CRM and ERP systems are transforming businesses worldwide, streamlining operations and enhancing customer relationships. This guide delves into the intricacies of these powerful tools, exploring their functionalities, benefits, challenges, and future trends. Understanding these systems is crucial for any business looking to optimize its processes and stay competitive.
From defining core functionalities and highlighting key differences to exploring integration strategies and successful implementations, this comprehensive resource provides a detailed overview of CRM and ERP systems, ensuring a complete understanding of their multifaceted nature. The insights presented will equip readers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions regarding system selection and implementation.
Introduction to CRM and ERP Systems
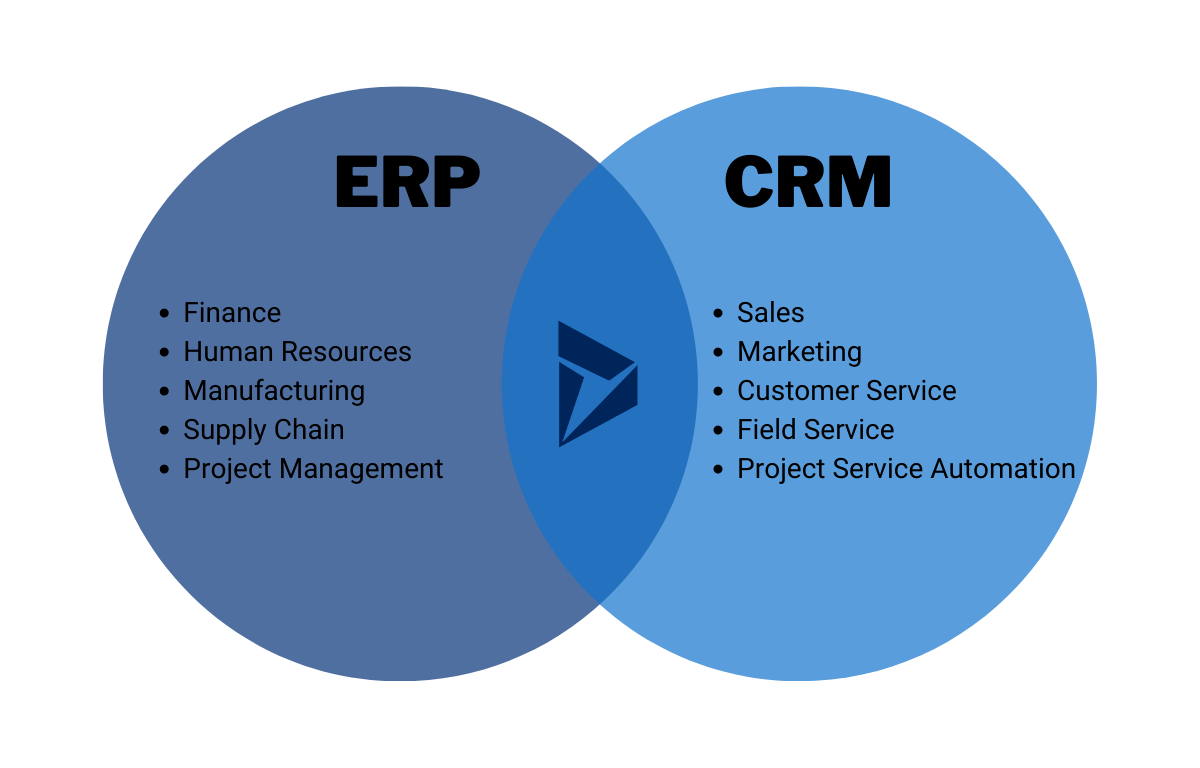
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are crucial tools for modern businesses. They streamline operations, improve data management, and enhance decision-making across various departments. Understanding their distinct functionalities and capabilities is essential for businesses seeking to optimize their workflows and achieve strategic goals.These systems, while often used in conjunction, serve different but complementary purposes.
CRM focuses on customer interactions, while ERP manages internal business processes. The interplay between these systems can lead to significant improvements in overall business performance.
