Broker CRMs are revolutionizing real estate operations. Imagine a streamlined system that manages clients, leads, and communication, all in one place. This guide dives deep into the world of Broker CRMs, exploring their features, benefits, and practical applications for real estate professionals.
From boosting agent productivity to enhancing client relationships, Broker CRMs offer a powerful toolkit for success. This exploration examines the essential components of a Broker CRM, including its core functionalities, integration capabilities, and considerations for implementation. We’ll uncover the advantages of choosing the right Broker CRM for your brokerage, ultimately equipping you with the knowledge to maximize ROI.
Introduction to Broker CRM
A Broker CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a powerful tool designed to streamline and enhance brokerage operations. It centralizes all client and prospect data, automating tasks and improving communication to boost productivity and profitability. This organized approach fosters stronger client relationships and facilitates better decision-making.Broker CRMs are crucial for managing the complexities of modern brokerage. They offer a comprehensive platform for tracking leads, managing clients, and automating various administrative tasks, ultimately contributing to improved efficiency and profitability.
These systems play a vital role in navigating the increasing demands of today’s market.
Core Functionalities of a Broker CRM
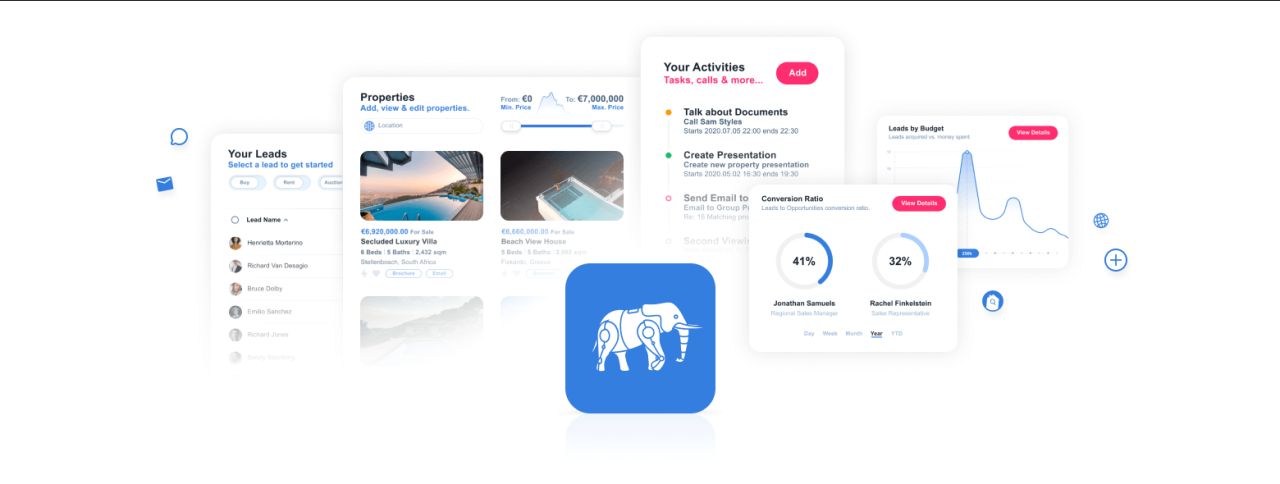
Broker CRMs provide a unified platform for managing all aspects of client interactions. They act as a central repository for information, ensuring that agents have access to complete and accurate details about each client. This comprehensive view enables better service delivery and informed decision-making.
Typical Features of a Broker CRM
Broker CRMs encompass a range of features categorized by their function. A robust system integrates client management, lead generation, and communication tools, all working together to improve efficiency.
- Client Management: This feature facilitates the creation and maintenance of detailed client profiles. Information such as contact details, transaction history, preferences, and financial information can be stored securely. This centralized data ensures agents have all necessary information at their fingertips, enabling personalized service and improved client retention.
- Lead Generation: Broker CRMs often include tools for capturing and tracking leads from various sources. This includes online forms, marketing campaigns, and referrals. The system can automatically categorize and prioritize leads based on various criteria, directing agents to the most promising opportunities. For instance, a CRM might flag leads with high net worth as a priority for follow-up.
