Vendor management platforms (VMPs) are revolutionizing how businesses interact with their suppliers, contractors, and service providers. From streamlining onboarding to enhancing communication, VMPs are transforming the vendor management landscape. This guide delves into the intricacies of VMPs, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and the considerations businesses face when implementing one.
This comprehensive overview covers the essential aspects of vendor management platforms, including their definition, functionalities, benefits, challenges, and future trends. We’ll examine various types of VMPs and explore their suitability across different industries.
Defining Vendor Management Platforms (VMPs)
A Vendor Management Platform (VMP) is a centralized software solution designed to streamline and optimize the entire vendor lifecycle, from initial onboarding to ongoing management and eventual termination. It serves as a single source of truth for all vendor-related data and interactions, improving visibility, control, and efficiency within an organization’s supply chain.A well-implemented VMP empowers businesses to effectively manage a diverse range of vendors, improving compliance, mitigating risks, and fostering strong vendor relationships.
This translates to cost savings, enhanced operational efficiency, and a reduced administrative burden.
Key Functionalities and Features of a VMP
A VMP typically offers a suite of features that encompass the complete vendor lifecycle. These functionalities facilitate improved oversight and collaboration across departments involved in vendor relationships. Key features often include vendor onboarding, contract management, risk assessment, performance monitoring, compliance tracking, and reporting.
Types of Vendors Supported by VMPs
VMPs can manage various types of vendors, encompassing suppliers, contractors, service providers, and other external partners. The specific types of vendors supported depend on the VMP’s functionalities and the particular needs of the organization.
Use Cases Across Industries
VMPs are applicable across diverse industries. For example, in the manufacturing sector, a VMP can help manage supplier relationships, track material deliveries, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. In healthcare, a VMP can facilitate the management of medical equipment providers, ensuring quality and adherence to safety protocols. Financial institutions leverage VMPs for regulatory compliance and risk management related to their vendor partners.
This diverse range of applications demonstrates the adaptability and utility of VMPs.
Types of VMPs
Different types of VMPs cater to varying organizational needs and technical infrastructure. The choice depends on factors such as budget, IT infrastructure, and the scale of vendor relationships.
| Type of VMP | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud-Based | Hosted on a cloud platform, accessible via the internet. Generally offers scalability, flexibility, and lower upfront costs. |
| On-Premises | Installed and maintained on the organization’s own servers. Provides greater control and customization but requires significant upfront investment and ongoing IT support. |
