Operational CRM systems are the backbone of modern businesses, streamlining interactions with customers and driving efficiency across departments. This guide dives deep into the world of operational CRM, exploring its various facets, from core functionalities to emerging trends. We’ll examine how these systems can revolutionize customer relationships and boost overall business performance.
From sales force automation to service automation, operational CRM encompasses a suite of tools designed to enhance every touchpoint with your customer base. This guide will walk you through the benefits, challenges, and key components of these powerful systems, along with considerations for specific industries.
Defining Operational CRM Systems
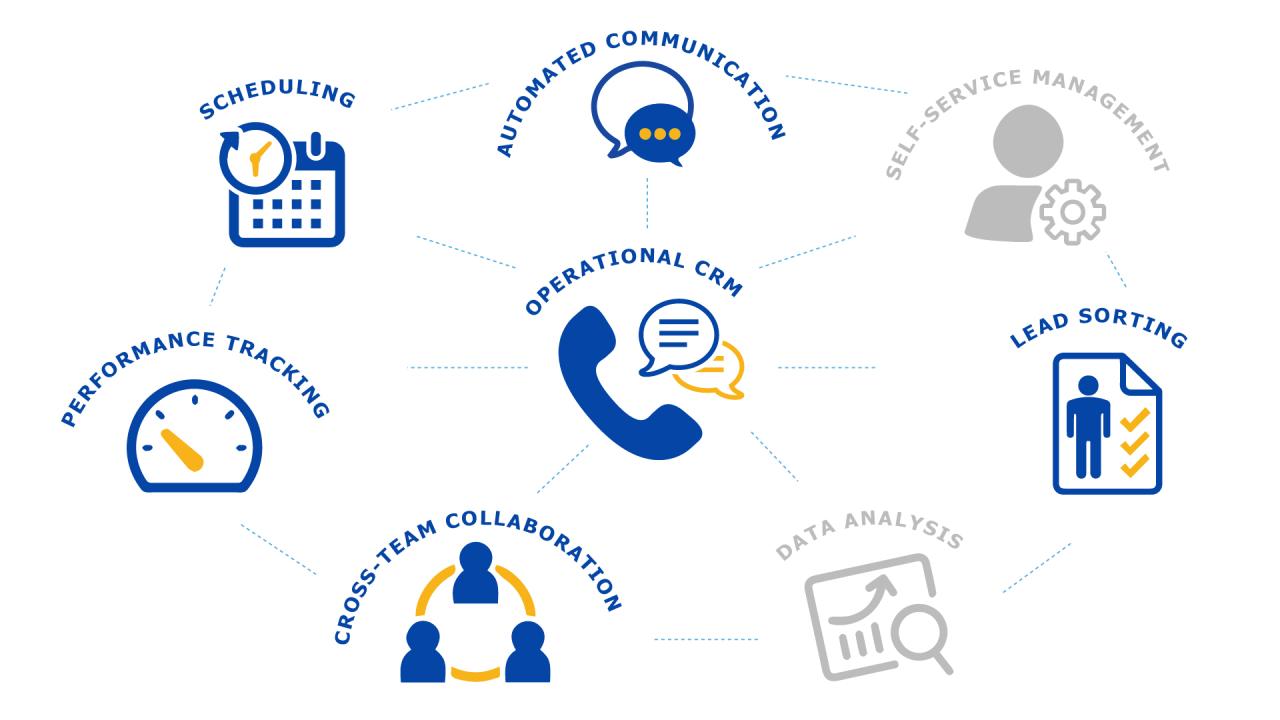
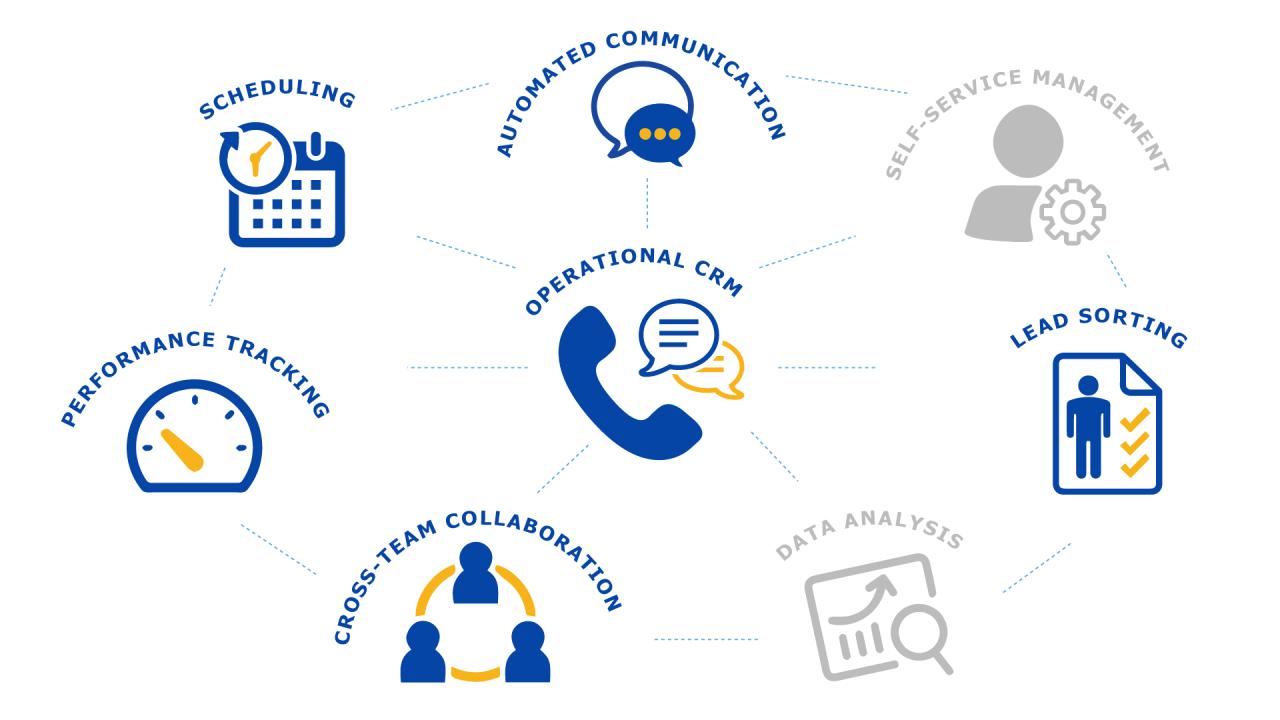
Operational CRM systems are designed to streamline and automate core business processes within a company’s customer interaction cycle. These systems focus on improving efficiency and effectiveness in sales, marketing, and customer service activities, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction and ultimately drive revenue growth. They are the backbone of many businesses, facilitating everyday interactions with customers.These systems are distinct from analytical CRM systems, which focus on data analysis and strategic decision-making.
Operational CRM systems, instead, are more focused on the day-to-day interactions and tasks involved in managing customer relationships. They are crucial for fostering customer engagement and satisfaction by automating tasks and improving communication flows.
Key Characteristics and Functionalities
Operational CRM systems are characterized by their ability to automate and integrate key business processes related to customer interactions. They typically provide tools for managing customer data, tracking interactions, and streamlining workflows. This comprehensive approach to customer interaction management fosters efficiency and improved customer experiences.
Types of Operational CRM Systems
Operational CRM systems encompass various modules designed to manage different facets of customer interaction. Key types include sales force automation, marketing automation, and service automation. Each of these specialized modules provides tailored tools to optimize specific business processes.
Sales Force Automation (SFA)
Sales force automation systems empower sales teams to manage leads, track sales opportunities, and close deals more efficiently. These systems typically provide tools for lead qualification, contact management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting. SFA systems facilitate a centralized view of customer interactions, streamlining communication and improving sales team productivity.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation tools assist in automating marketing campaigns and nurturing leads. These tools streamline tasks such as email marketing, social media management, and lead generation. They help to personalize customer interactions, improve marketing campaign effectiveness, and enhance customer engagement.
Service Automation
Service automation systems are designed to manage customer service requests and inquiries. These systems facilitate the automation of tasks such as ticket management, knowledge base access, and customer self-service portals. They contribute to improved customer satisfaction and reduced response times for customer service inquiries.
