Small businesses often face unique challenges in managing customer relationships. This guide delves into the realm of CRM (Customer Relationship Management) solutions, specifically tailored for small enterprises. We’ll explore how implementing a CRM can revolutionize communication, streamline sales, and ultimately, boost profitability.
From choosing the right software to nurturing customer relationships, this comprehensive resource covers every aspect of CRM implementation for small businesses. Understanding the nuances of various CRM types, essential features, and successful integration strategies is crucial for maximizing ROI.
Introduction to CRM for Small Businesses
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is a powerful tool that helps small businesses manage their interactions with customers. Essentially, it’s a centralized database that stores information about prospects, customers, and interactions, allowing businesses to track and manage customer relationships more effectively. This can be especially beneficial for businesses with a growing customer base, allowing them to easily access and organize important information.Using a CRM system can significantly improve customer service by enabling businesses to quickly access customer history, preferences, and previous interactions.
This knowledge allows for personalized and efficient support, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. Streamlined sales processes are another key benefit. CRMs track leads, manage sales pipelines, and automate tasks like follow-ups and reporting, ultimately leading to higher conversion rates and improved efficiency.
Benefits of CRM for Small Businesses
Implementing a CRM system offers several key advantages for small businesses. Improved customer service is a primary benefit, as access to comprehensive customer information enables personalized interactions. This leads to higher satisfaction and stronger customer relationships. Sales processes also benefit from streamlined workflows. Tracking leads, managing sales pipelines, and automating tasks like follow-ups and reporting can lead to improved efficiency and increased conversion rates.
Common Challenges in Implementing CRM
