Sales management software is rapidly transforming how businesses operate, automating tasks and enhancing efficiency. This guide delves into the intricacies of these tools, exploring their various types, benefits, features, and implementation strategies. From improving sales processes to fostering customer relationships, we’ll uncover the power of sales management software for businesses of all sizes.
The evolving landscape of sales management software necessitates a deep understanding of its key functionalities and the various categories it encompasses. We’ll explore the features, comparing and contrasting different software solutions, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. This exploration will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the market and make informed decisions.
Introduction to Sales Management Software
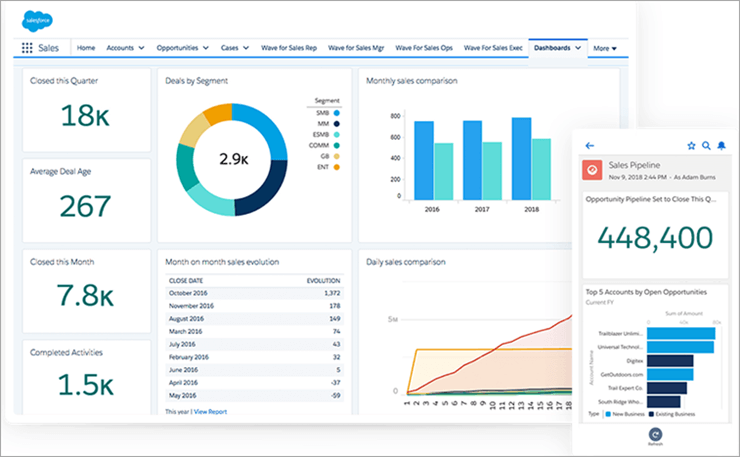
Sales management software plays a critical role in streamlining sales processes and improving overall efficiency for businesses of all sizes. It provides tools to manage leads, track sales activities, analyze performance, and ultimately boost revenue. This software has evolved significantly, offering diverse functionalities tailored to various sales strategies and company needs.This overview explores the core functionalities, categories, and current trends in sales management software, offering a comprehensive understanding of how these tools are transforming the modern sales landscape.
Definition of Sales Management Software
Sales management software encompasses a suite of applications designed to optimize the sales process. These tools automate tasks, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and provide insightful analytics, empowering sales teams to make data-driven decisions. By centralizing data and automating workflows, sales management software enables greater efficiency and productivity, ultimately improving revenue generation.
Key Functionalities of Various Sales Management Software Types
Sales management software offers a wide range of functionalities, catering to diverse sales strategies. Common features include lead management, contact management, opportunity tracking, sales forecasting, and performance reporting. Sophisticated systems integrate with customer relationship management (CRM) platforms for a holistic view of customer interactions. Specific features vary depending on the type of software and the particular needs of the user.
Categories of Sales Management Software
Sales management software falls into distinct categories. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are designed to manage customer interactions, track sales opportunities, and maintain a comprehensive customer database. Dedicated sales tools, on the other hand, focus on specific sales processes, like sales forecasting, lead nurturing, or sales performance tracking. This specialization allows for greater focus and efficiency within specific areas of the sales cycle.
Evolution and Current Trends in Sales Management Software
Sales management software has evolved from basic contact management tools to sophisticated, integrated platforms. Cloud-based solutions have become increasingly popular, offering accessibility and scalability. Integration with other business applications, such as marketing automation tools and accounting software, is another key trend. The increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is transforming sales forecasting and lead qualification, driving greater accuracy and efficiency.
For example, AI-powered chatbots can qualify leads and answer customer queries, freeing up sales representatives to focus on higher-value activities.
Comparison of Different Types of Sales Management Software
| Software Type | Key Feature 1 | Key Feature 2 | Key Feature 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRM | Centralized customer database | Comprehensive view of customer interactions | Sales opportunity tracking |
| Dedicated Sales Tool | Specialized sales process focus | Automated lead nurturing | Advanced sales forecasting |
Benefits of Using Sales Management Software
Sales management software is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses of all sizes aiming to thrive in today’s competitive market. By streamlining processes, improving communication, and providing actionable insights, these tools empower sales teams to maximize efficiency and achieve greater success. From small startups to large corporations, the advantages are substantial and impactful.
Advantages for Businesses of Various Sizes
Implementing sales management software provides significant benefits regardless of company size. Small businesses often lack the resources of larger corporations, but they can gain a competitive edge by leveraging the tools and insights provided by these systems. Larger companies can optimize their existing operations and improve scalability by using these systems. Software solutions offer standardized processes, improving consistency across teams and departments.
