Google Sheets CRM offers a surprisingly powerful way to manage customer relationships. Leveraging the familiar spreadsheet environment, this approach allows for straightforward data organization and analysis, particularly useful for smaller businesses or those needing a less complex CRM solution. While not a replacement for dedicated CRM software in large-scale operations, Google Sheets provides a viable alternative for streamlined customer interactions.
This guide explores the full potential of Google Sheets as a CRM, from foundational data organization to advanced reporting techniques. We’ll delve into practical applications, including formula-driven insights and collaborative tools. Ultimately, this exploration will equip you with the knowledge to maximize Google Sheets’ capabilities for managing your customer base efficiently.
Introduction to Google Sheets CRM
Google Sheets, a widely used spreadsheet application within the Google Workspace suite, can surprisingly be a powerful tool for managing customer relationships. While not a dedicated CRM platform, its flexibility and accessibility make it suitable for smaller businesses or teams needing a straightforward way to track customer interactions and data. This approach leverages the familiar spreadsheet environment, often reducing the learning curve for users already comfortable with data manipulation.This exploration delves into the potential and limitations of Google Sheets as a CRM, comparing its features with dedicated CRM software.
We’ll examine its historical context, highlight various use cases, and analyze its strengths and weaknesses. This discussion aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of when Google Sheets might be a viable option for CRM management.
History of Google Sheets
Google Sheets, initially released as a part of Google Docs in 2006, quickly gained popularity for its ease of use and cloud-based accessibility. Its iterative development incorporated features like formulas, data visualization, and collaboration tools, progressively enhancing its functionality. This continuous improvement, combined with the growing popularity of Google Workspace, solidified its position as a versatile data management platform.
Use Cases for Google Sheets as a CRM
Google Sheets shines as a CRM solution in specific scenarios. Its adaptability allows for various applications, such as tracking leads, managing contacts, logging customer interactions, and analyzing sales data. A smaller business with a limited budget and a small customer base might find Google Sheets ideal. The ability to customize columns and formulas allows tailoring the platform to specific needs.
- Lead Tracking: Creating a spreadsheet to track leads, including contact information, source, stage in the sales funnel, and notes on interactions, allows for a centralized record of potential customers.
- Contact Management: A simple spreadsheet can store detailed contact information, including email addresses, phone numbers, addresses, and any relevant notes. This can streamline communication and customer interaction management.
- Customer Interaction Logging: Recording every interaction with a customer (e.g., phone calls, emails, meetings) in a dedicated sheet allows for easy reference and analysis of customer history.
- Sales Data Analysis: Tracking sales figures, products sold, and customer demographics can be visualized and analyzed using charts and graphs within Google Sheets, offering valuable insights for sales strategy improvement.
Limitations of Google Sheets for Large-Scale CRM
While effective for smaller-scale operations, Google Sheets faces limitations as a CRM for larger organizations. Its scalability becomes a concern as the volume of data and users increases. Collaboration challenges, lack of advanced reporting tools, and the potential for data inconsistencies across multiple sheets can hinder efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Google Sheets CRM
Using Google Sheets for CRM can be cost-effective and readily accessible, especially for smaller organizations, but it lacks the robust features and scalability of dedicated CRM software.
| Feature | Google Sheets | Other CRM | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Cloud-based, accessible from various devices | Cloud-based or on-premises, often with more advanced security | Google Sheets is suitable for smaller datasets, while other CRMs excel in handling large volumes of data securely. |
| Reporting & Analytics | Basic reporting through charts and formulas | Advanced reporting dashboards and analytics | Dedicated CRMs offer comprehensive reporting capabilities for data analysis and informed decision-making, whereas Google Sheets provides limited analytic tools. |
| Automation | Limited automation through scripts | Robust automation for tasks like email marketing and lead nurturing | Other CRMs provide more extensive automation capabilities for efficiency, whereas Google Sheets offers basic scripting options. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability for large volumes of data and users | Scalable to accommodate growing businesses and data volumes | Google Sheets is restricted in handling large datasets, whereas dedicated CRM solutions are built for expansion. |
Data Organization and Management in Google Sheets
Effective data organization is crucial for a successful Google Sheets CRM. A well-structured spreadsheet facilitates efficient data entry, retrieval, and analysis, enabling informed business decisions. Properly managing data prevents errors and ensures the accuracy of your customer information, interactions, and transactions.A well-organized Google Sheets CRM allows for quick identification of trends, customer segments, and potential opportunities. This streamlined approach ensures you can respond effectively to customer needs and maximize business potential.