Definitions of CRM and ERP Systems
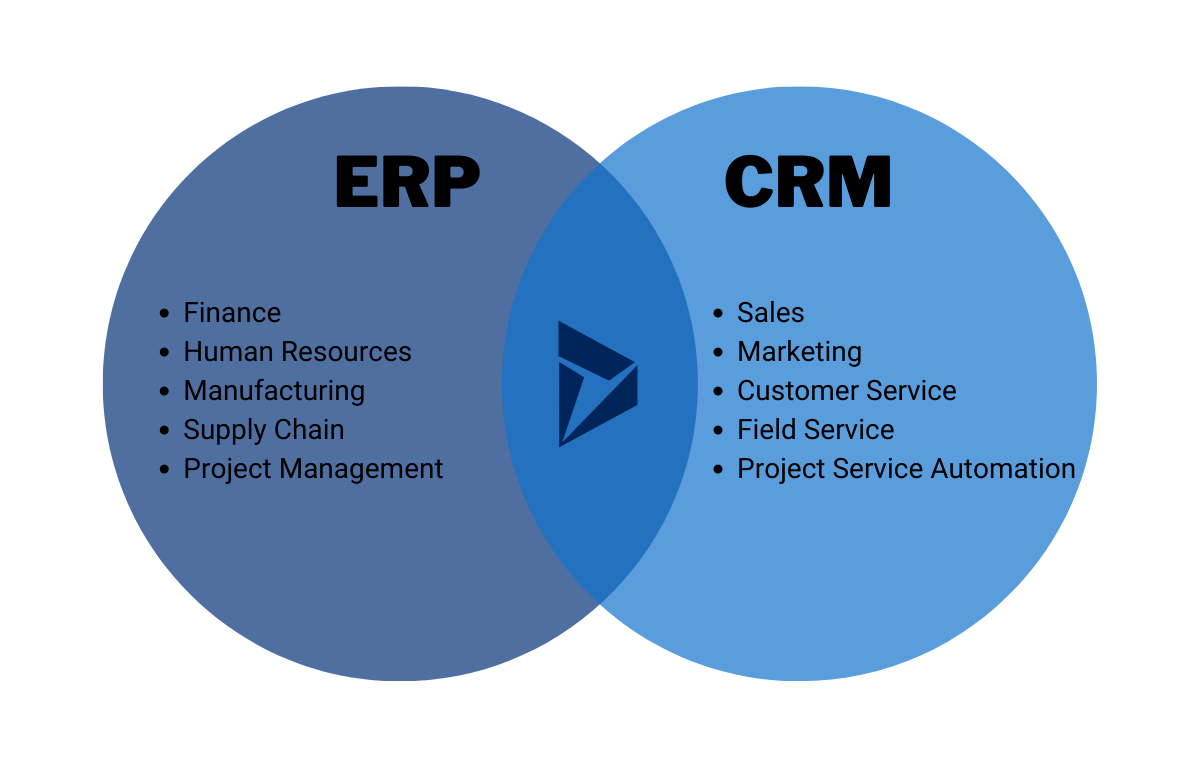
CRM systems are designed to manage and enhance interactions with customers. They provide tools for tracking customer interactions, managing leads, and improving customer service. ERP systems, on the other hand, encompass a broader scope, aiming to integrate and manage all core business processes across departments, including finance, human resources, supply chain, and manufacturing.
Core Functionalities of CRM Systems
CRM systems typically include features for managing customer data, tracking interactions, automating sales processes, and providing customer support. They empower businesses to understand customer needs, preferences, and behaviors, ultimately driving better customer satisfaction and loyalty. This data-driven approach helps identify trends, predict future needs, and tailor marketing strategies.
Core Functionalities of ERP Systems
ERP systems integrate various business functions by providing a unified platform for data storage and processing. They automate processes like order fulfillment, inventory management, and financial reporting, streamlining operations across departments. This integration leads to improved efficiency, reduced redundancies, and better data visibility across the organization.
Key Differences between CRM and ERP Systems
CRM systems are primarily focused on customer interactions, while ERP systems handle internal business processes. The core difference lies in their target audience and the scope of their functionalities. CRM systems address customer-facing operations, whereas ERP systems encompass the entire enterprise’s internal processes.