Improving Sales Processes and Productivity
Sales management software streamlines the sales process, automating repetitive tasks and freeing up valuable time for sales representatives. Automated tasks, like lead qualification and follow-up scheduling, allow teams to focus on building relationships and closing deals. This focused effort leads to increased sales productivity. The use of dashboards and reporting tools provides real-time visibility into sales performance, allowing teams to quickly identify areas for improvement and adjust strategies accordingly.
Enhancing Customer Relationship Management
Robust sales management software fosters stronger customer relationships. By centralizing customer data, these systems allow sales teams to gain a comprehensive view of each customer’s needs and preferences. This holistic view facilitates personalized interactions, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty. Effective communication tools built into the software, such as email integration and messaging platforms, facilitate seamless communication and foster stronger relationships.
Facilitating Data-Driven Decision Making
Sales management software generates a wealth of data, providing valuable insights into sales performance. These data-driven insights allow sales managers to make informed decisions, refine strategies, and optimize resource allocation. Detailed sales reports, customer analytics, and performance dashboards provide a clear picture of current trends and future potential. This enables companies to adapt their strategies in response to market changes and customer demands.
Measurable Benefits of Implementing Sales Management Software
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Sales Productivity | Automating tasks like lead qualification and follow-up scheduling frees up sales representatives to focus on building relationships and closing deals. Real-time visibility into sales performance via dashboards and reports allows for quick identification of areas for improvement and strategic adjustments. | Increased sales volume, reduced time to close deals, higher conversion rates, and more efficient use of sales resources. |
| Enhanced Customer Relationships | Centralized customer data provides a comprehensive view of each customer’s needs and preferences, enabling personalized interactions. Improved communication tools built into the software foster stronger relationships and ensure seamless communication. | Higher customer satisfaction, increased customer retention rates, stronger customer loyalty, and improved customer lifetime value. |
| Improved Sales Forecasting | Data-driven insights from sales management software allow for more accurate forecasting of future sales performance. Analyzing historical data, market trends, and sales patterns enables informed predictions about future sales figures. | Improved financial planning, optimized resource allocation, and better anticipation of market changes. |
| Reduced Sales Costs | Streamlined processes and automated tasks minimize administrative overhead. Efficient lead management and targeted marketing campaigns reduce wasted resources and improve return on investment (ROI). | Lower operational costs, increased profitability, and optimized use of marketing budgets. |
Features and Functionality
Effective sales management software equips sales teams with the tools they need to streamline operations, boost productivity, and ultimately drive revenue growth. This section dives into the core features, comparing different functionalities and highlighting the critical role of integrations. Understanding these features empowers businesses to select the right software to optimize their sales processes.
Lead Management
Lead management is a crucial aspect of sales software. Robust lead management systems enable sales teams to track, categorize, and nurture leads effectively. This involves capturing lead information, assigning leads to sales representatives, and automating follow-up tasks. Sophisticated systems allow for lead scoring, identifying high-potential leads, and prioritizing outreach efforts. Integration with marketing automation platforms enhances the lead generation process, providing a holistic view of the customer journey.
Sales Forecasting
Accurate sales forecasting is essential for strategic planning and resource allocation. Sales management software facilitates forecasting by leveraging historical sales data, market trends, and other relevant factors. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze past performance and predict future sales with varying degrees of accuracy. This data-driven approach empowers businesses to make informed decisions regarding inventory management, staffing, and overall business strategy.
For example, a company predicting a surge in sales during the holiday season can adjust its workforce accordingly, ensuring adequate coverage to meet demand. This allows for proactive adjustments and ultimately optimizes sales efforts.
Reporting & Analytics
Sales reporting and analytics are vital for assessing performance and identifying areas for improvement. Comprehensive reporting tools provide detailed insights into sales activities, performance metrics, and overall sales pipeline health. Data visualization tools transform raw data into actionable insights, allowing sales managers to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify trends. These tools facilitate data-driven decision-making and provide a clear picture of sales performance across different regions, products, or sales representatives.
For instance, detailed sales reports can reveal that a particular sales representative consistently excels in closing deals with a specific customer segment, enabling the company to replicate successful strategies across the team.
Integrations
Integration with other business systems, such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management), accounting, and marketing automation platforms, is critical for seamless data flow and enhanced efficiency. Seamless integration eliminates the need for manual data entry, reducing errors and saving valuable time. A well-integrated system provides a holistic view of customer interactions, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of customer needs and preferences.
For example, integrating with a CRM system ensures that sales representatives have access to complete customer profiles, including purchase history, support interactions, and other relevant information. This empowers them to tailor their approach to each customer, ultimately fostering stronger relationships.