Small businesses may encounter several challenges when implementing CRM systems. One common hurdle is the perceived complexity of the system. While a CRM system can be sophisticated, many solutions are tailored for small businesses with user-friendly interfaces. Data migration from existing systems can also be challenging, but careful planning and data cleansing can mitigate this. Resistance to change among employees may occur; however, training and demonstrating the benefits of the system can help address these concerns.
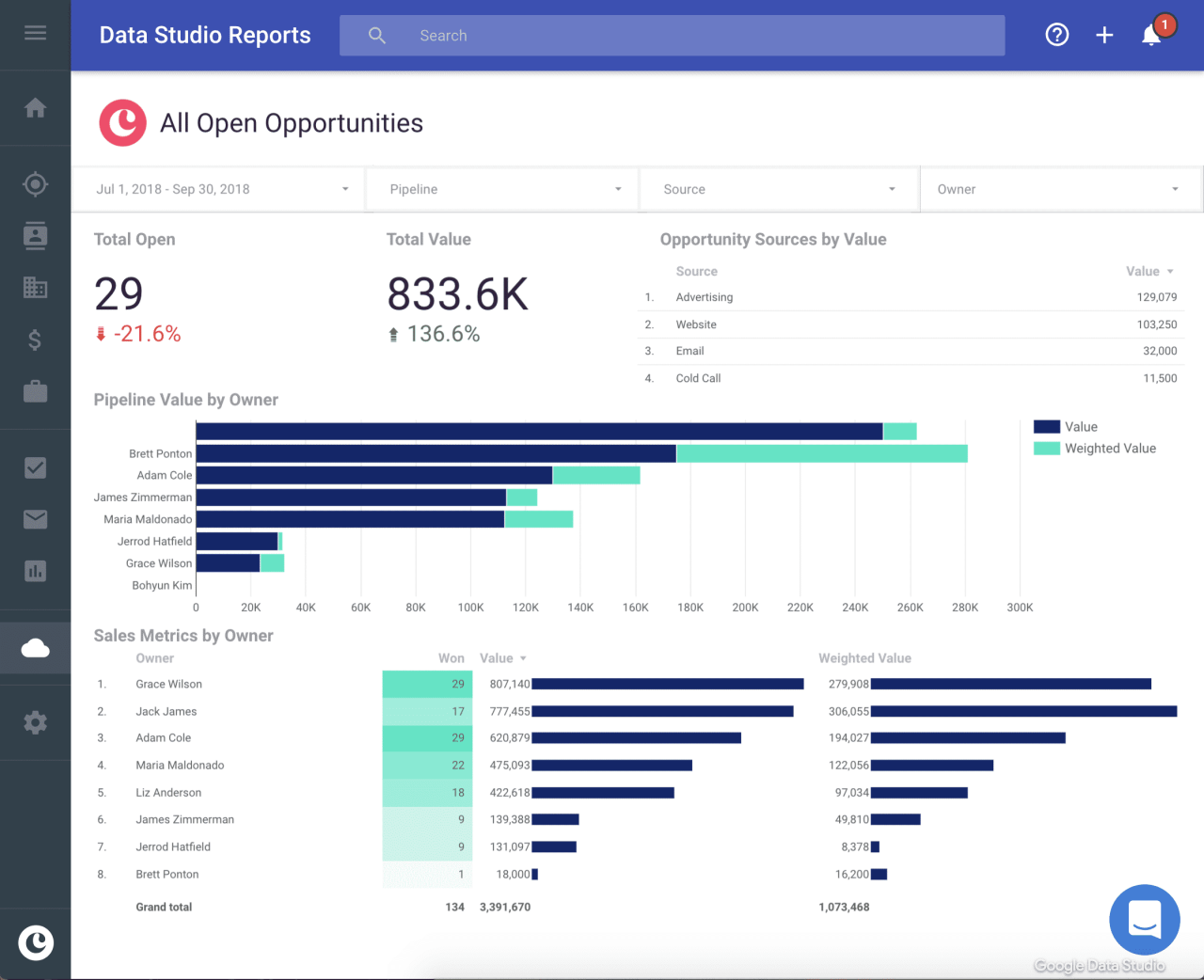
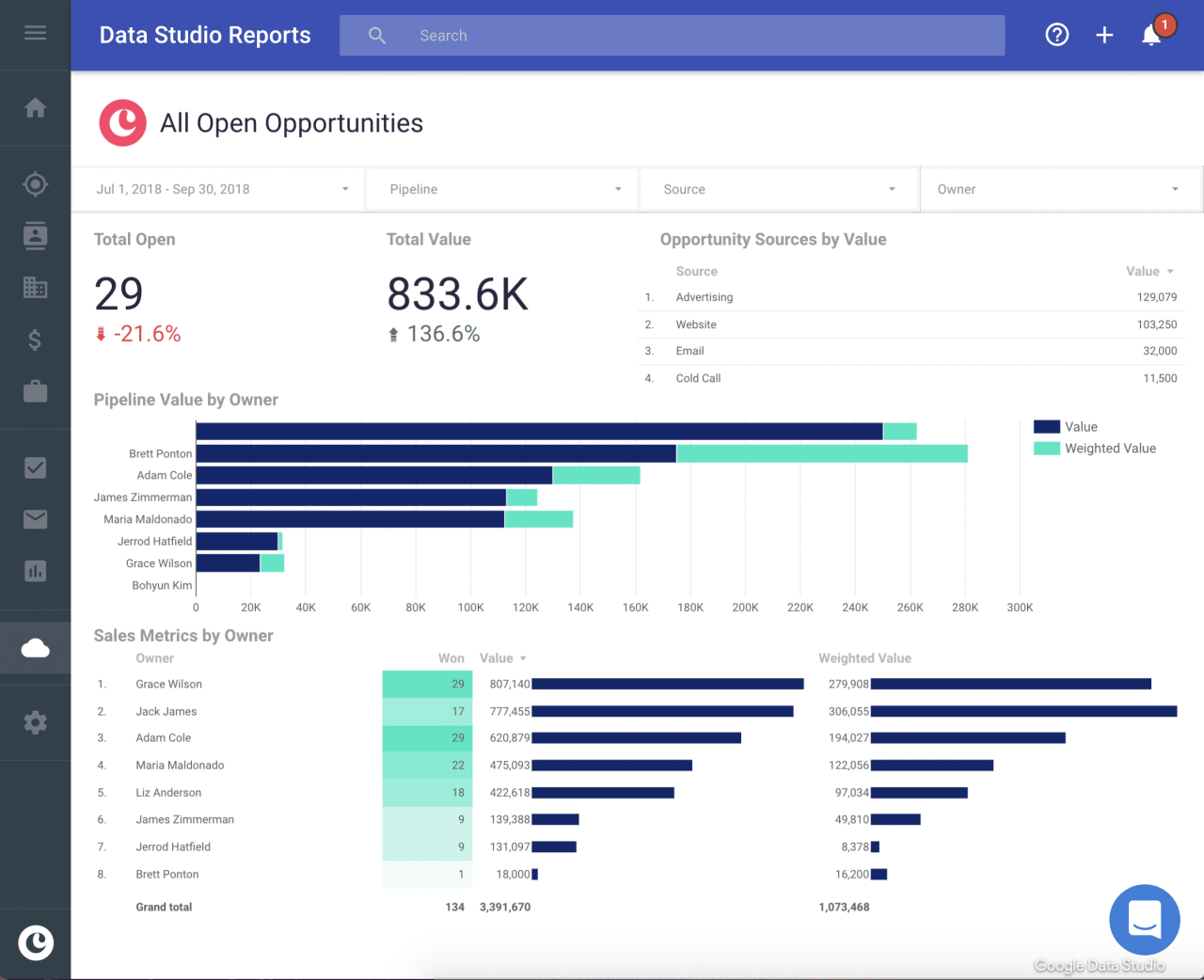
Illustrative Diagram of CRM Impact
The following diagram demonstrates how a CRM system can improve communication and data flow within a small business.
| Stage | Without CRM | With CRM |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Inquiry | Information scattered across emails, notes, and spreadsheets. Difficult to track the full history of interactions with a specific customer. | All customer interactions are recorded in a central database. Quick access to the complete customer history, including purchase history, support tickets, and communication logs. |
| Sales Process | Sales data is fragmented, making it hard to track progress and identify bottlenecks. Follow-up processes are often manual and inconsistent. | Leads are tracked through the sales pipeline. Automated follow-ups and reminders ensure timely communication. Sales team access to comprehensive data allows for more effective decision making. |
| Customer Support | Support requests are handled individually, potentially resulting in inconsistent responses and difficulty accessing previous interactions. | Support agents have access to a central repository of customer information, allowing for faster and more effective resolution of issues. |
This diagram visually represents how CRM centralizes customer data, improving communication and data flow across various departments within a small business.
Types of CRM Software for Small Businesses