- Communication Tools: These tools allow for efficient communication with clients and prospects. Features include email integration, SMS messaging, and scheduling reminders. This automation minimizes delays and ensures prompt responses, enhancing client satisfaction.
Impact on Brokerage Operations
Broker CRMs enhance brokerage operations by streamlining processes and optimizing resource allocation. By automating routine tasks, agents can dedicate more time to client interactions and building relationships. Improved communication and centralized data access facilitate better decision-making, leading to higher profitability. Reduced administrative overhead contributes to overall efficiency.
Comparison of Broker CRM Systems
Different Broker CRM systems vary in their functionality, deployment method, and pricing. A comparison table below highlights key distinctions:
| Feature | Cloud-Based | On-Premises |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Accessed via the internet; no need for local installation. | Installed on the broker’s own servers; requires IT infrastructure. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to accommodate growth; often with flexible pricing plans. | Scaling can be more complex and costly; requires upfront investment in hardware. |
| Security | Typically managed by the provider; often adheres to strict security standards. | Security is the broker’s responsibility; requires dedicated security measures. |
| Cost | Often subscription-based; potentially lower initial costs. | Higher upfront costs for software, hardware, and maintenance. |
| Technical Support | Provided by the vendor; typically accessible via phone, email, or online portal. | Requires in-house IT support or outsourced support; can be more time-consuming. |
Benefits of Using a Broker CRM
A Broker CRM is more than just software; it’s a strategic tool that empowers real estate agents to manage their businesses more effectively. By streamlining processes and centralizing crucial information, a Broker CRM fosters greater productivity, improves client relationships, and ultimately boosts profitability. This comprehensive system allows agents to focus on what they do best: connecting with clients and closing deals.Implementing a Broker CRM significantly enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of real estate operations.
This shift from traditional methods leads to a more organized and streamlined approach, allowing agents to dedicate more time to high-value activities such as client interaction and deal negotiation.
Impact on Agent Productivity and Efficiency
A Broker CRM significantly improves agent productivity by automating repetitive tasks. This automation frees up agents’ time to focus on client interactions, lead nurturing, and strategic business development. The ability to track leads, schedule appointments, and manage communication through a centralized platform significantly reduces time spent on administrative tasks. By organizing client data, communications, and market trends, agents can swiftly access the necessary information to make informed decisions.
Improved lead management and follow-up processes lead to higher conversion rates.
Comparison to Traditional Methods
Traditional methods of managing client and lead data, often relying on spreadsheets, email chains, and paper files, are prone to errors, inconsistencies, and lost information. Broker CRMs provide a secure, centralized repository for all client and lead data, eliminating the risks associated with manual record-keeping. The centralized nature of a CRM enables better collaboration and communication within the brokerage team, improving overall efficiency.
A CRM also allows for robust reporting and analysis, providing valuable insights into market trends and agent performance. This analytical capability empowers data-driven decision-making.
Streamlining Communication and Workflows
A Broker CRM streamlines communication by providing a single platform for managing client interactions. Agents can easily send personalized messages, track responses, and schedule follow-up activities, all within the CRM system. Workflow automation features can be implemented to ensure timely and consistent communication with clients and potential buyers/sellers, significantly improving response times and customer satisfaction. Automated reminders for appointments, follow-ups, and deadlines further enhance efficiency and prevent missed opportunities.
This automated system significantly reduces the risk of errors and ensures consistent communication.
Return on Investment (ROI) Potential
| Benefit | Potential Impact | Estimated ROI |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Lead Conversion | Higher conversion rates through targeted follow-ups and personalized communication. | 15-30% |
| Improved Client Retention | Stronger client relationships through personalized service and consistent communication. | 10-20% |
| Reduced Administrative Time | Automation of tasks like scheduling, reminders, and reporting. | 10-25% |
| Enhanced Collaboration | Improved communication and information sharing within the brokerage team. | 5-15% |
| Data-Driven Decision Making | Access to valuable market insights and agent performance data. | 5-10% |
The ROI potential of a Broker CRM is multifaceted and varies based on specific brokerage strategies and CRM features utilized. A strong CRM implementation can significantly boost profitability by enhancing productivity, optimizing workflows, and improving client satisfaction.
