Healthcare CRM software is revolutionizing how healthcare organizations manage patient relationships and streamline operations. From hospitals to clinics, this powerful tool enhances communication, improves patient care, and fosters better collaboration among staff. This guide dives deep into the intricacies of healthcare CRM systems, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and implementation strategies.
The core functionalities of a typical healthcare CRM system revolve around patient data management, communication tools, and reporting capabilities. These systems facilitate streamlined patient interactions, enabling providers to efficiently manage appointments, track patient history, and personalize care plans. Moreover, they offer a wealth of data insights that can be leveraged to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making.
Introduction to Healthcare CRM Software
A healthcare CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a specialized software designed to manage and optimize interactions with patients, improve operational efficiency, and enhance the overall healthcare experience. It acts as a central repository for patient information, streamlining communication and facilitating better care coordination.This software integrates various functionalities to provide a comprehensive view of each patient’s history, preferences, and interactions with the healthcare provider.
By centralizing patient data and automating tasks, healthcare CRMs help improve the efficiency of administrative processes, leading to cost savings and enhanced patient satisfaction.
Core Functionalities of a Healthcare CRM System
Healthcare CRM systems typically encompass a range of core functionalities to support the diverse needs of healthcare providers. These functionalities facilitate effective patient management and streamline administrative tasks.
- Patient Relationship Management: This involves managing patient data, including demographics, medical history, contact information, and appointment schedules. The system allows for efficient tracking of patient interactions and facilitates communication.
- Appointment Scheduling and Reminders: Automating appointment scheduling, sending reminders, and managing no-shows streamlines operations and reduces administrative overhead. This feature also enables the system to track patient compliance and predict potential issues.
- Communication Management: Healthcare CRMs facilitate communication between patients and providers, including email, SMS, and other messaging channels. This ensures timely communication regarding appointments, test results, and other crucial updates.
- Reporting and Analytics: The system generates reports on patient interactions, appointment trends, and other key metrics. This data-driven approach helps healthcare providers understand their patient base and identify areas for improvement.
Key Benefits of Implementing a Healthcare CRM System
Implementing a healthcare CRM system offers numerous advantages, impacting both operational efficiency and patient satisfaction.
- Improved Patient Care Coordination: A centralized system provides a holistic view of a patient’s health journey, allowing healthcare providers to access complete medical history and track progress more effectively. This fosters better care coordination across different departments and specialists.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Automation of tasks like appointment scheduling, communication, and data entry significantly reduces administrative burden. This frees up staff time for more patient-centric activities.
- Increased Patient Satisfaction: Streamlined communication, timely reminders, and personalized care experiences contribute to higher patient satisfaction. Improved access to information and responsive communication leads to greater patient engagement and satisfaction.
- Reduced Costs: By optimizing operational processes and reducing administrative errors, healthcare CRMs can lead to significant cost savings. This efficiency translates into increased profitability and resource optimization.
Different Types of Healthcare CRM Software
Different healthcare settings require tailored CRM solutions. The table below Artikels some common types of healthcare CRM software.
| Type of Healthcare Provider | CRM Software Focus |
|---|---|
| Hospitals | Managing large volumes of patient data, coordinating care across various departments, and supporting complex clinical workflows. |
| Clinics | Streamlining patient scheduling, communication, and administrative tasks in a smaller, more focused environment. |
| Pharmaceutical Companies | Managing relationships with healthcare providers, tracking sales data, and supporting marketing campaigns. |
| Home Health Agencies | Tracking patient visits, managing care plans, and ensuring timely communication between patients and caregivers. |
Features and Capabilities

Modern healthcare CRM software provides a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline operations, enhance patient care, and improve overall efficiency within healthcare organizations. These tools go beyond basic contact management, offering sophisticated functionalities for appointment scheduling, communication, and data analysis. The availability of such features has significantly impacted patient care management, leading to improved communication and more personalized treatment plans.
Core Functionality
Healthcare CRM systems offer a variety of core features, crucial for efficient patient management. These features often include robust contact management, enabling healthcare providers to maintain detailed patient records, including medical history, allergies, and contact information. Effective appointment scheduling and reminders are vital aspects, enabling better coordination between patients and providers. Automated communication tools, such as email and SMS messaging, facilitate seamless communication regarding appointments, test results, and other crucial information.