Customization
Sales management software should be adaptable to specific business needs. The software should allow for customization in terms of workflows, reporting, and user roles. This flexibility ensures that the software aligns with the unique structure and processes of each business. A company with a highly specialized sales process can tailor the software to accommodate unique steps, effectively mirroring their operational workflow.
By customizing the software, businesses can streamline their processes, improving efficiency and productivity. A flexible, customizable platform allows for ongoing adjustments and enhancements to match evolving business needs.
- Lead Management Features: Lead tracking, categorization, scoring, assignment, and automated follow-up tools.
- Sales Forecasting Features: Historical sales data analysis, market trend forecasting, predictive modeling, and sales pipeline visualization tools.
- Reporting & Analytics Features: Key performance indicator (KPI) tracking, sales pipeline visualization, sales performance reports, regional and product-specific sales data reports, and custom reporting options.
Implementation and Integration
Successfully implementing sales management software requires a structured approach that considers the specific needs of your business. This involves careful planning, seamless integration with existing systems, and robust training programs to ensure smooth adoption. A well-executed implementation strategy minimizes disruptions and maximizes the return on investment.The process of integrating sales management software into a business often requires careful planning and coordination to ensure minimal disruption.
The integration process can be complex and time-consuming, requiring collaboration between various departments and a thorough understanding of the existing systems and workflows.
Steps in Implementing Sales Management Software
Implementing new sales management software involves a series of key steps. Careful planning and execution are crucial for a successful rollout. A well-defined plan that addresses each step ensures a smooth transition and minimal disruption to ongoing operations.
- Assessment and Planning: Thoroughly evaluate your current sales processes, identify areas for improvement, and determine specific needs for the software. Define clear objectives for the implementation, including expected outcomes and timelines. Document existing processes and workflows. This crucial initial step lays the groundwork for a successful implementation.
- Selection and Customization: Carefully select software that aligns with your specific business needs and budget. Consider customization options to tailor the software to your unique workflows and requirements. Thorough research and comparisons are essential to ensure the chosen software meets the business needs effectively.
- Data Migration: Strategically plan the migration of existing data into the new system. Ensure data accuracy and consistency throughout the migration process. This is a critical step that can impact the software’s effectiveness and the team’s adoption of the new system.
- Testing and Training: Conduct thorough testing of the software with representative users to identify and resolve any potential issues. Provide comprehensive training to equip users with the necessary skills to effectively use the software. Pilot programs with a small group can be beneficial to identify and address potential problems early on. Training programs should be tailored to the roles and responsibilities of different users.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Deploy the software to all relevant users. Continuously monitor system performance and address any issues promptly. Establish a system for ongoing support and troubleshooting.
Integrating with Existing Business Systems
Integrating sales management software with existing business systems is a crucial aspect of implementation. A seamless integration minimizes data redundancy and ensures data consistency.
- API Integration: Utilize Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to connect the sales management software with existing systems, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, accounting software, or inventory management systems. APIs facilitate the exchange of data between systems. Careful consideration should be given to the security implications of API integrations.
- Data Mapping: Define the mapping between data fields in the sales management software and the existing systems to ensure accurate data transfer. Thorough data mapping is vital for seamless integration and consistent data. Visual representations of data mapping are useful tools to aid in the process.
- Workflow Integration: Automate workflows and processes by connecting the sales management software with other business systems. Streamlining processes can improve efficiency and reduce errors. Automating workflows can significantly increase productivity and reduce operational costs.
Importance of Training and User Adoption
Proper training and user adoption are critical for the successful implementation of sales management software. A well-trained user base ensures optimal software utilization and a positive return on investment.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Implement comprehensive training programs tailored to different user roles. Training should cover the software’s features, functionality, and best practices. Tailored training sessions for different user groups are highly effective.
- Hands-on Exercises: Provide hands-on training sessions to enable users to practice using the software in real-world scenarios. This allows users to apply their knowledge and build confidence in using the software.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support and resources to assist users in resolving issues and maximizing the software’s potential. User support is essential for long-term success with the new system.
Challenges of Implementation and Strategies for Overcoming Them
Implementation challenges can include resistance to change, data migration issues, and integration difficulties. Proactive strategies are essential to address these obstacles.
- Resistance to Change: Address concerns and anxieties surrounding the new software. Communicate the benefits of the software and demonstrate how it will improve their workflow. Transparent communication about the changes is key.
- Data Migration Issues: Develop a robust data migration plan to minimize errors and ensure data accuracy. Testing and validation steps are crucial to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable.
- Integration Difficulties: Plan and execute careful testing to identify and resolve integration issues. Work closely with technical teams to address technical challenges. A thorough integration plan minimizes issues.
Step-by-Step Guide for Integrating Sales Management Software with an Existing CRM System
- Assessment: Identify the specific data fields and functionalities required for integration. Analyze both systems thoroughly.