| Hybrid | Combines cloud-based and on-premises functionalities. Provides a balance between cloud benefits and on-premises control. Useful for organizations with specific data security requirements or legacy systems. |
Benefits of Implementing a VMP
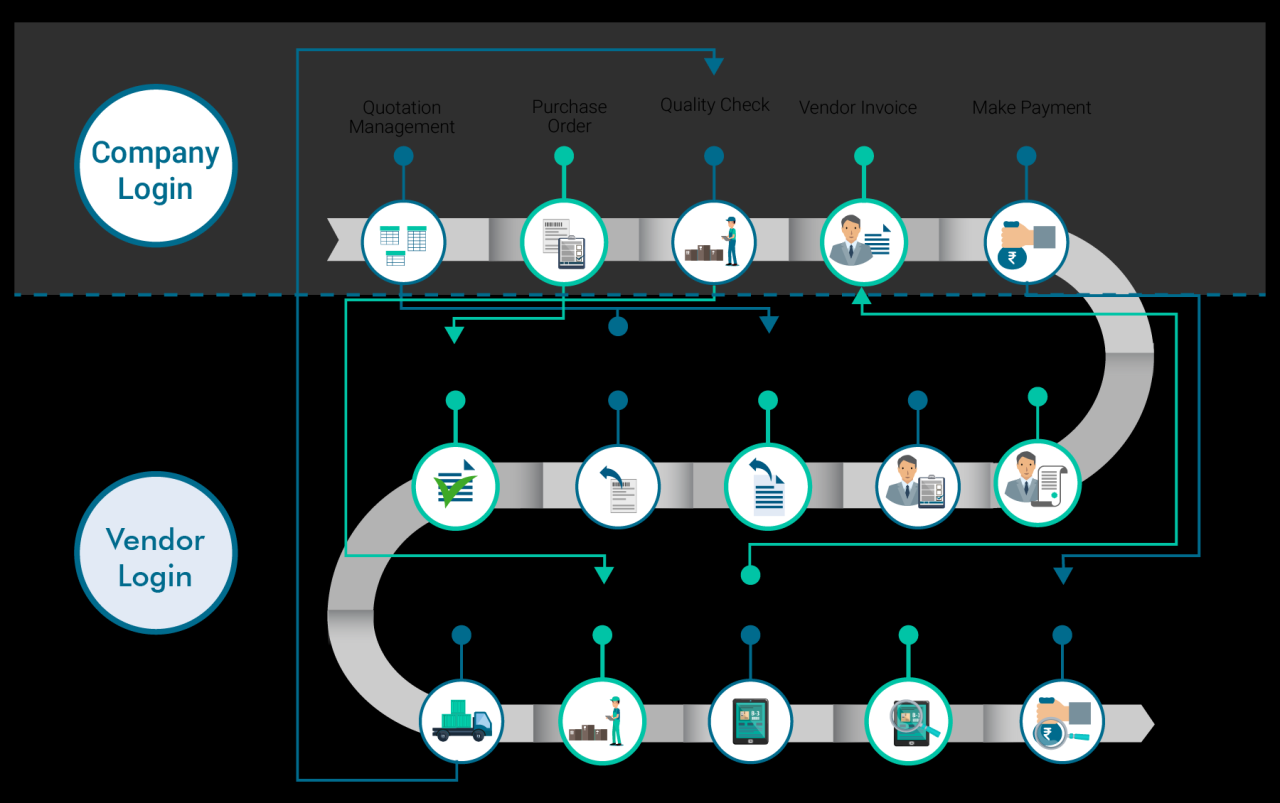
A Vendor Management Platform (VMP) offers significant advantages for businesses seeking to streamline vendor relationships and improve overall operational efficiency. By centralizing vendor data, communication, and processes, VMPs empower organizations to mitigate risks, enhance collaboration, and optimize resource allocation. This ultimately translates to improved profitability and enhanced business performance.Implementing a VMP facilitates a more structured and organized approach to vendor management, allowing for better control over costs, performance, and compliance.
The benefits extend from simplified contract management to proactive risk identification and mitigation, resulting in a more resilient and efficient supply chain.
Core Advantages of Using a VMP
A VMP provides a centralized repository for all vendor-related information, streamlining communication and reducing the risk of errors or omissions. This holistic view of vendor relationships allows businesses to make informed decisions regarding vendor selection, performance, and potential risks. Crucially, this centralized approach fosters better collaboration and communication, leading to improved vendor performance and stronger partnerships.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
VMPs automate many tasks traditionally handled manually, such as contract creation, performance tracking, and compliance monitoring. This automation significantly reduces administrative burden, freeing up valuable time and resources for other critical business functions. The standardized processes implemented through a VMP ensure consistency and accuracy in vendor interactions, minimizing errors and delays. For example, a well-implemented VMP can automatically flag potential compliance violations, allowing for proactive intervention and preventing costly penalties.
Enhanced Vendor Relationships and Communication
A VMP facilitates a more organized and transparent communication channel between the business and its vendors. Clearer communication channels foster mutual understanding and trust, improving vendor performance and responsiveness. With a centralized platform, businesses can track interactions, share information, and resolve issues more efficiently, ultimately strengthening the overall vendor relationship. This leads to a more collaborative and mutually beneficial partnership.
Role of a VMP in Risk Management and Compliance
VMPs play a critical role in proactively identifying and mitigating vendor risks. By centralizing vendor data and performance metrics, businesses can easily track compliance status and identify potential vulnerabilities or conflicts of interest. Furthermore, VMPs can facilitate the creation and enforcement of standardized contracts, ensuring consistency across all vendor agreements. This systematic approach to risk management reduces potential financial losses and operational disruptions, and enables businesses to meet regulatory requirements more effectively.