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for small businesses aiming to streamline their operations and boost customer relationships. Different types of CRM software cater to varying needs and budgets, and understanding their characteristics is essential for making an informed decision. This section explores the diverse options available, highlighting their unique features and suitability for small business contexts.
Comparing CRM Software Types
Various CRM software deployment models cater to diverse small business needs. The choice often depends on factors such as budget, technical expertise, and the level of customization required. Different models offer varying degrees of control and flexibility.
| CRM Type | Pricing | Features | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-Based | Typically subscription-based, ranging from free to premium tiers. | Scalable, accessible from anywhere with internet connectivity, often with robust reporting and analytics tools. | Generally user-friendly, requiring minimal technical expertise. |
| On-Premise | One-time purchase cost plus ongoing maintenance fees. | Provides complete control and customization, allowing for integration with existing systems. | May require IT expertise for installation and maintenance. |
| Open-Source | Generally free, with potential for customization and integration. | Offers high levels of customization and flexibility, often requiring more technical expertise. | Can range from very easy to moderately difficult depending on the specific software. |
Key Features of Each CRM Type
Cloud-based CRMs excel in their accessibility and scalability, ideal for businesses needing to expand quickly. On-premise solutions offer tailored control for businesses with specific data security or integration requirements. Open-source CRMs provide maximum flexibility, but often demand greater technical expertise.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each CRM Type
Cloud-based CRMs offer accessibility, scalability, and often a more user-friendly interface. However, data security and dependence on internet connectivity can be potential drawbacks. On-premise CRMs offer complete control and data security, but require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Open-source CRMs provide the most customization options, but may demand more technical expertise and have a higher learning curve.