Advanced Features
Beyond core functionality, many advanced features are becoming increasingly prevalent in healthcare CRM systems. These functionalities often include patient portal access, enabling patients to manage their health information, schedule appointments, and communicate with providers directly. Integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems streamlines data flow, ensuring accurate and readily accessible patient information. Advanced analytics and reporting capabilities offer valuable insights into patient trends, allowing healthcare providers to identify patterns, improve service delivery, and optimize resource allocation.
Vendor Comparison
Different vendors offer varying features and pricing tiers within their healthcare CRM software. Some systems excel in specific areas, such as robust patient portal integration or sophisticated analytics. For instance, vendor A might offer a highly customizable patient portal, while vendor B might emphasize integration with existing EHR systems. Thorough evaluation of specific requirements and the features offered by each vendor is essential for choosing the most suitable solution.
Consider the scale of the practice and the level of sophistication needed in data analysis and reporting when evaluating options.
Real-World Example
A small clinic utilizes a healthcare CRM to manage its patient database and schedule appointments. The clinic integrates the CRM with its EHR system, allowing for seamless data exchange. The system automates appointment reminders, sending notifications to patients via SMS and email. The clinic also utilizes the patient portal for secure messaging and appointment rescheduling. This system significantly reduces administrative burden and enhances communication between the clinic and its patients.
Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Benefit | Typical Pricing Tiers |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Centralized patient data, improved communication | Basic: Free/Low, Standard: $50-$200/month, Premium: $200+/month |
| Appointment Scheduling | Streamlined scheduling, reduced no-shows | Basic: Free/Low, Standard: $50-$200/month, Premium: $200+/month |
| Automated Communication | Proactive communication, timely updates | Basic: Free/Low, Standard: $50-$200/month, Premium: $200+/month |
| Patient Portal | Enhanced patient engagement, self-service options | Basic: Free/Low, Standard: $50-$200/month, Premium: $200+/month |
| EHR Integration | Seamless data flow, improved accuracy | Basic: Free/Low, Standard: $50-$200/month, Premium: $200+/month |
Pricing tiers can vary significantly based on vendor, features included, and the number of users.
Benefits and Use Cases
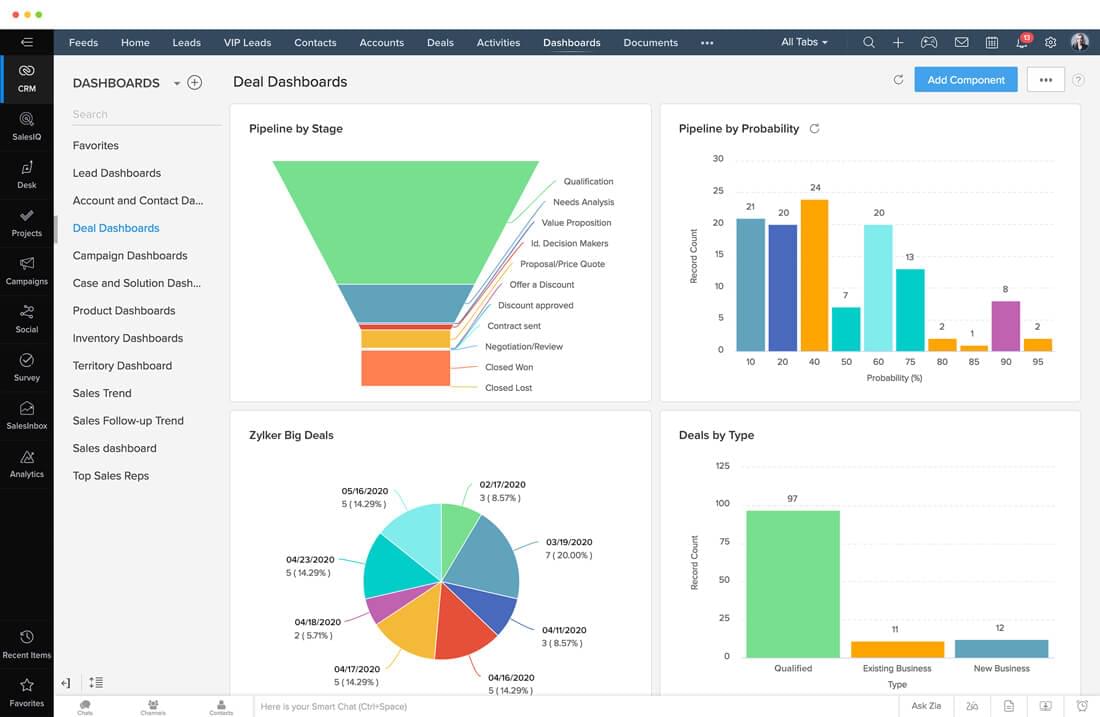
Healthcare CRM software offers substantial advantages for various healthcare settings, streamlining operations, enhancing communication, and bolstering compliance. This powerful tool empowers healthcare professionals to focus on patient care while efficiently managing administrative tasks. It fosters collaboration and data-driven decision-making, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced operational costs.