- API Connection: Establish API connections between the CRM system and the sales management software.
- Data Mapping: Map data fields between the CRM and the sales management software to ensure accurate data transfer.
- Testing: Thoroughly test the integration process to validate data transfer and ensure accuracy.
- Implementation: Implement the integration and monitor the system for issues.
Choosing the Right Software
Selecting the ideal sales management software is crucial for optimizing sales processes and achieving business objectives. A poorly chosen system can lead to wasted resources and hinder productivity. Thorough evaluation and consideration of specific business needs are key to finding the right fit.Evaluating sales management software demands a meticulous approach. It’s not just about features; it’s about how those features align with your team’s workflow, your company’s sales strategy, and your long-term growth plans.
Understanding your current challenges and desired outcomes will guide you in making the best decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Software
A comprehensive evaluation should encompass various factors. A thorough understanding of your sales process, team structure, and budgetary constraints is critical. This will help you filter potential solutions based on realistic needs and resources. Consider factors like:
- Scalability: Ensure the software can adapt to your company’s growth. A solution that struggles to handle increasing data volumes or user numbers could become a bottleneck as your business expands.
- Integration: Examine how the software integrates with existing systems, such as CRM, accounting software, or marketing automation tools. Seamless integration streamlines workflows and minimizes data duplication.
- User-Friendliness: Consider the learning curve and intuitiveness of the software. An overly complex interface can hinder adoption and decrease productivity. Evaluate user reviews and demos to gauge ease of use.
- Customer Support: Robust customer support is essential for troubleshooting issues and ensuring smooth implementation. Look for providers with readily available support channels like phone, email, or live chat.
- Pricing Model: Understand the pricing structure and associated costs, including licensing fees, maintenance charges, and potential add-ons. Evaluate the long-term financial implications to avoid hidden costs.
Evaluating Software Based on Specific Business Needs
The most effective approach to software selection is a tailored evaluation process. Begin by identifying your specific business needs and pain points. For instance, a small startup may prioritize ease of use and affordability, while a large enterprise might focus on scalability and integration with existing infrastructure.
“Matching the software’s capabilities to your specific business needs is paramount for success.”
This tailored evaluation process ensures the chosen software directly addresses your current challenges and supports your future growth.
Examples of Different Sales Management Software Solutions and Pricing Models
Numerous sales management software solutions cater to diverse business needs. Some popular options include:
- Software A: Focuses on small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) with a user-friendly interface and affordable pricing models. Pricing typically includes a tiered structure, offering varying levels of features and support based on the number of users or licenses.
- Software B: Targets enterprise-level organizations with advanced features, robust reporting capabilities, and customizable dashboards. Pricing is usually based on a per-user or per-seat model, with higher costs for more advanced functionalities.
- Software C: Provides a cloud-based solution with flexible pricing options. Pricing models often include subscription fees that vary depending on the chosen package and its features.
Comparison Table of Pricing Models and Features
The following table illustrates different pricing models and corresponding features for a few examples of sales management software.
| Software | Pricing | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Software A | Tiered pricing (Basic, Standard, Premium) with monthly subscription fees | Basic CRM, task management, email integration, reporting |
| Software B | Per-user pricing, with options for add-on modules | Advanced CRM, forecasting, analytics, complex reporting, mobile access |
| Software C | Subscription-based pricing, with various packages | Cloud-based CRM, real-time data access, extensive integrations, user-friendly interface |
Final Thoughts

In conclusion, sales management software empowers businesses to streamline their sales processes, foster stronger customer relationships, and drive data-driven decision-making. By understanding the diverse features, benefits, and implementation strategies, businesses can leverage these tools to achieve significant improvements in sales productivity and overall performance. Choosing the right software and implementing it effectively is crucial for maximizing returns on investment.
FAQ Explained
What are the common integrations for sales management software?
Many sales management software solutions integrate seamlessly with CRM systems, accounting software, marketing automation platforms, and project management tools. These integrations often streamline data flow and automate workflows, enhancing overall business efficiency.
How does sales management software help with forecasting?
Sophisticated sales management software often includes built-in forecasting tools that analyze sales data, identify trends, and predict future performance. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions about resource allocation and sales strategies.
What are the typical pricing models for sales management software?
Pricing models vary depending on the specific software. Common models include subscription-based pricing, per-user fees, and tiered pricing plans. It’s essential to consider the features offered and the number of users when evaluating different pricing structures.
What are the challenges in implementing sales management software?
Implementation challenges can range from user adoption and training to data migration and system integration with existing infrastructure. Careful planning, proper training, and a phased approach to implementation can mitigate these challenges.