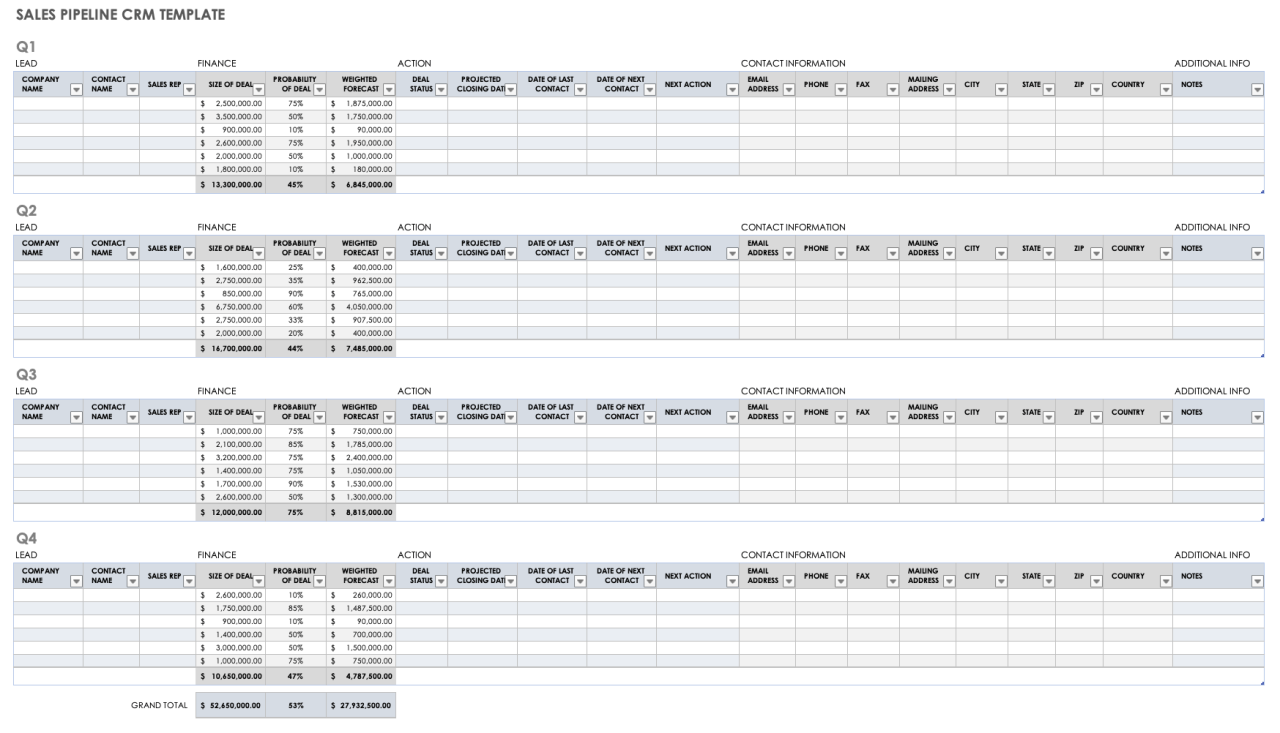
Sample Spreadsheet Structure for a Basic Google Sheets CRM
This structure provides a foundational framework for a basic CRM in Google Sheets. It can be expanded upon as your business needs evolve.
| Sheet Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Customers | Stores detailed customer information. |
| Interactions | Records interactions with customers, including calls, emails, and meetings. |
| Transactions | Tracks customer purchases and other financial transactions. |
Data for Customer Information, Interactions, and Transactions
Customer information should include fields like name, contact details, demographics, and any relevant notes. Interaction records should note the date, type of interaction, key discussion points, and outcome. Transaction data should comprise the date, description, amount, and related customer.
