaigns, enabling analysis of campaign effectiveness and customer responses. Examples include Marketo, Pardot, and HubSpot Marketing Hub. |
| Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence Tools | Facilitates the aggregation and analysis of data from multiple sources, enabling the creation of comprehensive customer profiles. Examples include Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense. |
Identifying and Mapping Customer Interactions
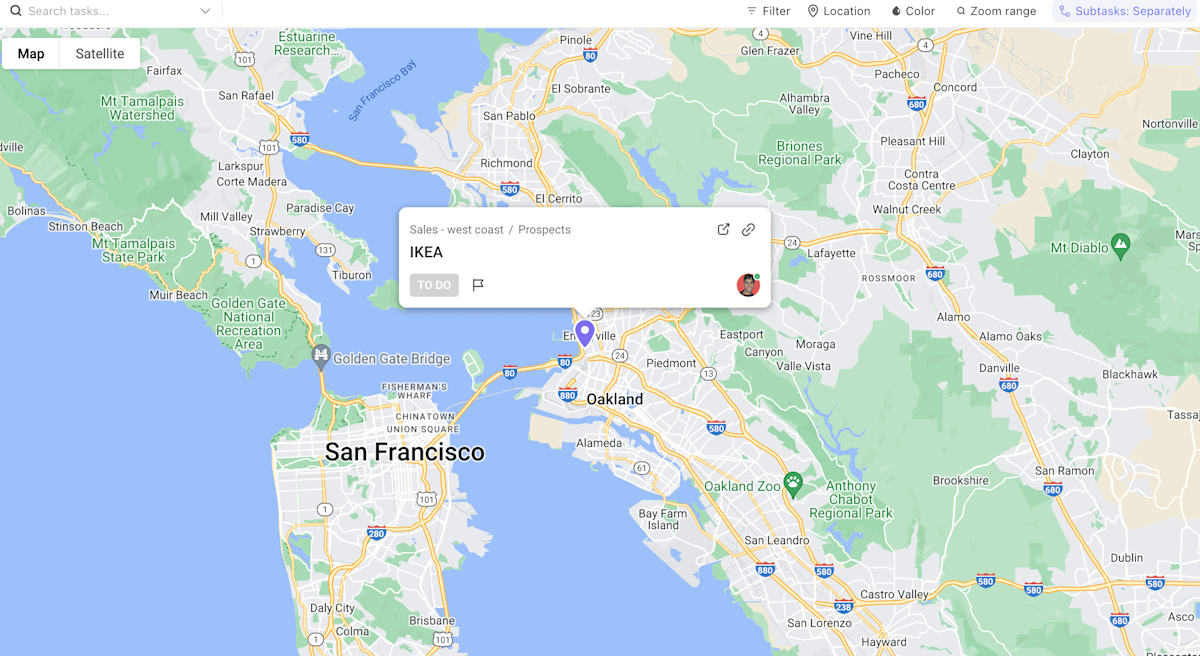
Understanding customer interactions is crucial for a successful CRM implementation. By meticulously documenting and analyzing how customers engage with your brand, you can identify pain points, optimize processes, and tailor your offerings to better meet their needs. This deeper understanding drives improved customer satisfaction and loyalty, ultimately leading to greater business success.Effective CRM mapping hinges on a thorough grasp of customer journeys.
This includes identifying every touchpoint where a customer interacts with your company, from initial awareness to post-purchase support. Detailed interaction data allows for the creation of actionable strategies, ensuring that all customer interactions contribute to a positive and seamless experience.
Importance of Identifying Key Customer Interactions
Accurate identification of key customer interactions is essential for crafting effective CRM strategies. Understanding the sequence and nature of these interactions allows businesses to pinpoint areas for improvement and tailor their approach to each customer segment. This detailed understanding of customer journeys fosters a more customer-centric approach.