Comparison of Different VMP Solutions
| Feature | Solution A | Solution B | Solution C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contract Management | Automated contract creation, versioning, and tracking. Robust contract negotiation tools. | Manual contract management with limited automation. Basic contract tracking. | Advanced contract lifecycle management, with features for e-signatures and contract analytics. |
| Vendor Performance Monitoring | Real-time performance dashboards and reporting. Customizable performance metrics. | Basic performance reports with limited data analysis. | Predictive analytics to anticipate potential issues and identify high-performing vendors. |
| Compliance Management | Automated compliance checks against industry regulations. Integration with regulatory databases. | Manual compliance monitoring with limited tools. | Centralized compliance repository with automated alerts for regulatory changes. |
| Integration Capabilities | Integrates with various enterprise systems, including ERP and CRM. | Limited integration capabilities. | Highly customizable integrations with a wide range of business applications. |
| Pricing Model | Tiered pricing based on user volume and features. | Fixed pricing regardless of features or user volume. | Subscription-based pricing with flexible plans. |
Note: The above table provides a general comparison. Specific features and pricing may vary depending on the individual VMP solution.
Key Features and Functionalities of VMPs
Vendor Management Platforms (VMPs) are crucial for streamlining vendor relationships and optimizing procurement processes. A robust VMP provides a centralized repository for managing all vendor-related information, facilitating efficient communication, collaboration, and performance tracking. This allows organizations to gain greater control over their supply chain and improve overall operational efficiency.Effective VMPs offer a suite of features that go beyond simple vendor directories.
These platforms empower organizations to proactively manage their vendor base, ensuring compliance, minimizing risks, and maximizing value from supplier relationships.
Essential Features of a VMP
A well-rounded VMP encompasses several key functionalities. These features are essential for effective vendor management and enable organizations to achieve their desired outcomes. Essential features often include detailed vendor profiles, comprehensive contract management tools, and robust performance evaluation metrics.
- Vendor Onboarding and Offboarding: A streamlined onboarding process reduces time-to-value and ensures new vendors meet established criteria. Offboarding procedures ensure a smooth transition when relationships end, minimizing disruption and facilitating the transition to a new vendor.
- Contract Management: Centralized contract management within a VMP allows for efficient tracking of agreements, renewals, and compliance. Automated reminders for renewals and standardized templates contribute to minimizing risks and improving contract visibility.
- Supplier Performance Management: Tracking vendor performance metrics, such as delivery times, quality, and cost, is critical for making informed decisions about supplier relationships. Performance dashboards provide key insights into overall supplier performance, enabling organizations to proactively address potential issues.
Importance of Vendor Onboarding and Offboarding
Efficient onboarding and offboarding processes are vital for maintaining a healthy and compliant vendor base. Onboarding new vendors involves ensuring they adhere to company policies and procedures. Offboarding ensures a smooth transition when a vendor relationship ends, minimizing disruption to operations.
- Onboarding: Detailed onboarding processes involve validating vendor credentials, conducting background checks (if necessary), and ensuring compliance with company policies.
- Offboarding: Clear offboarding procedures include a formal process for contract termination, return of assets, and data transfer, minimizing disruption and ensuring continuity.
Importance of Contract Management in a VMP
Contract management within a VMP streamlines the entire process, from creation to renewal and termination. A VMP facilitates the storage, retrieval, and analysis of contracts, enabling efficient contract management and reducing administrative overhead. This is essential for ensuring compliance and minimizing legal risks.
- Contract Storage and Retrieval: A VMP provides a centralized repository for all contracts, facilitating easy access and retrieval. This ensures contracts are readily available to authorized personnel.
- Automated Reminders: Automated reminders for contract renewals help prevent missed deadlines and ensure ongoing compliance.
Supplier Performance Management in a VMP
Effective supplier performance management within a VMP allows organizations to track vendor performance metrics, providing insights into their reliability and efficiency. This helps organizations make informed decisions about their vendor relationships and optimize their supply chain.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Tracking KPIs, such as on-time delivery rates, quality scores, and cost metrics, enables proactive identification of potential issues.
- Performance Dashboards: VMPs offer visual dashboards to present supplier performance data, providing a comprehensive overview of vendor performance.
Modules in a Typical VMP
A typical VMP comprises various modules to address different aspects of vendor management. These modules often include vendor profiles, contract management, performance management, and communication tools.