Data Entry Methods and Best Practices
For efficient data entry, utilize formulas and functions to automate tasks where possible. Implement consistent formatting for better readability and analysis. Consider using dropdown menus for frequently occurring data (e.g., customer status, interaction type).
Common Data Entry Errors and How to Avoid Them
Inconsistent data formats, typos, and missing information are common errors. Employing data validation rules and using clear templates minimizes these issues.
Data Validation Techniques
Implement data validation rules to ensure accuracy. These rules can specify the data type (e.g., text, number, date), acceptable values (e.g., specific choices from a list), and the length of entries. Validating data in real-time during entry helps to catch errors immediately. Using conditional formatting can visually highlight potential issues.
Data Types in a Google Sheets CRM
This table illustrates different data types commonly used in a Google Sheets CRM. Choosing the correct data type is vital for effective analysis and reporting.
| Data Type | Example | Description | Validation Rule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text | “John Doe” | Customer name, product descriptions | Length limit (e.g., 50 characters) |
| Number | 12345 | Order quantity, price | Range (e.g., quantity must be positive) |
| Date | 2024-10-27 | Order date, interaction date | Specific date range (e.g., past year) |
| Boolean | TRUE/FALSE | Customer satisfaction, product availability | Only TRUE or FALSE |
Formulas and Functions for CRM in Google Sheets
Harnessing the power of formulas and functions is crucial for transforming raw customer data into actionable insights within your Google Sheets CRM. These tools empower you to automate tasks, calculate key metrics, and analyze trends, allowing you to optimize your customer interactions and boost overall performance.Using formulas and functions allows for automated calculations and data analysis, freeing up time and minimizing manual errors.
This efficiency leads to faster insights, better decision-making, and ultimately, stronger customer relationships.
Calculating Customer Interaction Metrics
Formulas are essential for calculating key metrics related to customer interactions, such as average purchase value, customer lifetime value, and response times. Accurate calculation of these metrics provides valuable insights into customer behavior and helps you tailor strategies accordingly.
- Average Purchase Value: A simple formula, such as `=AVERAGE(B2:B100)` (assuming purchase values are in column B), directly calculates the average purchase value across a range of data. This formula provides a quick snapshot of the typical transaction amount. Applying this to your CRM helps determine the typical value of customer interactions, useful for budgeting and forecasting.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Estimating CLTV involves combining purchase history, frequency, and average purchase value. A more complex formula, incorporating these factors and potentially incorporating discount rates or other relevant factors, could provide a more sophisticated calculation.
Tracking Customer Activities
Tracking customer interactions and activities with functions like `COUNT`, `SUM`, and `AVERAGE` is fundamental for understanding customer behavior and engagement.
- Counting Interactions: The `COUNT` function is used to determine the total number of customer interactions within a specified timeframe. For example, `=COUNTIF(A2:A100,”Active”)` counts the number of “Active” customers. This provides insights into the overall activity level of your customer base.
- Summing Values: The `SUM` function calculates the total value of a particular metric, such as total revenue generated from a specific product or service. Example: `=SUM(C2:C100)` sums the values in column C.
- Averaging Values: The `AVERAGE` function computes the average value of a dataset. For example, `=AVERAGE(D2:D100)` finds the average response time to customer inquiries.
Conditional Formatting for Data Highlighting
Conditional formatting allows you to visually highlight important data points, making analysis easier and more efficient.
- Highlighting High-Value Customers: Conditional formatting can highlight customers exceeding a certain purchase value threshold or those who have interacted frequently with your business. This visual representation immediately draws attention to key individuals, allowing for targeted marketing campaigns and improved service.
Filtering and Sorting for Data Analysis
Filtering and sorting features provide quick and efficient data analysis, helping you pinpoint specific trends and patterns within your CRM data.
- Filtering Data: Filtering allows you to isolate specific subsets of data based on criteria. For example, you can filter customers based on location, purchase history, or other relevant factors. This focused view allows you to drill down and analyze specific segments of your customer base.