Comparison of CRM and ERP Systems
The following table highlights the key differences between CRM and ERP systems across various aspects:
| Aspect | CRM System | ERP System |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Customer interactions and relationships | Internal business processes and resource management |
| Data Integration | Focuses on customer data, often integrated with marketing and sales tools. | Integrates data from various departments (finance, HR, manufacturing) for a holistic view. |
| User Roles | Primarily used by sales, marketing, and customer service teams. | Used by various departments, including finance, operations, and human resources. |
| Business Processes | Focuses on sales, marketing, and customer service processes. | Manages all core business processes, including production, finance, and supply chain. |
| Typical Outcomes | Increased customer satisfaction, improved sales conversions, enhanced customer loyalty. | Increased operational efficiency, reduced costs, improved data visibility, and better decision-making. |
Benefits of Implementing CRM and ERP Systems

Implementing CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems offers significant advantages for businesses seeking to streamline operations, enhance customer relationships, and improve overall efficiency. These systems provide a centralized platform for managing various aspects of a business, leading to better decision-making and improved profitability.
Advantages of CRM Systems for Customer Relationship Management
CRM systems empower businesses to effectively manage customer interactions and data. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and retention. A well-implemented CRM system fosters a 360-degree view of each customer, providing a comprehensive understanding of their needs and preferences. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns, personalized service, and proactive problem resolution.
- Improved Customer Service: CRM systems facilitate quicker response times to customer inquiries and issues by centralizing customer information. This enables agents to access a complete history of interactions with a customer, enabling more informed and personalized support. For example, a customer service representative can quickly access previous orders, support tickets, and communication history, leading to a faster resolution of issues and increased customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Sales Performance: CRM systems provide sales teams with valuable insights into customer interactions and sales trends. This allows for more effective sales strategies, improved lead management, and targeted follow-up. For instance, a sales team can identify potential leads, track their interactions, and tailor their approach based on the customer’s profile, increasing the chances of closing deals.
- Increased Customer Retention: By providing personalized experiences and proactive support, CRM systems foster stronger customer relationships, ultimately increasing customer retention. A CRM can track customer preferences, buying habits, and communication history, enabling businesses to tailor their offerings and anticipate customer needs, leading to higher customer loyalty.
Advantages of ERP Systems for Business Process Optimization
ERP systems integrate various business functions into a single platform, optimizing processes and enhancing data flow. This integrated approach eliminates data silos and improves communication between departments, leading to greater efficiency and productivity. By automating tasks and streamlining workflows, ERP systems reduce manual errors and improve decision-making.
- Streamlined Operations: ERP systems automate various business processes, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity across the organization. For example, automating inventory management reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking, optimizing inventory levels and minimizing costs. The automated process also reduces the possibility of human error in recording transactions.
- Improved Financial Management: ERP systems offer a centralized view of financial data, enabling real-time tracking and analysis of financial performance. This allows for better financial planning, budgeting, and forecasting, improving overall financial stability. Accurate financial reports can be generated, aiding in quick and effective decision-making.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Management: ERP systems enable businesses to track materials and products throughout the supply chain, improving visibility and control over inventory and logistics. This allows for better coordination with suppliers, leading to faster delivery times, reduced costs, and improved supply chain efficiency. For example, real-time tracking of inventory levels helps in anticipating potential shortages and making proactive adjustments to ensure smooth operations.
How CRM and ERP Systems Improve Operational Efficiency
Integrating CRM and ERP systems creates a powerful synergy, enhancing operational efficiency. The combined data and insights provide a holistic view of the business, facilitating better decision-making and resource allocation. By streamlining processes and automating tasks, these systems reduce operational costs and improve overall productivity.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By automating tasks and optimizing processes, CRM and ERP systems can significantly reduce operational costs. This is achieved through minimized manual efforts, reduced errors, and improved resource allocation. For example, automating order processing can reduce the number of employees needed for this task and eliminate the risk of human error.
- Increased Productivity: The automation of tasks and improved workflow coordination within CRM and ERP systems leads to increased productivity across various departments. This means tasks get done faster and more efficiently, leading to better use of resources and higher output.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The centralized data management in CRM and ERP systems allows for data-driven decision making, leading to more informed choices about strategy and resource allocation. This leads to better business outcomes.
Examples of How CRM and ERP Systems Enhance Customer Service
CRM and ERP systems empower businesses to provide superior customer service. They enable personalized interactions, proactive issue resolution, and streamlined support processes. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Personalized Interactions: CRM systems allow businesses to gather customer data, enabling them to personalize interactions and tailor services to individual needs. This creates a more positive and valuable experience for customers.