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| Vendor Profiles | Comprehensive profiles of vendors, including contact information, financial data, and compliance details. |
| Contract Management | Centralized storage and management of vendor contracts, including tracking renewals and compliance. |
| Performance Management | Tracking and reporting on supplier performance metrics, enabling analysis and identification of improvement areas. |
| Communication Tools | Facilitating communication between the organization and its vendors. |
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing a VMP
Implementing a Vendor Management Platform (VMP) presents a range of challenges, extending beyond the initial setup. Careful planning and proactive strategies are crucial to a successful transition and long-term value realization. Understanding these hurdles and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies will lead to a smoother and more beneficial implementation.
Potential Obstacles to VMP Implementation
Several obstacles can hinder the successful implementation of a VMP. These range from resistance to change among personnel to issues in data migration and integration. A lack of clear communication and inadequate training can also significantly impede progress.
- Resistance to Change: Employees accustomed to existing processes may resist adopting a new system. Addressing this resistance through effective communication, showcasing the platform’s benefits, and providing comprehensive training can help overcome this hurdle. A well-defined change management plan is essential.
- Data Integration and Migration Challenges: Integrating data from various sources into the VMP can be complex. Migrating existing vendor data, ensuring accuracy, and mapping fields across systems are crucial steps. This process often requires significant time and resources.
- Lack of Clear Communication: Effective communication is paramount throughout the implementation process. Regular updates, clear documentation, and accessible support channels are critical to maintaining stakeholder engagement and minimizing confusion.
- Inadequate Training and Vendor Adoption: Failure to adequately train personnel on using the VMP and insufficient vendor training on the platform can lead to inefficiencies and adoption issues. A phased approach with comprehensive documentation and hands-on support is crucial.
Significance of Data Integration and Migration
Data integration and migration are critical components of VMP implementation. The accuracy and completeness of data within the VMP directly influence the platform’s effectiveness. Inaccurate data can lead to poor decision-making and inaccurate reporting.
Data migration requires careful planning and execution to avoid data loss or corruption. A robust migration strategy must include data validation, mapping, and transformation procedures. A well-defined data dictionary is essential to ensure data consistency and interoperability. A pilot program with a subset of vendors can identify potential issues and fine-tune the migration process before a full implementation.
Importance of Vendor Training and Adoption
Vendor training and adoption are essential to maximizing the value of a VMP. Empowering vendors with the knowledge and skills to use the platform efficiently is critical for smooth operation and successful collaboration.
- Vendor Training Programs: Comprehensive training programs tailored to the specific needs of vendors can foster a smooth transition. Clear documentation, interactive tutorials, and hands-on exercises can be incorporated into the program. Vendors should be encouraged to actively participate in the training process.
- Vendor Support Channels: Establish clear and accessible support channels for vendors to address questions and resolve issues. A dedicated support team or FAQs can help resolve queries efficiently.
Challenges of Maintaining Vendor Relationships Through a VMP
Maintaining positive vendor relationships is crucial for long-term success. The VMP should facilitate efficient communication and collaboration, not hinder it.
A VMP should be designed to streamline vendor communication, automate tasks, and improve transparency. However, potential challenges include the need to adapt existing processes and the potential for miscommunication between vendors and internal teams. Maintaining open communication channels and proactively addressing concerns can help mitigate these challenges.
Potential Issues and Mitigation Strategies
| Potential Issue | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Resistance to change among internal personnel | Comprehensive training, communication campaigns, and demonstrating the platform’s value. |
| Data integration and migration difficulties | Thorough data mapping, validation, and migration planning. Testing and piloting the process with a subset of vendors. |
| Vendor adoption and training challenges | Tailored training programs, accessible support channels, and clear documentation. |
| Maintaining vendor relationships | Proactive communication, regular feedback loops, and tools to facilitate communication. |
Future Trends in VMP Technology
Vendor Management Platforms (VMPs) are constantly evolving to meet the dynamic needs of modern organizations. These platforms are becoming increasingly sophisticated, leveraging emerging technologies to streamline vendor relationships, enhance transparency, and drive efficiency. This evolution promises significant improvements in vendor management practices across various industries.
AI and Machine Learning in VMPs
AI and machine learning are transforming vendor management by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing risk assessment. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict potential issues, and optimize vendor performance. For example, AI-powered tools can automatically assess vendor compliance with regulations, flag potential risks, and recommend proactive measures to mitigate them. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms can forecast vendor performance, enabling proactive contract negotiation and resource allocation.