- Sorting Data: Sorting allows you to arrange data in ascending or descending order based on various criteria. Sorting by purchase value, for example, quickly identifies your highest-value customers. This feature allows for a systematic review of the data and facilitates the identification of trends.
Custom Formulas for Automation
Custom formulas automate repetitive tasks, boosting efficiency and reducing manual effort within your CRM.
- Automating Task Assignment: Custom formulas can be designed to automatically assign tasks to team members based on specific criteria. For example, you could assign a customer to a specific agent based on their location or product interest. This automation minimizes delays and ensures timely responses to customer needs.
Customer Data Analysis Formulas
| Formula | Description | Usage Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
=AVERAGE(B2:B100) | Calculates the average value in a range. | Average Purchase Value of orders from B2 to B100 | $50.25 |
=COUNTIF(A2:A100,"Active") | Counts cells within a range that meet a criteria. | Count of Active Customers in column A | 250 |
=SUM(C2:C100) | Sums the values in a range. | Total Revenue from orders in column C | $12,500 |
=IF(B2>100,"High Value","Low Value") | Applies conditional logic to assign values. | Categorizes customers based on purchase value (B2). | High Value |
Collaboration and Sharing in Google Sheets CRM
![The Best Google Sheets CRM Free Template [+ How To Use] The Best Google Sheets CRM Free Template [+ How To Use]](https://budget.novel.or.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/6415b6903669f805050b1621_7b7ec1b9-a062-4ba8-a099-25fbe4e15274-2.png)
Sharing your Google Sheets CRM effectively is crucial for team collaboration and data accuracy. Properly configuring sharing permissions ensures that only authorized individuals access and modify the data, maintaining data integrity and preventing errors. Real-time collaboration facilitates seamless updates and fosters a unified understanding of the CRM’s contents. Integration with other tools streamlines workflows and enhances the CRM’s overall utility.
Sharing Methods for Team Members
Various methods facilitate sharing your Google Sheets CRM with your team. Direct sharing with specific individuals, or sharing with entire groups, allows for targeted access control. This targeted approach is essential for managing sensitive data and ensuring that only the necessary personnel have access.
- Sharing with Specific Users: You can directly invite specific individuals to access the sheet. This granular control is valuable for managing sensitive data. Example: Inviting sales representatives to view the sheet, or marketing personnel to edit the customer segment data.
- Sharing with Groups: Sharing with Google Workspace groups streamlines the process for granting access to multiple team members simultaneously. This is useful when you need to give multiple people the same access level. Example: Sharing with the entire sales team to view and update sales figures, or the marketing team to view customer data.
- Sharing via Links: Providing a shared link enables easy access for team members. This is suitable for temporary or ad-hoc access. Example: Sharing a link with a consultant for a specific project.
Setting Up Permissions and Access Control
Establishing clear permissions is vital for safeguarding data integrity. Different access levels ensure that individuals only perform actions they are authorized for. This protects the data from accidental modification or unauthorized access.
- Viewing Permissions: Allowing users to view data without the ability to edit is ideal for situations where updates are not required. This protects the data’s integrity by limiting modifications.
- Editing Permissions: Granting users the ability to modify the sheet’s data ensures timely updates and responsiveness. Careful consideration should be given to the users with this access to prevent accidental data corruption.
- Comment Permissions: Enabling comments allows users to provide feedback without directly altering the sheet’s content. This promotes collaboration without disrupting the data’s integrity.
Using Google Sheets Collaboration Features
Google Sheets’ collaboration features streamline real-time updates and discussions. Real-time edits and comments foster a unified understanding of the CRM data, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
- Real-Time Editing: Multiple users can edit the sheet simultaneously, ensuring quick and efficient data updates. This allows for concurrent modifications to the data, streamlining processes.
- Collaborative Comments: Comments facilitate discussions and feedback on data entries without disrupting the data itself. This is useful for clarifying data points or for getting feedback on changes.
Integrating Google Sheets CRM with Other Tools
Integrating the Google Sheets CRM with other tools streamlines workflows and enhances data management. This integration can improve efficiency by automating tasks or pulling data from other systems.