Methods for Tracking and Analyzing Customer Interactions
Various methods exist for tracking and analyzing customer interactions. Utilizing CRM software with robust tracking capabilities is crucial. These systems can log interactions across different channels, providing valuable insights into customer behavior. Analyzing interaction data helps in identifying patterns, trends, and common issues. This data-driven approach facilitates targeted improvements to customer experiences.
Other methods include customer surveys, feedback forms, and social media monitoring. Analyzing these data sources reveals valuable insights into customer sentiment and satisfaction levels. Customer support tickets, email exchanges, and website interactions are also key sources of data, each offering unique perspectives on the customer experience.
Role of Customer Journey Mapping in CRM Mapping
Customer journey mapping is an indispensable tool in CRM mapping. It visually represents the steps a customer takes when interacting with a company. This visual representation reveals pain points, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement in the customer experience. Mapping the journey from initial awareness to purchase and beyond is essential. This helps businesses understand where customers encounter friction, where the experience is positive, and where they can enhance interactions.
A detailed customer journey map provides a roadmap for enhancing the entire customer experience, ensuring that every interaction is positive and valuable.
Examples of Different Customer Interaction Points and How They Can be Mapped
Various customer interaction points can be mapped to create a comprehensive CRM map. Examples include website visits, email interactions, phone calls, social media engagement, in-store purchases, and customer support interactions. Each interaction can be categorized, analyzed, and tracked within a CRM system to create a complete picture of the customer experience. For example, a website visit could be mapped to show the pages viewed, the time spent on each page, and any issues encountered.
Email interactions can be tracked to understand open rates, click-through rates, and response times. Mapping these interaction points and analyzing the data provide actionable insights for process improvement.
Creating a Visual Representation of Customer Interactions
A flowchart is a powerful visual tool for representing customer interactions. A flowchart clearly displays the steps in a customer’s journey and the different points of interaction with the business. By connecting each interaction point with the subsequent steps, a visual representation of the entire customer journey is created. This helps in identifying areas for improvement and optimizing the overall customer experience.
For instance, a flowchart can illustrate the steps a customer takes to resolve a product issue through customer support, showing where potential delays or friction points exist. This visual representation allows for quick identification of bottlenecks and areas needing improvement.
Process Mapping and Optimization
A crucial step in CRM implementation is understanding and optimizing existing business processes related to customer interactions. This involves meticulously mapping these processes to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, ultimately leading to a more streamlined and effective customer experience. By visualizing and analyzing these workflows, organizations can pinpoint areas for improvement and implement solutions to enhance overall efficiency and productivity.
Mapping Existing Business Processes
To effectively map existing processes, a systematic approach is essential. Begin by defining the scope of the processes to be mapped. This involves identifying the key customer touchpoints and interactions, from initial contact to post-sale support. Next, document each step involved in these processes, outlining the tasks, responsibilities, and timelines associated with each stage. Detailed documentation helps in creating a comprehensive understanding of the current state of operations.
Crucially, involve relevant personnel from various departments throughout the process mapping phase. Their input ensures a holistic view of the process and identifies potential issues from multiple perspectives.
Identifying Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies
Once the processes are mapped, the next step is to scrutinize them for bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Analyze the time spent at each stage and identify any delays or redundancies. Consider factors like manual data entry, lengthy approval processes, or inadequate communication channels. Data collected during the mapping phase will reveal areas where processes are not optimized. By pinpointing these bottlenecks, organizations can focus on targeted improvements, leading to a more efficient workflow.
Optimizing Business Processes Based on the CRM Map
Optimizing business processes requires a strategic approach. Leveraging the insights gained from the CRM map, identify areas where automation, delegation, or process simplification can improve efficiency. For example, automating repetitive tasks like data entry can significantly reduce manual errors and processing time. Streamlining approval processes can expedite decision-making and accelerate customer interactions. Consider the use of technology to improve communication channels, enabling faster response times and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Flowchart Representation of Mapped Process
A flowchart provides a visual representation of the mapped process. It clearly illustrates the sequence of steps, decisions, and interactions involved in the process. The flowchart serves as a valuable communication tool, allowing stakeholders to readily understand the workflow. It facilitates discussions and approvals, enabling a more collaborative approach to process optimization. A simple example of a flowchart for order processing might show the steps from order placement to order fulfillment, including decision points like payment verification and inventory availability.