Advantages Across Healthcare Settings
Healthcare CRM systems provide benefits across diverse settings, from hospitals and clinics to physician practices and long-term care facilities. These systems facilitate better organization and communication, leading to more efficient workflows and enhanced patient care.
- Hospitals and Clinics: Streamlined appointment scheduling, reduced administrative overhead, and improved patient record management are key benefits. Efficient tracking of patient progress and treatment plans across departments enhances coordination and care continuity. For example, a hospital using a CRM can track a patient’s history, medications, and allergies across different departments, eliminating potential errors and ensuring consistent care.
- Physician Practices: CRM systems facilitate appointment scheduling, automated reminders, and improved communication with patients. They also assist with patient relationship management, enabling practices to nurture relationships and encourage positive feedback, leading to increased patient retention.
- Long-Term Care Facilities: CRM software supports managing resident information, medication schedules, care plans, and communication with families. This comprehensive view of resident care ensures continuity and improves the overall quality of care.
Operational Efficiency Improvements
CRM software streamlines various processes, leading to significant improvements in operational efficiency. Automated tasks, such as appointment reminders and report generation, free up staff time for direct patient care.
- Reduced administrative burden: Automation of tasks like appointment scheduling and follow-up reduces the workload on administrative staff. This allows them to focus on more complex tasks, improving overall efficiency.
- Improved appointment scheduling: Automated scheduling and reminders reduce no-shows and wasted appointment slots. This optimizes resource utilization and minimizes delays in patient care.
- Enhanced patient record management: Centralized patient records provide instant access to critical information for all relevant staff members. This improves coordination and reduces errors, leading to more efficient patient care.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
CRM systems facilitate communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals. Improved communication between physicians, nurses, and other staff members ensures that patients receive comprehensive and coordinated care.
- Improved communication channels: CRM systems provide various communication channels, such as email, messaging, and secure messaging, to facilitate efficient communication among healthcare providers. For example, if a patient’s condition changes, the CRM can automatically alert relevant staff, allowing for immediate action and better patient care.
- Enhanced collaboration tools: Shared access to patient records, task assignment, and real-time updates improve collaboration between healthcare teams. This fosters a more cohesive and effective work environment, leading to better patient outcomes.
Key Metrics for Tracking and Analysis
CRM systems allow healthcare organizations to track key metrics, enabling data-driven decision-making. Analysis of these metrics helps organizations understand performance trends and identify areas for improvement.
- Patient satisfaction scores: Tracking patient satisfaction scores provides insights into the quality of care and identifies areas needing improvement.
- Appointment scheduling efficiency: Analyzing appointment scheduling data helps identify trends, such as no-shows, and optimize scheduling practices.
- Staff productivity: Monitoring staff productivity metrics, such as time spent on various tasks, allows for the identification of bottlenecks and process improvements.
Supporting Compliance Requirements
Healthcare CRM systems can support compliance with various regulations and standards. Centralized data management and audit trails make it easier to meet regulatory requirements.
- HIPAA compliance: CRM systems designed for healthcare often incorporate security features to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient data, adhering to HIPAA regulations. Robust data encryption and access controls are crucial components of these systems.
- Data security and privacy: Protecting patient data is paramount. CRM systems can implement stringent security protocols to safeguard sensitive information, meeting legal and ethical requirements.
- Audit trails and documentation: Detailed audit trails help healthcare organizations maintain records of all actions taken, ensuring compliance with regulations and facilitating the verification of data integrity.