Key Features and Functions
A Broker CRM is more than just a contact management tool; it’s a comprehensive platform designed to streamline workflows, enhance communication, and boost productivity. Key features and functions are crucial for effective brokerage operations, enabling agents to efficiently manage leads, nurture client relationships, and track performance.The core functionality of a Broker CRM hinges on its ability to integrate various aspects of brokerage operations, from lead generation to client onboarding and property management.
A robust system will provide a centralized hub for all essential information, ensuring seamless access and improved collaboration among agents and support staff.
Lead Management
Effective lead management is a cornerstone of any successful brokerage. A Broker CRM streamlines this process by providing a structured approach to capturing, organizing, and nurturing potential clients. This includes features such as automated lead assignment, qualification criteria, and follow-up reminders. The system allows for tracking of lead interactions, allowing agents to personalize their approach and improve conversion rates.
For example, a CRM might automatically categorize leads based on their expressed interest, allowing agents to prioritize those most likely to become clients.
Communication Tools
A Broker CRM’s communication tools are vital for maintaining contact and building relationships with clients and prospects. Integration with email platforms, SMS messaging, and instant messaging services enables seamless communication across various channels. Task management features allow for scheduling appointments, setting reminders, and tracking correspondence. These functionalities minimize communication breakdowns and ensure timely follow-up.
Property Management and Client Relationship Tracking
A Broker CRM facilitates property management by allowing agents to store and access comprehensive information about listings, including details about the property, pricing, and transaction history. Furthermore, the system enables meticulous tracking of client interactions, allowing for a deeper understanding of their needs and preferences. This comprehensive record-keeping enhances client satisfaction and fosters long-term relationships. For example, agents can easily access past communications with a client to tailor their approach to future interactions, creating a personalized experience.
Reporting and Analytics
Regular reporting and insightful analytics are essential for performance evaluation and strategic decision-making. A Broker CRM can provide a range of reports on key metrics, including lead conversion rates, client retention, and property transaction data. These reports help agents identify areas for improvement and optimize their strategies.
| Report Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Lead Source Analysis | Identifies the most effective channels for generating leads. |
| Client Retention Rate | Measures the percentage of clients who return for future transactions. |
| Property Performance Report | Provides data on listing durations, pricing strategies, and transaction speeds. |
| Agent Performance Dashboard | Tracks key metrics for individual agents, including sales volume and lead conversion rates. |
Integration with Other Tools
Broker CRMs are designed to seamlessly integrate with other real estate tools, streamlining workflows and enhancing efficiency. This interconnectedness empowers agents to access critical data and tools in one centralized platform, reducing the need for manual data entry and improving overall productivity. This integration fosters a more cohesive and efficient real estate operation.
Integration with Multiple Systems
Broker CRMs are typically built with a modular architecture that allows for integration with a wide range of real estate systems. This modularity facilitates a dynamic, adaptable system, and empowers agents to tailor their workflow to best suit their needs. Crucially, this integration minimizes the need to switch between different platforms, which saves time and reduces the risk of data inconsistencies.
Integration with MLS (Multiple Listing Service)
A critical aspect of a Broker CRM’s functionality is its integration with the MLS. This integration allows agents to access the most up-to-date listings, enabling them to effectively manage their client interactions and present relevant properties. The system automatically updates the CRM with any changes in listing information, ensuring that agents always have the most accurate details available.
Integration with Marketing Platforms
Broker CRMs often integrate with marketing platforms, enabling agents to effectively manage and track their marketing campaigns. This integration allows agents to automate tasks like sending email blasts or scheduling social media posts, improving their marketing efficiency. Furthermore, the CRM can track the performance of these campaigns, providing valuable insights into what is working and what isn’t.