Cloud-Based VMP Solutions
Cloud-based VMP solutions are gaining significant traction due to their scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. These solutions offer businesses the flexibility to access and manage vendor data from anywhere, anytime, with secure access. The cloud environment allows for easy integration with other business systems, fostering a more unified and streamlined vendor management process. Organizations can leverage cloud-based tools for remote collaboration with vendors and streamline communication across different teams and locations.
This accessibility also fosters agility and adaptability in responding to evolving vendor requirements.
Blockchain Technology in Vendor Management
Blockchain technology offers a promising avenue for enhancing transparency and security in vendor management. By creating a tamper-proof record of transactions and interactions, blockchain can build trust and accountability between businesses and their vendors. This transparency can help mitigate risks and foster more collaborative vendor relationships. A key advantage of blockchain is its ability to track products and services throughout the supply chain, improving traceability and ensuring compliance.
Examples of this include tracking the origin of materials, verifying authenticity, and ensuring ethical sourcing practices.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in VMPs
VMPs are increasingly incorporating sustainability and ethical sourcing criteria into their functionalities. These platforms can track environmental impact, social responsibility, and labor practices of vendors. This allows businesses to make informed decisions about their supplier network, fostering sustainable practices and ethical behavior. The use of metrics to evaluate vendors on environmental factors such as carbon emissions, water usage, and waste generation allows businesses to build a sustainable supply chain.
Furthermore, ethical sourcing criteria can track labor standards, fair wages, and working conditions to promote responsible practices. Examples include platforms that enable companies to easily identify and evaluate suppliers based on environmental impact and ethical standards, allowing for sustainable sourcing initiatives.
Case Studies of Successful VMP Implementations
Vendor Management Platforms (VMPs) have proven invaluable for businesses seeking to optimize their supplier relationships and streamline vendor management processes. These platforms offer a centralized hub for managing all aspects of vendor interactions, from initial onboarding to ongoing performance monitoring. Successful VMP implementations demonstrate the significant improvements achievable through the adoption of such technology.Implementing a VMP effectively requires careful planning and execution.
A successful implementation hinges on thorough vendor analysis, robust data collection, and clear integration with existing business systems. This ensures the platform becomes a valuable asset, not just a new system to learn.
Example: A Retail Company’s Transition to a VMP
Retail giants often face complex supply chains and a vast network of vendors. A large apparel retailer, for instance, saw significant improvements after transitioning to a vendor management platform. Their prior approach relied on disparate spreadsheets and manual processes, leading to inefficiencies in vendor communication, contract management, and performance tracking.
- Improved Vendor Onboarding: The VMP streamlined the onboarding process, automating data entry and reducing manual effort. This resulted in a faster onboarding time, improving overall supply chain agility.
- Enhanced Contract Management: The VMP facilitated the storage and retrieval of vendor contracts, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of contractual disputes. This resulted in more efficient contract renewal processes and greater compliance with legal regulations.
- Optimized Performance Monitoring: The platform provided real-time visibility into vendor performance metrics, enabling proactive issue resolution and improvement of supplier relationships. The retailer was able to identify and address potential issues before they impacted production schedules or customer satisfaction.
- Centralized Communication and Collaboration: The VMP allowed for centralized communication and collaboration between the company and its vendors. This improved communication and reduced the chance of misunderstandings and miscommunications, resulting in a better overall business relationship.
Integration with Existing Systems
Successful VMP implementations often involve seamless integration with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. The retailer’s implementation, for example, integrated the VMP with their ERP system. This facilitated automatic data exchange, eliminating manual data entry and reducing the potential for errors. The automated data flow enabled real-time visibility into vendor performance, improving forecasting accuracy and decision-making. The streamlined process resulted in a more efficient supply chain.
Positive Outcomes and Results
The retail company’s implementation resulted in tangible improvements. A 20% reduction in vendor onboarding time was observed, and contract renewal times were reduced by 15%. Improved communication with vendors led to a 10% decrease in disputes. These improvements demonstrate the positive return on investment (ROI) associated with implementing a VMP. The retailer achieved these improvements through a carefully considered implementation process, including comprehensive vendor analysis and thorough integration with existing systems.