Implementation and Integration
Implementing a healthcare CRM system is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning and execution. Successful implementation hinges on meticulous data migration and seamless integration with existing systems, like Electronic Health Records (EHRs). This ensures a smooth transition, minimizing disruption to workflows and maximizing the system’s value. Challenges are inherent in such projects, but with a well-defined strategy, they can be effectively addressed.Effective implementation ensures the CRM system seamlessly integrates into the existing healthcare ecosystem, supporting improved patient care, enhanced operational efficiency, and data-driven decision-making.
Steps Involved in Implementing a Healthcare CRM System
The implementation process typically involves several key steps. These steps, when carefully followed, lead to a smoother transition and maximize the system’s impact on the organization. The process often begins with a thorough assessment of current workflows and requirements. This phase includes defining clear objectives, identifying key stakeholders, and establishing realistic timelines.
- Needs Assessment and Planning: Carefully analyze existing workflows, identify pain points, and define specific goals for the CRM system. This step involves gathering input from various stakeholders, including clinicians, administrators, and front-office staff, to ensure alignment with the organization’s overall objectives. Documentation of these requirements is crucial for a successful implementation.
- System Selection and Configuration: Choose a CRM system that aligns with the identified needs and budget. Configure the system to meet specific requirements, customizing fields, workflows, and user roles as needed.
- Data Migration: Migrate data from legacy systems to the new CRM, ensuring accuracy and completeness. This critical step often requires specialized tools and expertise.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the system with various user scenarios to identify and resolve potential issues before full deployment. This step ensures that the system operates as expected and that users can effectively utilize its features.
- Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training to all users on how to effectively utilize the CRM system. Implement a robust support system to address any questions or issues that may arise after deployment.
- Deployment and Go-Live: Execute a phased rollout or full deployment of the CRM system to all users. Monitor the system closely and address any initial issues promptly.
Importance of Data Migration and Integration
Data migration and integration are paramount to the success of a healthcare CRM implementation. The process involves transferring existing patient data, clinical records, and other relevant information into the new system. This ensures that the new CRM system has the necessary historical context for effective analysis and future decision-making.
- Data Accuracy and Completeness: Accurate and complete data is critical for generating reliable insights and supporting informed decisions. Thorough data validation procedures are essential to maintain the integrity of the migrated data.
- Workflow Continuity: Seamless data integration ensures the continuity of workflows, minimizing disruptions to daily operations. Maintaining the integrity of workflows is vital for maintaining productivity.
- Improved Decision-Making: Accurate and complete data enables data-driven decision-making, leading to more effective resource allocation, improved patient care, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Potential Challenges During Implementation
Several challenges can arise during healthcare CRM implementation. Careful planning and mitigation strategies can minimize the impact of these issues.
- Data Integrity Issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data from legacy systems can negatively impact the effectiveness of the new CRM. Robust data cleansing and validation procedures are essential.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating with existing EHR systems can be technically complex. Thorough planning and expertise are essential to ensure a smooth integration process.
- User Resistance: Resistance to change can hinder user adoption of the new CRM. Effective training and communication are vital to address these concerns.
Step-by-Step Guide for Data Migration from Legacy Systems
A systematic approach to data migration is crucial for ensuring accuracy and minimizing disruption. This detailed guide Artikels the steps involved.
- Assessment and Planning: Identify data sources, target fields, and migration tools.
- Data Extraction: Extract data from legacy systems using appropriate tools and techniques.
- Data Transformation: Transform the extracted data to conform to the new CRM’s data structure and format.
- Data Loading: Load the transformed data into the new CRM system.
- Validation and Verification: Validate the migrated data for accuracy and completeness.
Key Considerations for EHR Integration
Integration with EHRs is a critical aspect of a healthcare CRM implementation. This table Artikels key considerations for effective integration.
| Integration Area | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Data Exchange Protocols | Select standards (e.g., HL7) to facilitate secure and efficient data exchange. |
| Security and Privacy | Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive patient data. |
| Data Mapping | Precisely map data fields between EHR and CRM systems. |
| Workflow Integration | Ensure seamless workflows between the systems. |
| Testing and Validation | Thoroughly test integration functionality and data accuracy. |
Data Security and Privacy
Protecting patient data is paramount in healthcare CRM systems. Robust security measures are essential not only to maintain patient trust but also to comply with stringent regulations, preventing breaches and safeguarding sensitive information. This section delves into the critical aspects of data security within a healthcare CRM, emphasizing the importance of compliance and best practices.