Integration with Real Estate Websites
Integration with real estate websites is a key component of a modern Broker CRM. This integration allows agents to seamlessly share client data and property listings across various platforms, improving visibility and accessibility. This allows agents to efficiently manage their listings on multiple sites and keep their client information up to date across all platforms.
Data Transfer and Synchronization
Data transfer between the CRM and other tools is typically handled through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). These APIs allow for seamless data exchange, minimizing manual data entry and maximizing accuracy. This automated data transfer reduces the risk of errors and ensures data consistency across all platforms.
Examples of Seamless Integration
A Broker CRM might automatically import property listings from the MLS into the CRM, updating the database with the latest information. The CRM might also automatically update a real estate website with new listings or changes in client information. The system could even trigger automated marketing campaigns based on the CRM’s data.
Table of Integration Options
| Integration Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| MLS Integration | Connects to the Multiple Listing Service, providing real-time access to listings. | Access to current listings, automatic updates, reduced manual data entry. |
| Marketing Platform Integration | Integrates with marketing platforms to automate campaigns and track performance. | Automated marketing tasks, campaign tracking, improved efficiency. |
| Real Estate Website Integration | Connects to real estate websites to display listings and share client data. | Enhanced visibility, centralized data management, improved client communication. |
Choosing the Right Broker CRM
Selecting the right Broker CRM is crucial for a brokerage’s efficiency and success. A poorly chosen system can lead to wasted resources, inefficient workflows, and ultimately, reduced profitability. Careful consideration of various factors, including features, pricing, and vendor support, is paramount. This process requires a thorough understanding of your brokerage’s unique needs and goals.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Broker CRM
A comprehensive evaluation process is essential to ensure the chosen CRM aligns with the brokerage’s specific requirements. Several key factors should be evaluated before committing to a particular platform. These include the brokerage’s size, complexity of operations, current technology infrastructure, budget constraints, and the desired level of customization. Specific features required, like lead management, reporting, and communication tools, must also be assessed.
Questions to Ask Potential Vendors
Thorough due diligence is critical in evaluating potential CRM providers. Asking the right questions can reveal vital information about a vendor’s capabilities and suitability for the brokerage. Key inquiries include assessing the vendor’s experience in the real estate industry, their understanding of the brokerage’s unique needs, and the flexibility of the CRM to adapt to future growth. Understanding their support options and the process for customization is also important.
A vendor’s ability to provide comprehensive training and ongoing support should be carefully evaluated. Questions regarding pricing models, contract terms, and scalability options should also be part of the assessment.
Comparing Broker CRM Providers
Comparing different Broker CRM providers based on features, pricing, and support is a crucial step in the selection process. A comprehensive comparison should include a detailed evaluation of each platform’s key features, focusing on their strengths and weaknesses relative to the brokerage’s needs. Consider factors such as the level of customization, reporting capabilities, and integration options. The provider’s pricing models should be examined, including any hidden costs or limitations.
The vendor’s reputation and customer support should be scrutinized, as demonstrated through case studies, reviews, and testimonials.
Key Metrics to Assess CRM Suitability
Evaluating the suitability of a CRM for a brokerage requires a focus on key metrics. These metrics should be tailored to the brokerage’s specific needs and objectives. Crucial metrics include the efficiency gains observed in lead management, the reduction in administrative overhead, and improvements in agent productivity. The ability of the CRM to enhance communication, streamline workflows, and increase revenue generation are also critical aspects to consider.
Evaluating how the system contributes to data-driven decision-making is also vital.
Summary Table of Broker CRM Platforms
The following table provides a concise summary of the pros and cons of different Broker CRM platforms, enabling a more informed decision.
| Broker CRM Platform | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Platform A | Intuitive interface, strong reporting features, affordable pricing. | Limited customization options, average customer support. |
| Platform B | High level of customization, robust integrations, dedicated support team. | Complex interface, more expensive pricing. |
| Platform C | Excellent lead management tools, seamless communication features, user-friendly design. | Limited reporting options, occasional technical glitches. |
Implementation and Training
Implementing a Broker CRM effectively requires a well-defined plan and meticulous execution. A smooth transition ensures minimal disruption to daily operations and maximizes the system’s benefits. Thorough training empowers staff to utilize the CRM efficiently, driving adoption and optimal performance.Implementing a Broker CRM successfully involves several key stages. Careful planning and execution are crucial to avoid issues and ensure a productive transition.