- API Integrations: Connecting via APIs allows for data transfer between the CRM and other applications. This is beneficial for automation, such as automatically populating fields in the CRM based on data from another system.
- Import/Export Features: Import data from other systems or export to external tools, like spreadsheets or databases. This is a useful feature for data consolidation or for analysis in other tools.
Sharing Examples
Sharing for specific users or groups involves inviting specific individuals or groups to access the sheet with tailored permissions. This allows for efficient data management and collaboration.
- Sharing for Sales Team: Share the sheet with the sales team, allowing them to view and edit the customer data and sales figures.
- Sharing for Marketing Team: Share the sheet with the marketing team, granting them access to view customer data for marketing campaigns.
Sharing Options in Google Sheets
| Sharing Method | Description | Use Cases | Permissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sharing | Inviting specific users or groups. | Targeted access control, sensitive data management. | View, Edit, Comment |
| Sharing via Link | Providing a link for access. | Temporary access, ad-hoc collaboration. | View, Edit, Comment (depending on link settings) |
| Sharing with Groups | Sharing with Google Workspace groups. | Bulk access for team members. | View, Edit, Comment (depending on group settings) |
Automation and Reporting in Google Sheets CRM
Automating tasks and generating insightful reports are crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of a Google Sheets CRM. By leveraging Google Apps Script, you can streamline data entry, automate calculations, and generate reports that offer valuable insights into your customer interactions. This significantly reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and allows for a more data-driven approach to customer relationship management.
Automating Tasks with Google Apps Script
Google Apps Script provides a powerful mechanism for automating tasks within Google Sheets. This includes tasks like data entry, calculations, and report generation. You can create custom functions and macros to automate repetitive actions. For instance, if you need to populate customer data from a different source, a script can automatically fetch and import the information into your Google Sheets CRM.
Generating Reports from Collected Data
Generating reports is a fundamental aspect of any CRM system. A well-structured report provides insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) and customer behavior. These reports can be customized to answer specific questions, track progress, and identify trends.
Different Types of Reports and Their Use Cases
Various report types can be generated to suit specific needs. Simple summaries of customer demographics, such as the number of customers in each region, are beneficial for overall understanding. Detailed reports on sales performance, focusing on specific product lines, help track progress and identify potential areas for improvement. Moreover, customer churn analysis provides insight into why customers are leaving, enabling proactive measures to retain them.
Visual Representations for Customer Data Analysis
Visual representations, like charts, enhance data comprehension and identification of patterns. Bar charts are suitable for comparing values across categories. Line charts effectively show trends over time. Pie charts are useful for illustrating proportions within a whole. Scatter plots reveal relationships between two variables.
For instance, a line chart can visually represent sales trends over a period, while a bar chart can display the sales performance of different products.
Creating Custom Reports Tailored to Specific Needs
Custom reports are crucial for addressing specific business questions. For example, a report focusing on customer satisfaction scores and their correlation with purchase frequency could help identify factors driving customer loyalty. Similarly, a report analyzing customer demographics and their purchasing behavior allows businesses to target specific customer segments effectively.
Different Chart Types for CRM Reporting
| Chart Type | Description | Use Cases | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bar Chart | Compares values across categories. | Sales by product, customer acquisition by channel. | Visualizing the sales performance of different products in a given quarter. |
| Line Chart | Shows trends over time. | Sales growth over months, customer acquisition rate evolution. | Tracking customer acquisition trends over a year. |
| Pie Chart | Illustrates proportions within a whole. | Customer demographics (percentage of customers in each region), product sales distribution. | Representing the distribution of customers across different regions. |
| Scatter Plot | Reveals relationships between two variables. | Correlation between customer satisfaction scores and purchase frequency, customer engagement and lifetime value. | Analyzing the relationship between customer engagement and revenue generated. |
Advanced Features and Techniques
Leveraging advanced features in Google Sheets for CRM management allows for deeper insights and more streamlined workflows. This section explores powerful tools like pivot tables, data import/export, API integration, custom dashboards, and crucial security considerations. These advanced techniques enable users to transform raw data into actionable intelligence and integrate their CRM with other systems effectively.