Comparison of Operational CRM System Types
| System Type | Features | Benefits | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Force Automation (SFA) | Lead management, opportunity tracking, contact management, sales forecasting | Increased sales productivity, improved lead conversion rates, enhanced sales forecasting accuracy | Managing sales pipelines, tracking sales opportunities, generating sales reports |
| Marketing Automation | Email marketing, social media management, lead nurturing, campaign management | Improved marketing campaign effectiveness, increased lead generation, enhanced customer engagement | Automating marketing campaigns, segmenting audiences, personalizing customer interactions |
| Service Automation | Ticket management, knowledge base access, customer self-service portals, issue resolution | Reduced response times, improved customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs | Managing customer support inquiries, resolving customer issues, providing self-service options |
Common Software Solutions for Operational CRM
Several software solutions are available for operational CRM. Popular choices include Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, and SugarCRM. These platforms provide a comprehensive suite of tools to manage various aspects of customer interaction. Choosing the right software depends on the specific needs and resources of the organization.
- Salesforce: A comprehensive platform with a wide range of features for sales, marketing, and service automation.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A suite of applications that integrates CRM functionality with other business applications.
- HubSpot: A popular choice for small and medium-sized businesses, providing marketing, sales, and service automation tools.
- Zoho CRM: A cloud-based CRM platform offering a wide range of features for various business sizes.
- SugarCRM: An open-source platform offering flexibility and customization options.
Benefits of Implementing Operational CRM
Operational CRM systems offer substantial advantages for businesses seeking to streamline their processes and enhance customer relationships. By automating key interactions and providing a unified view of customer data, these systems unlock significant opportunities for improved efficiency and profitability. These benefits translate directly into tangible improvements in business performance.
Improved Business Processes
Operational CRM systems automate various tasks, such as lead qualification, sales order processing, and customer service interactions. This automation reduces manual effort and minimizes errors, resulting in more efficient and accurate business operations. Streamlined workflows improve response times to customer inquiries, leading to quicker resolutions and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Customer Relationships
These systems provide a centralized view of customer interactions, enabling businesses to personalize interactions and offer tailored services. By understanding customer preferences and purchase history, businesses can develop more effective marketing campaigns and provide targeted product recommendations. This personalized approach fosters stronger customer relationships and loyalty.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automation of tasks like data entry and order processing frees up personnel to focus on higher-value activities. This increased efficiency leads to significant productivity gains across the organization. By streamlining processes and eliminating redundancies, operational CRM systems improve overall operational efficiency.
Quantifiable Benefits
Operational CRM systems often yield substantial quantifiable benefits. For instance, improved lead qualification processes can increase sales conversion rates, leading to a direct increase in revenue. Streamlined order processing reduces errors and delays, lowering operational costs. A well-implemented system can demonstrably reduce the time required to fulfill customer orders, boosting customer satisfaction. A common example is a retail company that saw a 15% increase in sales after implementing an operational CRM system that effectively tracked customer preferences and purchasing history, leading to more targeted marketing campaigns.
Reduced costs from streamlined processes are also demonstrable benefits.
Return on Investment (ROI)
The ROI associated with operational CRM implementations varies depending on the specific system, business size, and industry. However, the potential returns are often substantial. A well-structured ROI analysis should take into account factors such as cost savings from reduced errors, increased sales revenue, and improved customer satisfaction. Here’s a table demonstrating a potential ROI scenario:
| Year | Cost Savings | Increased Revenue | Total Benefit | ROI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $10,000 | $20,000 | $30,000 | 30 |
| 2 | $15,000 | $30,000 | $45,000 | 45 |
| 3 | $20,000 | $40,000 | $60,000 | 60 |
Note: This table represents a hypothetical example. Actual ROI will depend on specific business circumstances.
Challenges of Implementing Operational CRM
Implementing an operational CRM system, while offering significant benefits, presents various challenges. These range from technical hurdles to organizational adjustments, demanding careful planning and execution. Success hinges on proactively identifying and mitigating these obstacles.Operational CRM implementations often face unforeseen difficulties. A well-defined strategy that anticipates potential issues is crucial for a smooth transition and optimal results. Careful consideration of technical, organizational, and change management aspects is essential for a successful deployment.
Technical Difficulties and Integration Issues
Careful planning is essential for the smooth integration of new CRM systems with existing infrastructure. Incompatible data formats, outdated software versions, and a lack of technical expertise can lead to significant problems. Data migration, a crucial step, can be complex, demanding significant time and resources. Ensuring data accuracy and integrity throughout the process is paramount. Poorly designed interfaces and a lack of user-friendly functionalities can decrease adoption rates and increase frustration among employees.