The process should be structured to minimize disruptions to existing workflows and maximize user adoption.
Implementation Steps
A structured implementation plan is essential for a successful CRM deployment. This plan should detail the project timeline, responsibilities, and milestones. It’s vital to allocate sufficient resources and ensure consistent communication throughout the process.
- Needs Assessment: Identifying specific needs and requirements is paramount. Understanding current workflows, pain points, and future goals helps tailor the CRM to address these needs effectively.
- System Selection: Choosing the appropriate CRM system is crucial. Factors to consider include functionality, scalability, integration capabilities, and cost-effectiveness. Thorough research and comparison are essential.
- Data Migration: Migrating existing data into the new CRM is critical. A well-defined plan ensures accurate and complete data transfer, minimizing errors and ensuring continuity.
- System Setup: Configuring the CRM to meet specific needs involves setting up user roles, permissions, and workflows. This stage should be performed meticulously to avoid future complications.
- Testing and Validation: Thorough testing across various user roles is necessary to ensure the system operates as expected. This step identifies potential issues and allows for adjustments before full deployment.
- Go-Live: Full deployment and launch of the CRM system to the intended users. Careful monitoring and support during this phase are crucial to addressing any immediate issues.
Training Staff
Effective training programs are essential for successful CRM adoption. This ensures staff members are comfortable and proficient in using the system.
- Develop a Training Curriculum: A comprehensive training curriculum tailored to different user roles is vital. The curriculum should cover core functionalities, best practices, and specific workflows.
- Hands-on Training Sessions: Practical sessions allow staff to apply knowledge and gain confidence in using the system. These sessions should address common use cases and troubleshooting techniques.
- Use Cases and Scenarios: Illustrating real-world scenarios helps users understand how the CRM can improve their daily tasks. Demonstrations and simulations should be included in the training process.
- Ongoing Support and Resources: Provide access to resources like FAQs, tutorials, and online help after the initial training. This allows staff to continue learning and adapting to new functionalities.
Data Migration and Security
Data migration and security are critical components of CRM implementation. Maintaining data integrity and confidentiality are paramount.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regular backups and recovery procedures are essential to protect against data loss. A robust backup strategy should be in place to restore data in case of any unforeseen events.
- Data Validation: Validating the accuracy of migrated data is vital. This process helps ensure data quality and avoids inconsistencies.
- Data Security Measures: Implementing robust security measures like access controls and encryption is necessary. Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access is crucial.
Customizing the Broker CRM
Customizing the CRM to meet specific needs involves adapting existing functionalities or adding new ones.
- Identify Specific Needs: Understanding the unique needs of the brokerage is the first step in customization. Identifying specific functionalities and workflows that need to be adapted or added is vital.
- Utilize Customization Options: CRM systems offer various customization options. Understanding the available options is crucial to tailoring the system effectively.
- Consult with Experts: Expert advice from the CRM vendor can assist in the customization process. They can help determine the most efficient and effective methods to customize the CRM.
Setting up a Broker CRM for Effective Use
This guide Artikels the steps to set up a Broker CRM for optimal use.
- Define Roles and Permissions: Clearly define roles and responsibilities for each team member. Appropriate permissions should be assigned to ensure efficiency and security.
- Customize Workflows: Tailor workflows to match the specific needs and processes of the brokerage. This improves efficiency and streamlines tasks.
- Establish Communication Channels: Set up internal communication channels for reporting, feedback, and support. This facilitates efficient collaboration and issue resolution.
- Regularly Review and Update: Regularly review and update the CRM configuration to accommodate evolving needs. This ensures the CRM remains effective and relevant.