- Proactive Issue Resolution: By tracking customer interactions and identifying trends, CRM systems can predict potential issues and offer proactive solutions. This minimizes negative customer experiences.
- Streamlined Support Processes: ERP systems integrate customer support processes with other business functions, streamlining workflows and improving efficiency. This leads to faster response times and resolution of customer issues.
Specific Benefits for Different Business Types
| Business Type | CRM Benefits | ERP Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Improved customer segmentation, personalized promotions, enhanced loyalty programs, better inventory management | Inventory management, optimized supply chain, efficient order processing, improved financial reporting |
| Manufacturing | Better customer relationship management, improved order fulfillment, effective supply chain management, enhanced quality control | Resource planning, optimized production schedules, improved quality control, enhanced supply chain management |
| Service Industry | Improved customer service, effective lead management, targeted marketing campaigns, increased customer retention | Resource allocation, scheduling management, efficient service delivery, better financial management |
Challenges in Implementing CRM and ERP Systems
Implementing CRM and ERP systems, while offering significant potential benefits, often presents numerous challenges. These challenges can range from technical difficulties to organizational hurdles, impacting the success of the implementation and the overall return on investment. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for organizations considering such system upgrades.A key aspect of successful implementation lies in recognizing and proactively addressing potential roadblocks.
This includes careful planning, meticulous execution, and strong communication throughout the entire process.
Potential CRM Implementation Challenges
Careful consideration of user needs and workflows is essential for successful CRM implementation. Resistance to change and inadequate training can hinder user adoption. Data migration and integration with existing systems often pose significant challenges, requiring careful planning and execution to avoid data loss or inaccuracies. Furthermore, the cost of implementation, including software licenses, hardware upgrades, and consulting fees, can be substantial.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new processes and technologies, leading to decreased efficiency and slower implementation timelines. This can be mitigated through clear communication, demonstrating the value proposition of the system, and providing comprehensive training.
- Data Migration Issues: Migrating data from legacy systems to a CRM can be complex, prone to errors, and time-consuming. Careful planning, data validation, and data cleansing are crucial to avoid data loss or inconsistencies.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating the CRM with existing business applications (e.g., accounting software, marketing automation tools) may present technical difficulties. Careful planning and selection of compatible systems are essential.
- Lack of User Adoption: If employees do not understand how to use the CRM system effectively, the system will not achieve its full potential. Comprehensive training programs and ongoing support are essential.
Potential ERP Implementation Obstacles
ERP implementation often involves significant organizational change. The complexity of the system and the extensive data migration required can lead to delays and cost overruns. The need for extensive customization and configuration may add to the complexity and cost. Ensuring seamless integration with existing legacy systems is critical.
- High Implementation Costs: ERP systems can be expensive to implement, including software licenses, hardware upgrades, consulting fees, and training. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is critical.
- Data Migration and Integration Issues: Migrating large volumes of data from multiple legacy systems can be extremely complex and error-prone. This often leads to data inconsistencies and inaccuracies, impacting reporting and decision-making.
- Lack of Skilled Personnel: Implementing and maintaining an ERP system requires specialized skills. Finding and retaining qualified personnel for system administration, customization, and support can be a challenge.
- Customization Complexity: ERP systems often need customization to align with a specific company’s processes. Extensive customization can increase implementation time and cost, and lead to technical debt.
Data Migration and Integration Issues
Data migration and integration are crucial aspects of CRM and ERP implementation. Inaccurate data or missing data can lead to inaccurate reporting and flawed business decisions. Proper planning and testing are critical to ensuring a smooth transition.
- Data Validation and Cleansing: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data is critical. Duplicate records, missing values, and inconsistencies in data formats can lead to inaccurate reports and flawed decisions. Data validation and cleansing processes should be carefully planned and executed.
- Data Mapping and Transformation: Mapping data from legacy systems to the new CRM or ERP system is essential. Transforming data into the correct format for the new system can be complex and requires careful planning.
- Data Loss Prevention: Careful planning and implementation are essential to prevent data loss during the migration process. Redundant backups and a comprehensive data recovery plan are crucial.