Importance of Data Security in Healthcare CRM Systems
Healthcare data, including patient medical records and financial information, is highly sensitive. Compromised data can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions for healthcare organizations. A secure CRM system is crucial to maintain patient trust and uphold legal obligations.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements for Healthcare Data
Strict regulations govern the handling and protection of healthcare data. These regulations, like HIPAA in the US, and GDPR in Europe, mandate specific security measures to safeguard patient information. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in substantial penalties.
Measures to Protect Patient Data within a CRM System
Implementing comprehensive security measures is critical for safeguarding patient data. These measures include:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest is essential. This process transforms readable data into an unreadable format, preventing unauthorized access. This is particularly vital for storing and transmitting patient information.
- Access Control: Implementing strict access control policies and user authentication is paramount. Only authorized personnel should have access to specific patient data, with privileges tailored to their roles. Role-based access controls restrict access based on job function, ensuring that only necessary information is available to each user.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits and penetration testing are vital for identifying vulnerabilities and patching weaknesses before they can be exploited. These assessments should be performed on a regular basis to detect and mitigate any vulnerabilities in the system’s security architecture.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Robust data backup and recovery procedures are critical to ensure business continuity in the event of a data breach or system failure. Regular backups, with redundant copies stored in secure locations, mitigate the impact of data loss.
Importance of User Access Controls and Authentication
User access controls and authentication mechanisms are crucial components of a secure healthcare CRM. These mechanisms limit access to authorized personnel, ensuring only those with legitimate need to access patient data are granted access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security. Requiring multiple forms of authentication (e.g., password, security token, biometric data) makes it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to accounts.
- Regular Password Management: Enforcing strong, unique passwords and implementing regular password updates ensures that compromised credentials do not lead to widespread access issues.
- Regular User Training: Training users on security protocols and best practices is vital to preventing human error and intentional misuse. Understanding the importance of secure passwords and the risks of phishing attempts is crucial.
Examples of Best Practices for Data Security in a Healthcare CRM Context
Several best practices can enhance data security in a healthcare CRM:
- Regular Security Awareness Training: Educating staff on security risks, such as phishing and social engineering, is critical. Training should be conducted regularly to keep employees updated on emerging threats.
- Incident Response Plan: Developing and regularly testing an incident response plan is vital for handling security breaches promptly. A well-defined plan ensures that the organization is prepared to address any data security incidents efficiently and effectively.
- Data Minimization: Collecting and storing only the minimum amount of data necessary for healthcare operations is important. This minimizes the potential impact of a data breach.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in Healthcare
Patient relationship management (PRM) in healthcare is crucial for fostering positive patient experiences and achieving better health outcomes. Effective PRM goes beyond simply managing patient data; it emphasizes building and maintaining meaningful relationships with patients throughout their healthcare journey. This involves understanding their needs, preferences, and expectations to provide personalized care and improve overall satisfaction.
Patient Engagement and Satisfaction in Healthcare
Patient engagement and satisfaction are paramount in modern healthcare. High levels of engagement correlate with improved adherence to treatment plans, reduced hospital readmissions, and enhanced patient well-being. Satisfied patients are more likely to recommend the healthcare provider to others, contributing to positive reputation and growth. Active patient participation fosters a collaborative relationship, empowering patients to take ownership of their health.
How CRM Systems Enhance Patient Experience
CRM systems in healthcare can significantly enhance the patient experience by streamlining communication, personalizing interactions, and providing a more efficient and responsive service. By centralizing patient data and enabling access for various healthcare professionals, CRM systems facilitate coordinated care, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring a seamless experience for the patient. This coordinated approach fosters trust and strengthens the patient-provider relationship.
Improved Patient Communication and Follow-up
CRM systems can dramatically improve patient communication and follow-up. Automated reminders for appointments, medication refills, and test results enhance patient compliance. Personalized communication tailored to individual patient preferences ensures that messages are relevant and timely. Proactive communication fosters trust and encourages patients to actively participate in their care. By proactively reaching out to patients for check-ins or follow-ups, providers can address concerns, provide necessary support, and ensure that patients are receiving the best possible care.