Choosing the Right VMP for Your Business
Selecting a Vendor Management Platform (VMP) is a critical decision that significantly impacts your vendor relationships and overall operational efficiency. A well-chosen VMP can streamline processes, improve communication, and foster greater transparency throughout your vendor network. Conversely, an unsuitable VMP can lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and strained vendor partnerships.A careful selection process ensures that the chosen platform aligns with your specific business needs and goals, allowing for optimal utilization of its features and functionalities.
This process involves a thorough understanding of your requirements, a comprehensive evaluation of potential vendors, and a strategic approach to implementation.
Steps in Selecting a Suitable VMP
Careful planning is crucial in the selection process. A structured approach will help you navigate the various options and make an informed decision. Begin by defining your specific needs and requirements. Consider factors like the size of your vendor base, the types of vendors you manage, and the key performance indicators (KPIs) you wish to track. This initial assessment lays the foundation for evaluating potential VMP solutions.
Considering Business Needs and Requirements
Understanding your business needs is paramount. Evaluate your current vendor management processes, identify pain points, and Artikel specific functionalities you need. Consider the scale of your operations, the number of vendors you manage, and the complexity of your procurement processes. These considerations will help narrow down the list of potential VMP solutions.
Vendor Comparison and Evaluation
Comparing and evaluating different VMP vendors is a vital step. It requires a systematic approach to assess various factors. This includes evaluating their capabilities, functionalities, pricing models, and customer support. A thorough comparison will ensure you select a VMP that best suits your needs.
Factors to Evaluate When Choosing a VMP Solution
Several key factors should be considered when assessing potential VMP solutions. Consider factors such as:
- Scalability: Assess the platform’s ability to accommodate future growth in vendor numbers and data volume. Consider how easily the platform can adapt to changing business needs.
- Integration Capabilities: Evaluate the platform’s compatibility with existing systems, such as your ERP, CRM, and other business applications. A seamless integration minimizes data redundancy and improves overall efficiency.
- User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX): A user-friendly interface is crucial for effective vendor management. Consider ease of navigation, clarity of reporting, and intuitive data entry. Test the platform’s user interface to determine its effectiveness for your team.
- Security Features: Assess the platform’s security protocols and measures to protect sensitive vendor data. Look for features like data encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications.
- Vendor Support and Training: Evaluate the level of support provided by the vendor, including documentation, tutorials, and dedicated customer service. A robust support system is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining system functionality.
VMP Vendor Comparison Table
The following table provides a comparative overview of various VMP vendors and their key features. This table is intended to provide a high-level overview, and a detailed evaluation should be performed by your team.
| Vendor | Key Features | Pricing Model | Scalability | Integration | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor A | Robust reporting, strong security, scalable | Tiered pricing | High | Excellent | 24/7 support |
| Vendor B | Intuitive interface, flexible customization, good mobile access | Subscription-based | Medium | Good | Dedicated account managers |
| Vendor C | Excellent data visualization, industry-specific features, strong security | Per-user pricing | High | Excellent | Self-service portal |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, vendor management platforms offer significant advantages for businesses seeking to optimize their vendor relationships. By streamlining processes, enhancing communication, and improving risk management, VMPs empower organizations to achieve greater efficiency and productivity. Choosing the right VMP requires careful consideration of your business needs, but the potential rewards are substantial. The future of VMPs looks promising, with continuous advancements in technology poised to further transform the landscape of vendor management.
Questions Often Asked
What are the typical costs associated with implementing a VMP?
Implementation costs vary significantly depending on the chosen platform, the size of your vendor base, and the level of customization required. Factors like licensing fees, training, data migration, and potential integration with existing systems influence the overall expenditure.
How does a VMP help with vendor compliance?
VMPs provide a centralized repository for vendor information, enabling businesses to track and manage compliance requirements effectively. Automated checks, alerts, and reporting features within the platform ensure adherence to industry regulations and internal policies, mitigating compliance risks.
What are the common integration challenges when implementing a VMP?
Data migration and integration with existing systems are often significant challenges. Careful planning, a well-defined integration strategy, and close collaboration between IT and vendor management teams are crucial for successful implementation.
How can I ensure successful vendor adoption of a VMP?
Thorough vendor training and clear communication about the platform’s benefits are key to successful adoption. Making the platform user-friendly and intuitive will increase the likelihood of vendor engagement and participation.