Examples of Optimized Processes and Their Impact on Efficiency
| Optimized Process | Description | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Order Processing | Integrating an automated system for order processing, eliminating manual data entry. | Reduced order processing time by 25%, decreased data entry errors by 15%, and improved accuracy. |
| Centralized Customer Support | Establishing a central customer support hub to manage inquiries and requests. | Reduced response time to customer inquiries by 10%, improved customer satisfaction scores by 5%, and reduced operational costs by 2%. |
| Streamlined Approval Workflow | Implementing a streamlined approval process for sales orders, reducing approval cycle times. | Decreased order processing time by 12%, improved sales team productivity by 8%, and reduced order backlog by 10%. |
Technology Integration and Automation
Technology plays a crucial role in modern CRM mapping, enabling businesses to streamline processes, automate tasks, and gain actionable insights from customer interactions. Effective CRM mapping requires integrating various technologies to create a unified view of the customer journey. This integration enhances data analysis, improves decision-making, and ultimately, drives customer satisfaction.Integrating technology into CRM mapping is not just about choosing the right software; it’s about strategically connecting different systems to provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions.
This holistic approach allows businesses to identify trends, personalize experiences, and optimize customer engagement. The key is to leverage technology to automate manual tasks and focus resources on higher-value activities.
Role of CRM Software in CRM Mapping
A robust CRM system is fundamental to CRM mapping. It serves as the central repository for customer data, interactions, and insights. CRM software facilitates the tracking of customer journeys, providing a comprehensive view of each customer’s engagement with the business. This detailed understanding of customer interactions is crucial for identifying areas of improvement and optimizing processes.
Examples of CRM Software Supporting CRM Mapping
Several CRM software platforms excel at supporting CRM mapping. Examples include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SugarCRM. These platforms offer features like custom dashboards, reporting tools, and workflow automation capabilities, enabling users to visualize customer interactions, identify patterns, and create actionable strategies. Salesforce, for instance, allows for detailed customization of dashboards, enabling businesses to tailor their views of customer data to their specific needs.
Strategies for Integrating Different Technologies into the CRM Map
Integrating different technologies into the CRM map requires a strategic approach. The integration should be designed to seamlessly connect various data sources and applications, ensuring a unified view of the customer. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are crucial in this process, enabling data exchange between different systems. For example, connecting marketing automation tools like Marketo or Pardot with a CRM platform allows for synchronized customer data, leading to a more holistic customer view.
This synchronized view helps businesses create personalized marketing campaigns and improve customer engagement.
Benefits of Automating Tasks Based on the CRM Map
Automating tasks based on the CRM map offers numerous benefits. It frees up staff from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on more strategic activities. This automation also enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and improves the consistency of customer interactions. For instance, automating follow-up emails or scheduling reminders based on specific customer interactions ensures timely responses and personalized experiences.
This proactive approach to customer interaction can significantly improve customer satisfaction.
Comparison of CRM Software Platforms for CRM Mapping Capabilities
| CRM Software | Data Visualization | Customization | Integration Capabilities | Automation Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce | Excellent, with custom dashboards and reports | High, allowing for extensive customization | Strong, through APIs and integrations with various apps | Advanced, with workflow automation and automation tools |
| HubSpot | Good, with built-in reporting and visualization tools | Moderate, with pre-built templates and custom options | Good, integrating with various marketing and sales tools | Good, with automation features for tasks like email marketing and lead nurturing |
| Zoho CRM | Good, with customizable dashboards and reports | Moderate, with customizable modules and integrations | Good, with a range of integrations through APIs | Good, with automation for tasks like email campaigns and reminders |
Note: This table provides a general comparison. Specific capabilities may vary depending on the specific CRM software package and its configuration.