Pivot Tables for Analysis and Reporting
Pivot tables are a robust tool for summarizing and analyzing large datasets within Google Sheets. They allow users to quickly generate reports and identify trends, patterns, and insights from CRM data. By grouping and aggregating data based on specific criteria, users can extract meaningful information from potentially complex datasets. For instance, a pivot table can easily show sales performance by region, product category, or sales representative.
This granular analysis is invaluable for identifying areas of strength and weakness within the CRM.
Data Import and Export
Importing and exporting data are crucial aspects of a robust CRM. Google Sheets supports various import and export options, enabling seamless data exchange with other applications. This flexibility is vital for integrating data from other systems into the CRM or extracting data for analysis in external tools. This seamless transfer allows for a more holistic view of the business data.
Google Sheets API Integration
The Google Sheets API allows for programmatic interaction with Google Sheets data. This is essential for integrating the CRM with other applications or automating tasks. By leveraging the API, users can create custom scripts to automatically update data, trigger actions in other systems, and build custom applications. For instance, a script could automatically update a sales pipeline in Google Sheets when a new contact is added to a CRM platform.
This automation streamlines workflows and improves data accuracy.
Custom Dashboards for Monitoring Key Metrics
Custom dashboards are a powerful way to visualize key metrics and monitor performance in real-time. By combining various data points and formatting them into interactive charts, users can easily track key performance indicators (KPIs) and gain quick insights into the CRM’s performance. A dashboard could display sales figures, customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, and other important metrics in a single view.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Protecting customer data is paramount. Robust security measures are essential for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of customer information. Using appropriate access controls, limiting access to sensitive data, and employing data encryption techniques are crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding data breaches. Regularly reviewing and updating security protocols is critical.
Import/Export Options for Google Sheets CRM Data
| Method | Description | Supported Formats | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copy and Paste | Simple method for transferring data between applications. | Various formats supported by copy-paste. | Limited to smaller datasets, potential data loss, no automatic updates. |
| File Upload/Download | Transferring data using files (CSV, XLSX, etc.). | CSV, XLSX, ODS, etc. | Requires manual intervention, may not handle very large datasets efficiently. |
| Google Workspace APIs | Programmatic interaction with Google Sheets via APIs. | JSON, other formats based on API specifications. | Requires coding knowledge, potentially higher overhead, best for automated and frequent data transfer. |
| Third-party add-ons | Dedicated tools for data exchange. | Various formats based on add-on functionality. | May have licensing or cost considerations, specific features may be limited. |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, Google Sheets can be a valuable CRM tool for various needs. Its accessibility and familiar interface make it attractive for smaller businesses or those seeking a less expensive solution. While limitations exist for large-scale operations, the detailed examples and practical guidance provided highlight the impressive potential of this platform. By mastering the techniques presented, users can harness the power of Google Sheets to streamline their customer relationship management and gain actionable insights.
FAQ Compilation
Can Google Sheets CRM handle a large number of customers?
While Google Sheets can manage a substantial amount of customer data, its scalability is limited compared to dedicated CRM software. For extremely large datasets, dedicated CRM solutions may be more suitable.
What are some common integrations with Google Sheets CRM?
Google Sheets integrates well with various other Google Workspace applications, such as Google Forms for data input, and other third-party tools through APIs. The possibilities are extensive, but careful consideration of data flow is essential.
How secure is customer data stored in a Google Sheets CRM?
Data security in Google Sheets relies on the user’s adherence to Google’s security protocols and best practices, including proper access controls. Careful consideration of data privacy is crucial.
What are some limitations of using Google Sheets for CRM?
Limitations include potential performance issues with very large datasets, lack of advanced features found in dedicated CRM software, and the need for ongoing maintenance to ensure data integrity.
![The Best Google Sheets CRM Free Template [+ How To Use] The Best Google Sheets CRM Free Template [+ How To Use]](https://budget.novel.or.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/6415b6903669f805050b1621_7b7ec1b9-a062-4ba8-a099-25fbe4e15274-2-1.png)