Patient Relationship Management Strategies
Effective patient relationship management involves a multifaceted approach. Strategies should be tailored to individual patient needs and preferences.
| Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Proactive Communication | Reaching out to patients proactively for check-ins, reminders, and updates. | Sending automated appointment reminders, providing educational materials, or scheduling follow-up calls. |
| Personalized Care | Tailoring communication and interactions to individual patient needs and preferences. | Using patient data to recommend specific resources or treatments, offering customized appointment scheduling options, or providing support in different languages. |
| Data-Driven Insights | Leveraging patient data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement in patient care. | Analyzing patient feedback to identify pain points in the patient journey, or identifying patients at high risk of readmission. |
| Enhanced Accessibility | Providing multiple channels for communication and support, ensuring patients can easily access information and connect with healthcare providers. | Offering online portals, mobile apps, and phone support to patients. |
Future Trends and Developments
The healthcare CRM landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing patient expectations. Emerging trends in software solutions are shaping how healthcare providers manage relationships and deliver personalized care. This section explores key future developments, focusing on the impact of AI, cloud computing, and mobile technology.The future of healthcare CRM hinges on its ability to adapt to these technological advancements.
Integrating innovative tools like AI and machine learning will be crucial to optimizing workflows, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing overall efficiency. Cloud-based systems and mobile access are also changing the way healthcare providers interact with patients, fostering greater accessibility and responsiveness.
Emerging Trends in Healthcare CRM Software
Several emerging trends are reshaping the healthcare CRM landscape. These include the increasing use of AI-powered tools for automating tasks, personalized patient communication, and predictive analytics for risk assessment. Furthermore, a focus on interoperability and data sharing between different healthcare systems is driving the development of more integrated CRM platforms.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on CRM Systems
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize healthcare CRM systems. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine inquiries, freeing up staff to focus on more complex patient needs. Machine learning algorithms can analyze patient data to identify patterns, predict potential health issues, and personalize treatment plans. For instance, AI can analyze patient records to predict the likelihood of readmissions, allowing proactive interventions to reduce hospital readmissions and improve patient outcomes.
Evolution of Cloud-Based CRM Systems
Cloud-based CRM systems are transforming the healthcare industry by providing scalable, secure, and accessible platforms. Cloud solutions offer greater flexibility, allowing providers to access and manage patient data from any location with an internet connection. They also facilitate real-time collaboration among healthcare teams, leading to more coordinated and efficient care delivery. This is particularly valuable for telehealth services and remote patient monitoring.
Role of Mobile Technology in CRM Implementation
Mobile technology is fundamentally changing how healthcare providers interact with patients. Mobile apps allow patients to access their health records, schedule appointments, communicate with their care team, and track their health progress. For providers, mobile access to CRM data empowers them to provide more personalized care and respond to patient needs more effectively. For example, providers can access patient history and medication lists during consultations, enabling a more comprehensive and personalized approach.
Future Roadmap for Healthcare CRM
The future roadmap for healthcare CRM focuses on creating more integrated, intelligent, and accessible systems. This involves leveraging AI and machine learning to personalize patient interactions, improve care coordination, and enhance decision-making. A key aspect of this roadmap is building secure and reliable cloud-based platforms to enable seamless data sharing and collaboration among different healthcare stakeholders. Furthermore, mobile access and seamless integration with existing healthcare systems will remain critical to empowering providers and patients alike.
Case Studies and Success Stories

Real-world implementations of healthcare CRM software demonstrate its potential to streamline operations, enhance patient care, and drive significant improvements in healthcare organizations. These case studies highlight the tangible benefits, illustrate effective strategies for overcoming challenges, and showcase the long-term value proposition of a well-implemented CRM system.
Examples of Successful CRM Implementations
Several healthcare organizations have successfully leveraged CRM systems to achieve positive outcomes. These implementations showcase the diverse applications of CRM software within the healthcare industry.
- A large hospital system implemented a CRM to manage patient interactions across various departments. This streamlined communication, reduced wait times, and improved patient satisfaction. Data integration allowed for a comprehensive view of each patient’s history, facilitating more personalized care plans. The system also improved staff efficiency by automating tasks and providing real-time information.