Ensuring seamless integration with existing systems, including legacy systems, is essential for a successful deployment. This may involve custom coding, third-party integrations, or significant data mapping efforts. Furthermore, issues with scalability, performance, and security need to be addressed before and during implementation.
Organizational Challenges
Implementing a new CRM system often requires a shift in organizational workflows and processes. Resistance to change among employees, insufficient training, and inadequate support structures can hinder adoption. Effective communication, clear training materials, and a well-structured change management plan are critical. Identifying and addressing potential roles and responsibilities within the new system is crucial for organizational alignment.
A lack of buy-in from management can significantly impact the success of the project. Moreover, the CRM system must align with existing business strategies and goals to ensure maximum efficiency and impact.
Change Management Strategies
Effective change management is paramount for successful CRM implementation. A comprehensive plan that addresses employee concerns and fosters a positive attitude towards the new system is critical. Training programs must be tailored to the specific needs of different user groups and provide ample opportunities for hands-on practice. Open communication channels, regular feedback sessions, and dedicated support resources are all essential components of a successful change management strategy.
Building a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability is essential for sustained use of the new system.
Implementation Strategies Comparison
Different implementation strategies offer varying degrees of risk and reward. A phased approach, where the system is rolled out incrementally to different departments or user groups, can minimize disruption. A big bang approach, deploying the system to all users simultaneously, may be faster but carries greater risk. A hybrid approach combines elements of both, offering a balance between speed and control.
- Phased Approach: This approach involves deploying the CRM system in stages, typically starting with a pilot group before a broader rollout. It allows for testing and refinement before full implementation, minimizing potential risks and disruptions. However, it can be slower and more complex than a big bang approach.
- Big Bang Approach: This involves deploying the CRM system to all users at once. While it can be quicker, it also carries a higher risk of widespread disruption and user resistance. This approach often demands robust training and support mechanisms.
- Hybrid Approach: This approach combines elements of both phased and big bang approaches. It allows for a balance between controlled rollout and speed of implementation, making it a suitable option for organizations seeking to minimize disruption while accelerating the adoption process.
Potential Pitfalls and Mitigation Strategies
| Potential Pitfall | Mitigation Strategy ||—|—|| Data migration issues | Employ robust data validation and cleansing processes. Conduct thorough testing and data mapping before migration. || Resistance to change | Implement a comprehensive change management plan. Offer extensive training and support. || Lack of user adoption | Design user-friendly interfaces.
Provide ongoing support and training. || Integration challenges | Conduct thorough testing and planning before integration. Utilize third-party tools or expert consultants for support. || Inadequate resources | Allocate sufficient resources, including budget, personnel, and time, to the project. |
Key Components and Features
Operational CRM systems are crucial for businesses aiming to foster strong customer relationships. These systems leverage technology to manage and enhance interactions with customers across various touchpoints, from initial contact to ongoing support. A well-designed operational CRM system streamlines processes, enabling businesses to efficiently manage customer data and interactions, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.Operational CRM systems are multifaceted, encompassing several key components and features.
These elements work together to create a comprehensive platform for managing customer interactions and data, driving efficiency and improved customer relationships. Effective data collection, storage, and analysis are essential for gaining insights into customer behavior and preferences. Automation plays a vital role in streamlining tasks, freeing up resources for more strategic initiatives. Integration with other business systems is crucial for a holistic view of customer interactions.
User-friendly interfaces and intuitive experiences are paramount to ensure smooth adoption and user satisfaction.
Essential Components
Operational CRM systems rely on several key components to function effectively. These components include customer relationship management (CRM) databases, contact management tools, sales force automation (SFA) tools, marketing automation tools, and service automation tools. These components are interconnected, working together to provide a unified view of the customer and enable streamlined processes.
Data Management
Effective data collection, storage, and analysis are paramount to understanding customer behavior and preferences. CRM systems collect data from various sources, including customer interactions, purchase history, and demographics. This data is stored securely and systematically, allowing for detailed analysis and reporting. Advanced analytics tools can identify trends, patterns, and customer segments, enabling businesses to personalize interactions and tailor marketing campaigns.
For instance, a retailer might use data analysis to identify customers who frequently purchase specific product categories, enabling targeted promotions and personalized recommendations.