Measuring and Evaluating CRM Mapping Effectiveness
Assessing the effectiveness of CRM mapping is crucial for demonstrating its value and ensuring ongoing improvement. This involves a structured approach to measure the impact of the mapping on business processes and outcomes. Successful CRM mapping should lead to tangible improvements in efficiency, customer satisfaction, and revenue generation.A robust evaluation framework allows businesses to understand the ROI of the mapping project and adapt strategies for future CRM implementations.
This process requires a clear understanding of the initial objectives and goals of the mapping, along with measurable indicators of success.
Metrics for Evaluating CRM Mapping
Evaluating the effectiveness of CRM mapping requires a set of well-defined metrics. These metrics must align with the initial objectives and goals of the mapping project, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of its impact. Key areas for evaluation include customer interactions, process efficiency, and business outcomes.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring Success
A variety of KPIs can be used to gauge the success of CRM mapping. These KPIs provide a quantifiable measure of the impact of the mapping process on different aspects of the business.
- Customer Interaction Metrics: Increased response times to customer inquiries, reduced customer service escalations, and improved customer satisfaction scores are all indicators of effective CRM mapping. These metrics reflect how efficiently the CRM system handles customer interactions.
- Process Efficiency Metrics: Reduced cycle times for key business processes (e.g., order fulfillment, lead qualification), fewer errors in data entry, and streamlined workflows are crucial indicators of process optimization. These metrics highlight the improvements in operational efficiency.
- Business Outcome Metrics: Increased sales revenue, higher customer lifetime value (CLTV), and improved customer retention rates are direct indicators of the positive impact of CRM mapping on business outcomes. These metrics represent the overall financial and customer-centric results.
Methods for Tracking and Analyzing Impact
Tracking and analyzing the impact of CRM mapping requires a systematic approach. Tools for tracking and analyzing CRM data can help provide valuable insights into the impact of the mapping process.
- CRM System Reporting: Utilize built-in reporting features of the CRM system to track key metrics, such as customer interactions, service tickets, and sales conversions. These reports provide a snapshot of the current performance against the defined KPIs.
- Data Visualization Tools: Employ dashboards and visualization tools to present CRM data in a clear and concise manner. Visual representations of data facilitate the identification of trends and patterns.
- Performance Metrics Reports: Generate regular reports summarizing the key performance indicators discussed earlier. This helps to track progress over time and identify areas needing adjustments.
Adjusting and Refining the CRM Map
Continuous monitoring and adjustment are essential for ensuring the CRM map remains effective. The CRM map is not a static document; it needs to adapt to changing business needs and customer behavior.
- Regular Review and Analysis: Regularly review the CRM map to ensure it continues to align with business goals and customer needs. This may require re-evaluation of processes and workflows.
- Data-Driven Adjustments: Use performance data to identify areas where the map needs improvement. Data-driven adjustments are crucial to optimize the CRM system for improved performance.
- Feedback Incorporation: Gather feedback from employees who use the CRM system to understand their experience and identify areas for improvement in the CRM map. Incorporating employee feedback is essential to ensure user adoption and satisfaction.
Generating Reports on CRM Mapping Effectiveness
Regular reporting is essential for demonstrating the value of CRM mapping and informing future decisions.
- Comprehensive Reports: Develop comprehensive reports that cover all relevant KPIs, providing a holistic view of CRM mapping effectiveness. The reports should be presented in a clear and concise manner, facilitating understanding.
- Key Performance Indicator Tracking: Track KPIs over time to identify trends and patterns. Visualizations of trends can highlight areas of success and areas needing attention.
- Actionable Insights: Provide actionable insights derived from the collected data. Recommendations for improvements should be clearly Artikeld in the reports, enabling informed decision-making.