CRM Software Options
The market offers various CRM software options to suit different needs and budgets. Free or freemium solutions often provide a starting point for small businesses, while paid options offer more comprehensive features.
| CRM Software | Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zoho CRM | Cloud-Based | Comprehensive features, user-friendly interface, affordable pricing tiers. | Limited customization options compared to on-premise solutions. |
| Salesforce | Cloud-Based | Highly scalable, robust reporting, extensive integrations. | Can be expensive, especially for small businesses with limited needs. |
| Freshsales | Cloud-Based | Excellent for sales teams, intuitive interface, affordable. | May lack advanced features for complex businesses. |
| HubSpot CRM | Cloud-Based | Free plan with essential features, powerful marketing tools, integrates with other HubSpot tools. | Free plan might have limited storage. |
| Open CRM | Open-Source | Highly customizable, potentially cost-effective in the long run. | Requires significant technical expertise, may have limited support resources. |
Key Features of Effective CRMs for Small Businesses
A robust CRM system is crucial for small businesses to manage their interactions with customers effectively. By streamlining processes and centralizing data, CRMs empower small business owners to focus on growth and customer satisfaction. This allows for better organization and a more proactive approach to sales and customer service.A well-designed CRM system provides a single source of truth for all customer information, eliminating the need to juggle disparate spreadsheets and databases.
This streamlined approach to data management translates to better decision-making and more targeted marketing efforts.
Contact Management
Effective contact management is fundamental to any successful CRM. A good CRM system should allow for detailed profiles of each customer, encompassing contact information, purchase history, communication preferences, and any other relevant details. This comprehensive view of the customer allows businesses to tailor their interactions and offers, ultimately fostering stronger customer relationships. For example, knowing a customer prefers email communication allows the business to focus its marketing efforts accordingly.
Sales Tracking
Sales tracking is vital for understanding sales performance and identifying areas for improvement. A CRM should facilitate the tracking of leads, opportunities, and sales deals, providing insights into the sales pipeline. This feature enables businesses to monitor the progress of deals, forecast future sales, and identify potential bottlenecks in the sales process. For example, a CRM can track the stages of a sales deal from initial contact to final close, enabling businesses to analyze where potential delays occur and make necessary adjustments.
Customer Service Tools
Modern CRMs integrate robust customer service tools, empowering businesses to respond promptly to customer inquiries and resolve issues efficiently. This includes features like ticketing systems, email integration, and knowledge bases. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also reduces response times and streamlines the overall customer service process. For example, a customer service ticket system can track the status of each issue, ensuring timely resolution and preventing issues from piling up.
Communication Enhancements
CRMs can significantly enhance communication within a small business. These systems often integrate with various communication channels like email, phone, and messaging apps. This consolidated approach to communication streamlines the flow of information and ensures that important updates and messages are not missed. The system allows for better collaboration among team members and ensures everyone has access to the most up-to-date information.
For example, a sales representative can instantly see all previous interactions with a potential customer, helping them tailor their approach and maintain consistency.
Marketing Capabilities
Effective CRMs offer robust marketing capabilities. These systems allow for targeted marketing campaigns based on customer segmentation and preferences. This personalized approach to marketing maximizes the impact of campaigns, increasing engagement and conversion rates. Features like automated email marketing and campaign tracking provide a more efficient and effective way to manage marketing efforts. For instance, segmenting customers by purchase history allows for the delivery of targeted promotions and special offers.