Advanced Uses and Customization
Broker CRMs are not just record-keeping tools; they are powerful platforms that can be tailored to a brokerage’s specific needs. Beyond basic functions, advanced customization options allow brokers to leverage their CRM for targeted marketing, streamlined workflows, and insightful data analysis. This section will explore the versatility of Broker CRMs, highlighting advanced features and practical applications.
Marketing Campaign Management
Broker CRMs offer robust capabilities for managing marketing campaigns. By segmenting client databases based on various criteria, brokers can craft highly targeted email campaigns, promotional materials, and personalized outreach. This precision marketing approach increases campaign effectiveness and minimizes wasted resources. For instance, a brokerage can segment clients by property type, location, or past purchase history to tailor marketing messages, ensuring relevant and engaging content reaches the right audience.
Customizable Dashboards and Reports
Broker CRMs often provide the flexibility to create custom dashboards and reports. This feature allows brokers to visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) in a format that best suits their business needs. For example, a brokerage might want a dashboard that displays the number of new listings, client interactions, and pending transactions in a single view. Furthermore, customized reports can provide insights into lead generation effectiveness, sales conversion rates, and overall brokerage performance, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Task Automation
Automation is a crucial aspect of modern broker CRMs. Automating routine tasks, such as sending follow-up emails, scheduling appointments, or generating reports, frees up valuable time and reduces the risk of errors. Implementing automated workflows streamlines processes, ensuring that essential tasks are completed efficiently and on time. This automation can be further enhanced with integration to other tools.
Tailoring to Specific Brokerage Processes
Brokerage processes vary, and a CRM should be adaptable to these differences. Customizable workflows within the CRM allow brokers to map their unique processes, ensuring that the CRM aligns seamlessly with their daily operations. This can include setting up specific approval workflows, defining task assignments, and creating unique data entry forms. For example, a brokerage specializing in luxury properties may require a CRM with fields dedicated to high-end amenities and custom reporting features.
Customization Levels Comparison
| Customization Level | Features | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Standard features, limited customization options. | Brokerages with simple operational needs. |
| Intermediate | Customizable dashboards, basic workflows, and some data integrations. | Brokerages with moderate operational complexity. |
| Advanced | Extensive customization options, custom fields, advanced reporting, and integration with various third-party tools. | Brokerages with highly complex and specific operational needs. |
Data Security and Privacy
Protecting client data is paramount in the real estate industry. Brokerage CRM systems must prioritize the security and privacy of sensitive information, adhering to strict compliance regulations and industry best practices. This section details how broker CRMs safeguard client data, ensuring trust and maintaining a high level of professionalism.
Data Security Measures in Broker CRMs
Broker CRMs employ various security measures to protect client data. These measures include robust encryption protocols for data transmission and storage. Access controls are implemented to limit data access to authorized personnel only. This helps prevent unauthorized access and potential misuse of sensitive information.
Compliance with Data Security Regulations
Real estate data security is governed by various compliance regulations, including GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, depending on the jurisdiction. Broker CRMs must comply with these regulations to maintain legal compliance and avoid penalties. These regulations Artikel specific requirements for data storage, access, and disposal, and adherence is critical for maintaining client trust.
Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
Regular data backups are crucial for restoring lost or corrupted data. Broker CRMs employ automated backup systems to protect against data loss due to hardware failure, software errors, or malicious attacks. Recovery procedures are essential for restoring data quickly and efficiently in the event of a disaster. These procedures must be documented and tested regularly to ensure they are effective.
Ensuring Data Privacy Within the Broker CRM System
Data privacy is paramount. Broker CRMs implement features to ensure data privacy, including data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques. These techniques protect sensitive data while still allowing for analysis and reporting. Strict data retention policies are also implemented to comply with regulatory requirements.