User Adoption and Training Challenges
Successful CRM and ERP implementations rely heavily on user adoption. Inadequate training and a lack of clear communication can lead to low user engagement and system underutilization. Effective training programs and ongoing support are essential for long-term success.
- Lack of User Engagement: If employees are not actively involved in the implementation process and do not understand the system’s benefits, user adoption will be low. Involving users early on and providing opportunities for feedback are crucial.
- Poor Training Programs: If the training provided is not comprehensive or engaging, users will struggle to utilize the system effectively. Tailoring training to different user roles and providing ongoing support is essential.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new systems and processes, leading to decreased efficiency and slow implementation. Clear communication, demonstrating the value proposition, and offering incentives can help overcome this challenge.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Resistance to change | Comprehensive training, clear communication, and demonstrating the system’s benefits. |
| Data migration issues | Careful planning, data validation, and data cleansing, utilizing migration tools. |
| Integration challenges | Careful planning and selection of compatible systems, engaging technical experts. |
| Lack of user adoption | Comprehensive training, ongoing support, and user involvement in the implementation process. |
| High implementation costs | Careful budgeting, cost-benefit analysis, and exploring cloud-based solutions. |
CRM and ERP System Integration
Integrating CRM and ERP systems is crucial for modern businesses aiming to optimize operations and enhance decision-making. A seamless flow of data between these systems eliminates data silos, providing a holistic view of the business. This unified perspective fosters better customer relationships, streamlines processes, and ultimately boosts profitability.
Importance of Integrating CRM and ERP Systems
Integrating CRM and ERP systems provides a single source of truth for all business data. This unified data view allows for better forecasting, improved customer service, and optimized resource allocation. The synergy between customer interactions (CRM) and operational processes (ERP) enables businesses to react more effectively to market demands and customer needs. For instance, real-time visibility into inventory levels within the ERP system allows the CRM team to accurately inform customers about product availability and potential delays.
Methods for Integrating CRM and ERP Systems
Several methods facilitate the integration of CRM and ERP systems. These methods range from custom-built solutions to utilizing pre-built integration platforms. Choosing the right method depends heavily on the specific needs and resources of the organization.
- API Integrations: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allow for direct communication between the CRM and ERP systems. APIs facilitate data exchange in a structured format, enabling real-time updates and data synchronization. This approach is generally preferred for its flexibility and scalability.
- Middleware Solutions: Middleware acts as a bridge between the CRM and ERP systems, handling data transfer and transformation. This approach often provides a standardized way to connect diverse systems, making it suitable for organizations with complex or heterogeneous IT environments.
- Custom Integrations: For businesses with unique requirements, a custom integration tailored to their specific workflows and data structures can be implemented. This approach ensures a perfectly matched system, but it can be more expensive and time-consuming than other options.
Examples of Successful CRM and ERP System Integrations
Numerous organizations have successfully integrated their CRM and ERP systems. These integrations have resulted in significant improvements in efficiency and customer satisfaction. For example, a retail company integrated its CRM and ERP systems to track customer purchase history, preferences, and loyalty programs within the ERP system. This integration enabled targeted marketing campaigns, personalized product recommendations, and improved customer service responses.
Similarly, a manufacturing company integrated their CRM and ERP systems to manage sales orders, inventory levels, and production schedules in a unified manner.
Challenges Associated with Integrating CRM and ERP Systems
Integrating CRM and ERP systems presents several challenges. These challenges can range from data migration issues to system compatibility problems.
- Data Migration Complexity: Migrating data from disparate systems to a unified platform can be complex and time-consuming. Ensuring data accuracy and consistency during the migration process is critical.
- System Compatibility Issues: Different CRM and ERP systems may not be fully compatible, requiring significant customization or modifications to ensure seamless data exchange.
- Integration Costs: Integration projects can be expensive, requiring significant investments in software, personnel, and training.
Integration Methods Table
| Integration Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| API Integrations | Direct communication between systems using APIs. | Flexible, scalable, real-time data exchange. | Requires technical expertise, potential for errors if not well-managed. |
| Middleware Solutions | Use of intermediary software to connect disparate systems. | Handles data transformation, simplifies integration for heterogeneous environments. | Can be expensive, may introduce latency. |
| Custom Integrations | Tailored solutions for specific business needs. | Perfect fit for unique requirements. | High cost, long implementation time, potential for complex maintenance. |
Case Studies of CRM and ERP System Use
CRM and ERP systems are transforming businesses across various industries. Understanding how these systems are applied in real-world scenarios provides valuable insights into their effectiveness and potential benefits. This section delves into practical examples of CRM and ERP implementations, showcasing successful applications and highlighting crucial considerations for successful deployments.