- A multi-specialty clinic used a CRM to manage patient appointments, track medication adherence, and enhance communication with patients. Improved appointment scheduling reduced no-shows and improved patient engagement. The system’s ability to track medication adherence helped the clinic identify patients at risk and proactively intervene. Furthermore, the CRM facilitated personalized communication, strengthening the doctor-patient relationship.
- A public health organization utilized a CRM to manage disease outbreaks and track contact tracing. This approach allowed for swift and efficient responses to outbreaks, reducing the spread of infectious diseases and improving public health outcomes. The system’s ability to store and analyze data provided valuable insights into disease patterns and facilitated targeted interventions.
Challenges and Solutions
Implementing a CRM system in a healthcare setting can present specific challenges. Effective solutions are crucial to ensure successful integration and long-term value.
- Data Migration and Integration: Migrating existing patient data to a new CRM system often presents challenges. A phased approach, involving careful planning and data validation, can mitigate these issues. Using tools and expertise to ensure data accuracy and consistency during the transition is essential.
- Staff Training and Adoption: Successful CRM implementation relies on staff understanding and adoption. Comprehensive training programs, clear documentation, and ongoing support are vital to ensure staff effectively use the system. Training should focus on the practical applications and benefits of the CRM.
- Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare organizations must adhere to stringent regulations regarding patient data privacy and security. Choosing a CRM system that complies with HIPAA and other relevant regulations is crucial. Organizations must also establish robust data security protocols to protect patient information.
Long-Term Benefits of CRM in Healthcare
The long-term benefits of implementing a CRM extend beyond initial implementation. Sustained use and ongoing refinement yield substantial advantages.
- Improved Patient Care: A comprehensive view of patient data empowers healthcare providers to offer more personalized and effective care plans. The CRM facilitates better coordination among different departments, leading to a seamless patient experience.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Automation of tasks and streamlined workflows increase operational efficiency, freeing up staff time for patient care. The CRM facilitates efficient management of appointments, billing, and other administrative tasks.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The ability to collect and analyze data from the CRM provides insights into patient needs, trends, and patterns. This data-driven approach facilitates informed decisions about resource allocation, program development, and strategic planning.
Key Case Study Summaries
This table provides a concise summary of key case studies, highlighting the positive outcomes, challenges, and long-term benefits of using a CRM system in healthcare.
| Case Study | Positive Outcomes | Challenges Faced | Solutions Implemented | Long-Term Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital System A | Reduced wait times, improved patient satisfaction, enhanced communication | Data migration complexities | Phased approach, data validation | Improved patient care, increased operational efficiency |
| Clinic B | Reduced no-shows, improved patient engagement, enhanced communication | Staff resistance to change | Comprehensive training programs | Streamlined workflows, improved patient satisfaction |
| Public Health Organization C | Swift response to outbreaks, reduced disease spread | Data security concerns | Robust data security protocols, compliance with regulations | Improved public health outcomes, efficient disease surveillance |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, healthcare CRM software is proving to be a crucial asset in the modern healthcare landscape. Its ability to improve patient experience, streamline workflows, and boost operational efficiency makes it a valuable investment for healthcare organizations of all sizes. This comprehensive guide has highlighted the multifaceted benefits and functionalities of these systems, equipping readers with a thorough understanding of their implementation and utilization.
FAQ Compilation
What are the typical pricing tiers for healthcare CRM software?
Pricing varies significantly based on the specific features, vendor, and the size of the organization. Some providers offer tiered pricing models, while others might use a subscription-based approach. Factors like the number of users, storage capacity, and advanced functionalities all influence the cost.
How does healthcare CRM software support regulatory compliance?
Healthcare CRM systems can be configured to meet specific regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA in the US. This includes robust data security measures, secure data storage, and user access controls. Compliance is often a key factor in selecting a healthcare CRM system.
What are some common challenges encountered during CRM implementation?
Data migration from legacy systems, integrating with existing EHRs, and ensuring staff training are common hurdles. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, thorough data analysis, and a robust implementation strategy. Often, expert consultation is needed.
How does mobile technology impact healthcare CRM implementation?
Mobile-friendly CRM applications allow healthcare professionals to access and manage patient information on the go. This enhances accessibility, enabling quick responses to patient queries and improving overall efficiency. Cloud-based CRM systems are crucial to enabling this.