Future Trends and Considerations
CRM mapping is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business needs. Staying ahead of the curve requires a proactive approach to integrating emerging trends and adapting strategies accordingly. This section explores key future trends and considerations for effective CRM mapping in the dynamic business landscape.Businesses are increasingly recognizing the importance of a holistic view of customer interactions.
Effective CRM mapping enables this by providing a clear, actionable framework for understanding customer journeys, pain points, and potential areas for improvement.
Emerging Trends in CRM Mapping Technology
Modern CRM mapping leverages a range of technologies, including AI, machine learning, and cloud computing. These technologies are automating tasks, improving data analysis, and offering more insightful data visualizations. This automation frees up human resources for more strategic initiatives, enabling businesses to better adapt to changing market conditions. AI-powered insights, for instance, can predict customer churn or identify potential upselling opportunities, significantly enhancing the efficacy of CRM strategies.
Impact on Business Practices
The adoption of these advanced technologies is fundamentally changing business practices. Automated data analysis, for example, allows for real-time identification of trends and patterns in customer behavior. This empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, personalize customer experiences, and optimize marketing campaigns. Businesses can now respond to changing market demands more rapidly, fostering stronger customer relationships. For instance, an e-commerce company could utilize AI to analyze customer purchase history and proactively suggest relevant products, thereby improving customer satisfaction and increasing sales.
Future Directions and Considerations
The future of CRM mapping will likely see an increased focus on personalization and predictive analytics. Companies will increasingly leverage AI and machine learning to anticipate customer needs and tailor interactions accordingly. This personalized approach is expected to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Another critical consideration is the need for seamless integration across different channels. As customers interact through various platforms (e.g., social media, mobile apps, websites), CRM mapping must ensure data consistency and a unified customer view across all touchpoints.
Adaptability and Flexibility in CRM Mapping Strategies
A key element of future-proofing CRM mapping is adaptability. The rapid pace of technological advancement and evolving customer expectations necessitate flexible strategies. CRM mapping should not be viewed as a static process but as a dynamic system that evolves alongside business needs. Regular reviews and adjustments are crucial to maintain alignment with the changing landscape.
Potential Future Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Data security and privacy concerns | Implementing robust security protocols, adhering to data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR), and educating employees on data handling best practices. |
| Maintaining data accuracy and consistency across multiple systems | Implementing data quality controls, utilizing data cleansing tools, and establishing clear data governance procedures. |
| Keeping pace with rapidly evolving technology | Investing in ongoing training and development for employees, staying informed about emerging technologies, and proactively seeking opportunities for innovation. |
| Ensuring seamless integration with existing systems | Conducting thorough system audits, choosing adaptable and scalable CRM platforms, and prioritizing clear communication and collaboration among teams. |
| Managing the complexity of large-scale CRM mapping projects | Employing project management methodologies, fostering cross-functional collaboration, and using robust reporting and visualization tools to track progress and identify potential roadblocks. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, effective CRM mapping is a dynamic process that requires careful consideration of data, customer interactions, and business processes. By implementing the strategies Artikeld in this guide, businesses can optimize their customer relationships, streamline operations, and drive greater efficiency. Adapting to future trends and continuously evaluating performance is key to long-term success.
FAQ Resource
What are some common CRM mapping methodologies?
Various methodologies exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some common approaches include process mapping, customer journey mapping, and interaction mapping. The best approach will depend on your specific business needs and goals.
How can I measure the success of my CRM mapping efforts?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as increased customer satisfaction scores, reduced customer churn, improved sales conversion rates, and enhanced operational efficiency can help you measure the success of your CRM mapping initiatives.
What tools are available for CRM mapping?
Many software tools are available to assist in CRM mapping, from dedicated CRM software platforms to data visualization and process mapping tools. Your choice will depend on the complexity of your needs and your budget.
What are some common challenges in implementing CRM mapping?
Common challenges include data quality issues, resistance to change, and integrating different systems and processes. Careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and clear communication are vital to overcome these hurdles.