CRM Application in Retail
Retail businesses often leverage CRM systems to personalize customer experiences and improve sales. A retail company might use a CRM to track customer purchase history, preferences, and communication interactions. This data allows for targeted marketing campaigns, personalized recommendations, and proactive customer service. For instance, a clothing retailer could use CRM data to identify customers who frequently purchase specific styles and tailor promotional offers accordingly.
This personalized approach can significantly boost customer loyalty and drive sales. By analyzing customer purchase patterns and feedback, retailers can optimize inventory management and product offerings, ultimately enhancing profitability.
ERP Application in Manufacturing
ERP systems are critical for manufacturing organizations to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. A manufacturing company can use ERP to manage various aspects of its production process, from raw material procurement to finished goods delivery. This integrated system provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, production schedules, and order fulfillment. This facilitates optimized resource allocation and reduced lead times.
For example, an automotive manufacturer can use ERP to track the movement of parts throughout the production line, ensuring timely delivery and minimizing delays. This data-driven approach to manufacturing processes leads to improved production output and reduced operational costs.
Successful CRM Implementation Case Study
A prominent example of a successful CRM implementation is seen in a large telecommunications company. By implementing a robust CRM system, the company streamlined its customer service operations, significantly reducing customer service response times. This led to increased customer satisfaction and retention rates. The CRM system enabled the company to track customer interactions, manage customer accounts, and personalize communication, resulting in a superior customer experience.
Moreover, the system provided insights into customer behavior and preferences, facilitating targeted marketing strategies and personalized service offerings.
Successful ERP Implementation Case Study
A food processing company successfully implemented an ERP system to manage its complex supply chain. The system integrated various departments, including procurement, production, logistics, and finance. The implementation resulted in improved inventory management, reduced lead times, and increased profitability. The real-time visibility provided by the ERP system allowed the company to optimize its production schedules, ensuring efficient resource allocation and minimizing waste.
Furthermore, the integrated financial module enhanced the company’s financial reporting and decision-making capabilities.
CRM and ERP System Implementation Examples Across Sectors
| Sector | CRM Example | ERP Example |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Tracking customer purchase history, providing personalized recommendations, enhancing customer service | Managing inventory, optimizing supply chain, improving order fulfillment |
| Manufacturing | Managing customer relationships, providing personalized product support, enhancing marketing campaigns | Managing production schedules, optimizing resource allocation, streamlining logistics |
| Healthcare | Managing patient records, scheduling appointments, tracking medical history | Managing patient information, optimizing resource allocation, enhancing financial reporting |
| Finance | Managing customer accounts, providing personalized financial advice, tracking transactions | Managing financial transactions, optimizing resource allocation, streamlining reporting |
Future Trends in CRM and ERP Systems

The landscape of CRM and ERP systems is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business needs. Organizations are increasingly seeking solutions that offer greater efficiency, enhanced customer experiences, and improved decision-making capabilities. This necessitates a forward-thinking approach to understand and adapt to the emerging trends in these critical business tools.
Emerging Trends in CRM Technology
Modern CRM systems are evolving beyond basic contact management. Focus is shifting towards personalized customer experiences, predictive analytics, and seamless integration with other business applications. This includes utilizing AI to analyze customer data, predict future behavior, and tailor marketing campaigns. These insights allow businesses to better anticipate customer needs and improve customer satisfaction. A key component is the integration of social media data, providing a holistic view of the customer journey.
Upcoming Trends in ERP Technology
ERP systems are transforming from simple transaction processing tools to comprehensive business management platforms. A significant trend involves integrating various business functions, including supply chain management, human resources, and finance, to provide a single, unified view of the organization. This data-driven approach fosters better collaboration and decision-making across departments. Advanced analytics and reporting capabilities are becoming essential for identifying trends and optimizing processes.