Automation
Automation plays a crucial role in streamlining operational processes within a CRM system. Automating tasks such as data entry, email marketing, and lead qualification frees up employees to focus on more complex and strategic tasks. For example, automated email sequences can nurture leads, while automated responses to common customer inquiries can improve support efficiency. Automation not only increases efficiency but also reduces errors, ensuring consistency in customer interactions.
System Integration
Integration with other business systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, is essential for a holistic view of the customer. This integration allows for a seamless flow of information between different departments, providing a comprehensive view of the customer’s history and interactions. For instance, an ERP system can provide real-time inventory information, enabling accurate order fulfillment and personalized recommendations.
This integration ensures that all departments have access to the same customer data, fostering better collaboration and improved decision-making.
User Interface and User Experience
User-friendly interfaces and positive user experiences are critical to ensure CRM system adoption and usage. A well-designed UI and UX make the system intuitive and easy to navigate, minimizing training time and maximizing user engagement. Clear dashboards, intuitive navigation, and customizable features contribute to a seamless user experience. Modern CRM systems often incorporate mobile applications, allowing users to access and manage customer interactions from anywhere.
Interplay of Components
| Component | Description | Interaction with Other Components |
|---|---|---|
| CRM Database | Stores and manages customer data | Provides data for contact management, sales force automation, marketing automation, and service automation. |
| Contact Management | Tracks and manages customer interactions | Integrates with CRM database for comprehensive customer profiles and interactions. |
| Sales Force Automation | Automates sales processes | Integrates with CRM database for lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting. |
| Marketing Automation | Automates marketing campaigns | Leverages CRM data for targeted campaigns and personalized messaging. |
| Service Automation | Automates service processes | Integrates with CRM database to track customer issues and resolve problems efficiently. |
Operational CRM in Different Industries
Operational CRM systems are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Their effectiveness hinges on tailoring features and functionalities to the specific needs of each industry. This involves understanding unique customer interactions, sales processes, and support requirements. This adaptation allows businesses to maximize the benefits of CRM and improve customer relationships.
Application Across Industries
Operational CRM systems find widespread application across diverse industries, each with its own nuances. Retail, healthcare, and finance, for instance, all have distinct customer interaction patterns, demanding specific CRM adaptations. Understanding these variations is crucial for successful implementation and optimal ROI.
Tailoring to Industry Needs
CRM systems are designed to be adaptable. In retail, CRM might focus on inventory management, customer segmentation, and targeted marketing campaigns. Healthcare CRM could prioritize patient records management, appointment scheduling, and communication with medical staff. Financial institutions might emphasize customer relationship management, risk assessment, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Successful Implementations
Numerous successful CRM implementations demonstrate the value of tailored solutions. A retail company might use CRM to track customer preferences, personalize offers, and predict future needs. In healthcare, a CRM system could streamline patient data, optimize appointment scheduling, and improve communication between doctors and patients. A financial institution might leverage CRM to manage customer accounts, track transactions, and provide personalized financial advice.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Successful operational CRM implementations demonstrably enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. By providing personalized experiences, streamlined processes, and efficient communication channels, CRM systems contribute to customer retention and advocacy. Retailers, for instance, see increased repeat business through personalized offers and promotions.
Industry-Specific Requirements Shaping Design
Industry-specific requirements significantly influence CRM design. Regulatory compliance is a prime example. Financial institutions must adhere to strict regulations when handling customer data. Similarly, healthcare organizations are bound by HIPAA regulations. These factors necessitate tailored CRM systems that address these mandates and facilitate compliance.
Comparison of Operational CRM Features Across Industries
| Industry | Customer Segmentation | Sales Force Automation | Service Automation | Marketing Automation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Based on purchase history, demographics, and online behavior | Managing sales processes, tracking leads, and generating reports | Handling customer inquiries, managing returns, and providing support | Personalized email campaigns, targeted advertising, and promotional offers |
| Healthcare | Based on patient demographics, medical history, and treatment needs | Scheduling appointments, managing patient records, and tracking treatments | Managing patient inquiries, scheduling follow-up appointments, and handling billing | Sending appointment reminders, managing medical records, and tracking patient outcomes |
| Finance | Based on financial history, risk profile, and investment preferences | Managing accounts, tracking transactions, and providing financial advice | Handling customer inquiries, resolving disputes, and providing account support | Sending personalized financial advice, managing investments, and providing market updates |
Future Trends in Operational CRM
Operational CRM systems are constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the ever-increasing demands of modern businesses. These systems are becoming more sophisticated and integrated, enabling companies to gain a deeper understanding of their customers and deliver more personalized experiences. This evolution hinges on emerging trends, particularly the adoption of AI, cloud-based solutions, and mobile technology, alongside a growing emphasis on data security.The future of operational CRM is characterized by a more sophisticated approach to customer interaction and management.