Data Analysis
A CRM system should empower data analysis within a small business. Data analysis tools allow for the extraction of valuable insights from customer interactions, sales performance, and marketing campaigns. This analysis allows businesses to make informed decisions about product development, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns. For example, analyzing sales data across different customer segments helps identify the most profitable customer groups, allowing for more focused sales efforts.
Improved Sales Efficiency
CRMs improve sales efficiency by streamlining the sales process and automating tasks. These systems often include features like lead scoring, sales forecasting, and automated follow-up emails. This automated process ensures that leads are nurtured effectively, and sales representatives can focus on high-value opportunities. For instance, lead scoring helps prioritize leads based on their likelihood of converting, enabling sales representatives to focus on the most promising prospects.
Implementing a CRM System in a Small Business
Implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system in a small business can significantly improve efficiency and profitability. A well-chosen and effectively utilized CRM can streamline customer interactions, automate tasks, and provide valuable insights into customer behavior. However, successful implementation requires careful planning and execution.Implementing a CRM is not a one-size-fits-all process. The steps involved need to be tailored to the specific needs and resources of the small business.
Careful consideration of each stage, from initial assessment to ongoing training, is crucial for maximizing the benefits of the CRM system.
Assessing Business Needs and Resources
Before selecting a CRM, a thorough assessment of the business’s current processes and resources is essential. This assessment helps determine the specific needs and limitations, ensuring the chosen CRM system aligns with the company’s objectives and capabilities. Consider factors such as the size of the sales team, the volume of customer interactions, and the complexity of the existing database.
This detailed analysis will help identify the most suitable CRM solution.
Selecting the Right CRM System
Selecting the right CRM system is a critical step. This process should involve a thorough evaluation of various available options. Consider factors such as the system’s features, pricing, scalability, and ease of use. Evaluate different CRM providers, considering their customer support and the overall reputation within the industry. Look for systems that offer integrations with existing software, such as accounting or email platforms.
Employee Training and Onboarding
Comprehensive training is crucial for successful CRM adoption. A structured training program should be implemented to equip employees with the necessary skills to use the system effectively. This includes demonstrations of key features, hands-on practice, and access to readily available resources like online tutorials and FAQs. Regular follow-up sessions and ongoing support can help employees overcome challenges and utilize the system to its full potential.
Data Migration and System Integration
Migrating data and integrating the CRM with existing systems is a critical aspect of the implementation process. Careful planning and execution are essential to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition. A well-defined migration plan should Artikel the steps involved, including data cleansing and verification to maintain data integrity. The integration process should consider how the CRM will interact with existing platforms, such as accounting software or email marketing tools.
A phased approach to integration can reduce potential errors and maintain operational efficiency during the transition. This ensures data consistency and minimizes the risk of information loss.
Measuring CRM Success for Small Businesses
A properly implemented CRM system can significantly boost a small business’s efficiency and profitability. However, simply installing the software isn’t enough; it’s crucial to track key metrics to understand its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This process allows businesses to fine-tune their CRM strategy and optimize its return on investment.Effective CRM measurement goes beyond basic data collection.
It involves a deep dive into the data, looking for patterns, trends, and insights that reveal how the CRM is supporting business goals. This data-driven approach allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to the ever-changing business landscape.
Key Metrics for Sales Efficiency
Understanding sales efficiency within a CRM is vital. Tracking these metrics provides a clear picture of how well the CRM is supporting the sales process.
- Sales Cycle Length: Monitoring the time it takes to close a deal from initial contact to finalization. A shorter sales cycle often indicates more efficient sales processes. For example, a company transitioning from a manual process to a CRM-driven system might see a reduction in the sales cycle from 60 days to 45 days.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads that convert into customers. A higher conversion rate suggests effective lead nurturing and qualification strategies facilitated by the CRM.
- Average Deal Size: The average revenue generated per sale. Analyzing this metric can highlight opportunities to upsell or cross-sell to existing customers, which a CRM system can facilitate by providing comprehensive customer profiles.