AI and Machine Learning in CRM and ERP Systems
AI and machine learning are rapidly transforming CRM and ERP systems. AI-powered chatbots are becoming increasingly sophisticated, providing 24/7 customer support and handling routine inquiries. These systems can also analyze customer interactions to identify patterns and tailor marketing campaigns. Machine learning algorithms in ERP systems are being used to optimize inventory management, predict demand, and automate various business processes.
For example, AI-powered tools can identify potential fraud or errors in financial transactions, improving security and accuracy.
The Role of Cloud Computing in Modern CRM and ERP Systems
Cloud-based CRM and ERP solutions are becoming the norm. This shift allows for greater scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Organizations can access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, enhancing flexibility and collaboration. Cloud solutions often provide built-in security features and regular updates, minimizing the need for in-house IT support. Cloud deployment also allows for rapid scaling, enabling businesses to adjust their resources quickly in response to changing demands.
The Potential Impact of Mobile Technology on CRM and ERP Systems
Mobile technology is revolutionizing how businesses interact with CRM and ERP systems. Mobile apps provide real-time access to data and tools, enabling employees to make informed decisions on the go. Sales representatives can access customer information and update records directly from their mobile devices, improving sales efficiency. Field service technicians can access work orders and inventory information on their phones, optimizing service delivery.
This access fosters greater agility and responsiveness.
How Emerging Technologies Are Changing CRM and ERP Systems
| Technology | Impact on CRM | Impact on ERP ||—|—|—|| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Personalized customer experiences, predictive analytics, automated customer support | Optimized inventory management, demand forecasting, automated processes, fraud detection || Machine Learning (ML) | Customer segmentation, targeted marketing, personalized recommendations | Improved supply chain optimization, predictive maintenance, dynamic pricing || Cloud Computing | Scalability, accessibility, cost-effectiveness, improved security | Scalability, accessibility, reduced IT infrastructure costs, enhanced data sharing || Mobile Technology | Real-time access to customer data, enhanced sales efficiency, improved service delivery | Real-time access to operational data, field service optimization, enhanced collaboration || Internet of Things (IoT) | Enhanced customer insights through connected devices, personalized experiences | Real-time tracking of inventory and assets, predictive maintenance, optimized supply chain |
Best Practices for CRM and ERP System Selection
Selecting the right CRM and ERP system is crucial for business success. A poorly chosen system can lead to wasted resources, decreased efficiency, and ultimately, hinder growth. Careful consideration of various factors, from specific needs to integration capabilities, is paramount. This section Artikels best practices for selecting these vital business tools.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a CRM System
Selecting a CRM system requires a thorough understanding of business requirements. Key factors include the size and structure of the sales team, the desired level of automation, and the types of customer interactions anticipated. Addressing these considerations proactively ensures the CRM system aligns with current and future business goals.
- Sales Process Analysis: A comprehensive understanding of the sales process, from lead generation to closing, is essential. This allows for the selection of a CRM system that effectively supports each stage, optimizing workflows and maximizing conversion rates. Consider the specific needs of each team member and how the CRM can be tailored to meet them.
- Scalability and Future Growth: The chosen CRM system should be scalable enough to accommodate future growth and changing business needs. A rigid system may hinder adaptability, potentially leading to issues down the line. Assess the anticipated expansion in terms of team size, customer base, and data volume.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamless integration with existing systems, such as marketing automation platforms or accounting software, is vital for streamlined operations. A CRM that doesn’t integrate well can create redundancies and hinder data flow. Evaluate the integration capabilities of various CRM options before making a decision.
- User-Friendliness and Training: A user-friendly interface minimizes training time and maximizes adoption rates. Consider the technical proficiency of your team and choose a system that’s intuitive and easy to navigate. Assess the available training resources and support offered by the vendor.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an ERP System
Selecting an ERP system involves evaluating a broader range of business functions. The chosen system must support all aspects of the organization, from inventory management to financial reporting. Factors like the industry, company size, and existing processes are key determinants in the selection process.
- Business Processes and Requirements: Analyze existing business processes and identify areas where the ERP system can improve efficiency. Customization capabilities are vital for tailoring the system to specific needs and workflows. A system that doesn’t adequately support existing procedures will lead to resistance and a slower implementation.