This involves leveraging advanced technologies to automate tasks, personalize interactions, and ultimately, drive customer loyalty and business growth. The integration of AI and ML is a key component of this shift, enabling systems to analyze vast amounts of customer data and provide actionable insights.
AI and Machine Learning in Operational CRM
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing operational CRM by automating tasks, enhancing personalization, and providing predictive insights. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. Machine learning algorithms can analyze customer data to identify patterns and predict future behaviors, enabling targeted marketing campaigns and proactive customer support. For example, a company can use AI to anticipate customer churn based on purchase history and engagement metrics, enabling them to proactively reach out and retain valuable customers.
Cloud-Based Solutions and Operational CRM
Cloud-based CRM solutions are transforming the landscape by providing accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Companies can access their CRM data from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and global collaboration. Cloud solutions often offer greater scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust their CRM capacity to meet fluctuating demands. The inherent cost-effectiveness of cloud-based solutions makes them an attractive option for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to streamline operations and reduce IT overhead.
Many businesses have successfully migrated their CRM systems to the cloud, experiencing significant improvements in accessibility and scalability.
Mobile Technology and Customer Interactions
Mobile technology is transforming customer interactions by providing convenient access to information and support. Mobile apps allow customers to manage their accounts, track orders, and access customer support anytime, anywhere. This accessibility enhances customer satisfaction and engagement. A company can utilize mobile technology to provide customers with personalized recommendations based on their purchase history, enhancing the overall customer experience.
For example, a retail company can use a mobile app to offer personalized coupons and promotions, driving in-store traffic and sales.
Data Security and Privacy in Operational CRM
Data security and privacy are paramount in modern operational CRM systems. Protecting sensitive customer data from breaches is crucial for maintaining customer trust and avoiding regulatory penalties. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular audits, are essential. Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, is vital to maintain customer trust and avoid legal issues.
A robust security framework, including data encryption, access control, and regular audits, is critical to protecting customer data and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Anticipated Developments and Potential Impact
| Anticipated Development | Potential Impact on Businesses |
|---|---|
| Increased automation of tasks | Improved efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer service response times |
| Enhanced personalization of customer experiences | Increased customer satisfaction, improved customer retention, and targeted marketing campaigns |
| Greater integration with other business systems | Improved data flow, enhanced decision-making, and more holistic view of customer interactions |
| Enhanced security and data privacy | Increased customer trust, reduced risk of data breaches, and improved compliance with regulations |
| Focus on ethical AI practices | Improved customer trust, reduced bias in algorithms, and increased transparency in decision-making |
Final Summary
In conclusion, operational CRM systems offer significant advantages for businesses seeking to optimize customer interactions and boost productivity. While implementation may present challenges, careful planning and strategic execution can yield substantial returns. The future of operational CRM is bright, with continued innovation in areas like AI and cloud-based solutions. This guide provides a solid foundation for understanding and leveraging these powerful tools.
Popular Questions
What are some common integration issues when implementing operational CRM?
Integration issues can arise when existing systems lack compatibility with the new CRM. Data migration and ensuring consistent data formats across different platforms can also be challenging. Furthermore, training staff on the new processes and workflows is crucial to a successful implementation.
How can businesses measure the ROI of operational CRM implementations?
Quantifiable benefits include increased sales, reduced customer service costs, and improved customer retention rates. Tracking key metrics like conversion rates, customer lifetime value, and average handle time can help demonstrate the return on investment.
What are some examples of industry-specific customizations for operational CRM systems?
In retail, CRM systems might emphasize inventory management and personalized recommendations. Healthcare systems could focus on patient records and appointment scheduling. Finance systems might prioritize risk assessment and compliance with regulations.
What are the key differences between sales force automation, marketing automation, and service automation within operational CRM?
Sales force automation focuses on streamlining the sales process, marketing automation targets customer acquisition and engagement, and service automation optimizes customer support and issue resolution. Each component plays a unique role in the overall customer journey.