Comparison of Data Security Measures in Different Broker CRM Systems
| Broker CRM System | Encryption Protocols | Access Controls | Data Backup Frequency | Data Privacy Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRM1 | 256-bit AES encryption | Multi-factor authentication, role-based access | Daily, incremental backups | Data masking, anonymization tools |
| CRM2 | 128-bit TLS encryption | Password policies, audit trails | Weekly full backups | Pseudonymization, data retention policies |
| CRM3 | 256-bit AES encryption | Biometric authentication, granular permissions | Daily, incremental backups with monthly full backups | Data encryption at rest, access logging |
This table provides a simplified comparison. Actual security measures may vary depending on the specific CRM and its features. It’s essential to thoroughly research each CRM’s security features before selecting one for your brokerage. The listed examples highlight some standard practices, and brokers should evaluate a CRM based on its specific implementation and documentation.
Case Studies of Broker CRMs
Broker CRM solutions have proven invaluable in streamlining real estate operations and enhancing productivity. Analyzing successful implementations across various brokerage settings provides insights into the tangible benefits and outcomes achievable with the right CRM. These case studies highlight the diverse applications and positive impacts of Broker CRMs in different real estate landscapes.
Real Estate Brokerage A: Streamlined Lead Management
Brokerage A, a mid-sized firm specializing in residential properties, implemented a CRM to manage their lead flow more efficiently. Prior to implementation, lead tracking was inconsistent, often resulting in missed opportunities. The CRM system automated lead capture, categorization, and follow-up, significantly improving lead conversion rates. The system provided a centralized repository for all client interactions, allowing agents to access comprehensive client profiles and tailor their communication strategies effectively.
As a result, the brokerage experienced a 15% increase in closed deals within the first year of CRM implementation.
Commercial Real Estate Firm B: Enhanced Deal Tracking
Firm B, a commercial real estate brokerage, used a CRM to enhance deal tracking and management. Complex commercial deals often involved multiple parties, intricate timelines, and extensive documentation. The CRM system allowed the brokerage to track every stage of a deal, from initial contact to closing, ensuring that all parties were kept informed and on schedule. This improved transparency and accountability, ultimately resulting in a 10% reduction in deal closure time and a 20% increase in successful commercial transactions.
Independent Agent C: Personalized Client Communication
Agent C, an independent agent, utilized a CRM to personalize client communication and foster stronger relationships. The CRM allowed the agent to track client preferences, needs, and past interactions. This data-driven approach enabled the agent to tailor communication strategies, ensuring clients felt valued and understood. As a result, Agent C experienced a 20% increase in repeat business and a 15% increase in referrals.
Table: Key Takeaways from Broker CRM Case Studies
| Brokerage | CRM Focus | Key Result |
|---|---|---|
| Brokerage A | Lead Management, Client Interaction | 15% increase in closed deals |
| Firm B | Deal Tracking, Collaboration | 10% reduction in deal closure time, 20% increase in successful commercial transactions |
| Agent C | Client Relationship Management, Personalized Communication | 20% increase in repeat business, 15% increase in referrals |
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Broker CRM is a game-changer for real estate brokerages. By streamlining processes, enhancing communication, and maximizing data management, brokerages can unlock significant advantages in today’s competitive market. The key is selecting a CRM that aligns with your specific needs and implementing it strategically. This comprehensive guide provided a roadmap to navigate the intricacies of Broker CRM technology and equip you with the tools for success.
Essential FAQs
What are the common integration issues with Broker CRMs?
Integration challenges can arise from compatibility issues between the CRM and other tools, like MLS systems or marketing platforms. Data transfer processes might also encounter roadblocks. Thorough vendor research and careful configuration are crucial to minimize these problems.
How can I measure the ROI of a Broker CRM?
ROI is typically measured by evaluating metrics like increased agent productivity, improved lead conversion rates, reduced administrative overhead, and enhanced client satisfaction. A detailed analysis of pre- and post-implementation data provides concrete evidence of the CRM’s return on investment.
What security measures are typically in place for Broker CRMs?
Modern Broker CRMs employ various security protocols, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Brokers should verify these measures and comply with relevant data privacy regulations.
What are some cost considerations for different Broker CRM platforms?
Broker CRM pricing varies based on features, user capacity, and customization needs. Factors such as cloud-based vs. on-premise solutions and the inclusion of premium add-ons influence the overall cost. It’s essential to get detailed pricing information from vendors to compare options.