- Financial Management Capabilities: An ERP system’s financial capabilities are critical. It must effectively manage accounts payable, accounts receivable, and general ledger functions. Evaluate the system’s reporting capabilities to ensure accurate and timely financial insights. Assess its ability to integrate with existing financial software.
- Inventory Management: For businesses with significant inventory, the ERP system should provide accurate and real-time inventory tracking. This feature streamlines order fulfillment, reduces stockouts, and minimizes holding costs. Evaluate the system’s ability to manage different inventory types and locations.
- Scalability and Future Needs: The chosen ERP system must accommodate future growth and evolving business needs. Consider the potential increase in data volume, transactions, and user base. A system that can’t scale with the business will become a bottleneck in the long run.
Key Features to Look for in a CRM System
Effective CRM systems offer a range of features to enhance sales processes and customer relationships.
- Lead Management: A robust lead management system allows for efficient tracking and nurturing of potential customers. This includes features for lead scoring, qualification, and assignment to sales representatives.
- Contact Management: Effective contact management is essential for building strong customer relationships. The system should allow for comprehensive contact information storage, tracking of interactions, and historical data retrieval.
- Sales Forecasting: Accurate sales forecasting helps in strategic planning and resource allocation. A system that provides reliable sales forecasts is vital for informed decision-making.
- Reporting and Analytics: Detailed reporting and analytics tools are essential for gaining insights into sales performance and customer behavior. This facilitates data-driven decision-making.
Crucial Functionalities to Consider in an ERP System
An ERP system’s core functionalities must address all critical business processes.
- Financial Accounting: Accurate financial record-keeping is paramount for any business. ERP systems must provide functionalities for general ledger, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and financial reporting.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management is crucial for minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency. ERP systems must track inventory levels, manage orders, and forecast demand.
- Supply Chain Management: Managing the supply chain effectively is essential for smooth operations. ERP systems should integrate with suppliers and distributors, tracking materials, orders, and deliveries.
- Human Resources Management: HR functionalities can streamline HR processes, including payroll, benefits administration, and employee performance management. ERP systems often incorporate these modules to enhance efficiency.
Criteria for Evaluating CRM and ERP System Choices
A structured evaluation process is essential for making informed decisions.
| Criteria | CRM System Evaluation | ERP System Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Lead management, contact management, sales forecasting, reporting | Financial accounting, inventory management, supply chain management, HR management |
| Scalability | Adaptability to future growth in sales team and customer base | Adaptability to future growth in data volume, transactions, and user base |
| Integration | Integration with marketing automation, e-commerce platforms | Integration with existing financial systems, inventory systems, and other relevant software |
| User Experience | Ease of use for sales representatives, intuitiveness | Ease of use for various departments, user-friendliness |
| Cost | Licensing fees, implementation costs, maintenance | Licensing fees, implementation costs, customization costs, maintenance |
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, CRM and ERP systems are powerful tools for modern businesses, offering a wide range of benefits from improved customer relations to optimized operational efficiency. While implementation challenges exist, successful integration and ongoing maintenance are key to realizing the full potential of these systems. By carefully considering the specific needs of your organization and choosing the right solutions, you can unlock significant advantages in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Question Bank
What are the typical costs associated with implementing CRM and ERP systems?
Implementation costs vary significantly depending on the chosen system, the scale of the project, and customization requirements. Factors such as software licensing fees, consulting services, data migration expenses, and ongoing maintenance play a role in the total cost of ownership. A thorough cost analysis is crucial to budgeting effectively for these projects.
How can businesses effectively train their employees to use CRM and ERP systems?
Comprehensive training programs are essential for user adoption and successful implementation. These programs should encompass both technical training on system functionalities and practical application scenarios. Tailored training modules, hands-on workshops, and ongoing support can significantly enhance user proficiency and ensure the systems are effectively utilized.
What are some common data security concerns related to CRM and ERP systems?
Data breaches and security vulnerabilities are major concerns. Implementing robust security protocols, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, is critical. Employee training on data security best practices and incident response plans are also important components of a comprehensive security strategy.
How do I choose the right CRM and ERP system for my business?
The best system for a business depends on its specific needs and resources. Careful evaluation of factors like scalability, customization options, integrations with existing systems, and vendor support are essential to finding the ideal solution. It is crucial to conduct thorough research, gather feedback from potential users, and conduct pilot programs to validate the suitability of a system for a specific business.