- Sales Team Performance: Tracking individual and team performance against sales targets. This can reveal areas where additional training or support might be needed.
Metrics for Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is crucial for long-term business success. A CRM system can be a powerful tool to enhance customer relationships.
- Customer Retention Rate: The percentage of customers who remain loyal to the business over a period. A high retention rate suggests a strong customer relationship management strategy, potentially improved by the CRM.
- Customer Feedback: Gathering feedback from customers through surveys, reviews, or direct communication. This feedback provides valuable insights into areas for improvement.
- Customer Support Resolution Time: The time taken to resolve customer issues. A CRM system can help streamline customer support by centralizing customer information and facilitating communication.
CRM Performance Dashboard Examples
Dashboards provide a visual representation of key performance indicators (KPIs).
- A sales dashboard might display key metrics such as sales cycle length, conversion rate, and average deal size. This allows sales teams to identify areas of strength and weakness in real-time.
- A customer support dashboard could show metrics like resolution time, customer satisfaction scores, and customer churn rate. This allows support teams to address customer issues promptly and proactively.
CRM Performance Report Template
A structured report template is essential for tracking CRM performance over time.
| Metric | Target | Actual | Variance | Action Items |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Cycle Length | 30 days | 35 days | +5 days | Review sales process and identify bottlenecks. |
| Conversion Rate | 15% | 10% | -5% | Enhance lead qualification and nurturing strategies. |
| Customer Retention Rate | 85% | 80% | -5% | Improve customer service and communication. |
Integration and Data Management
Integrating a CRM with existing business software streamlines workflows and avoids data silos. Effective data management is crucial for accurate reporting, insightful decision-making, and ultimately, improved business performance. This section details how to seamlessly integrate your CRM with your existing systems and maintain a robust data management strategy.A well-integrated CRM system, synchronized with your accounting software, email marketing platform, and other crucial tools, creates a unified view of your customers.
This unified view, enriched by accurate and consistently updated data, empowers informed decisions across all departments.
Integrating CRM with Existing Software
Integrating a CRM with existing business software like accounting packages and email marketing platforms is essential for a streamlined workflow. This integration eliminates manual data entry and ensures consistency across different systems. Consider using APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to facilitate seamless data exchange between applications. Look for CRM solutions that offer pre-built integrations with common business software or those that allow for custom integrations through APIs.
For example, a CRM might directly import sales data from your accounting system, reducing errors and updating customer records in real-time.
Best Practices for Customer Data Management
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date customer data is critical for a successful CRM implementation. Implement clear data entry procedures to ensure consistency and accuracy. Establish roles and responsibilities for data entry and update to prevent errors and inconsistencies. Regular data audits can identify and resolve discrepancies. For example, a clear process for updating customer contact information after a move will prevent outdated data from affecting marketing campaigns and sales follow-ups.
Data Security and Privacy for Small Businesses
Data security and privacy are paramount for any business, especially those handling sensitive customer information. Implement robust security measures, such as strong passwords, access controls, and data encryption, to protect customer data from unauthorized access. Comply with relevant data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) to ensure you are handling customer data responsibly. Employ regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
For example, encrypting sensitive customer financial data and limiting access to specific personnel is crucial.
Data Backups and Recovery Procedures
Regular data backups and recovery procedures are essential to mitigate the risk of data loss due to system failures, cyberattacks, or human errors. Establish a backup schedule and ensure regular backups are performed. Store backups offsite to protect against localized disasters. Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to restore data quickly in case of an incident. Regular testing of backup and recovery procedures is vital.
For instance, regularly backing up your CRM data to a cloud storage service ensures data protection even in the event of a server crash.
Future Trends in CRM for Small Businesses
The landscape of CRM technology is constantly evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities for small businesses. Understanding emerging trends allows small business owners to strategically adapt and leverage these advancements to optimize customer relationships and drive growth. This section explores key future directions in CRM for small businesses, focusing on innovations, potential challenges, and the anticipated role of AI.The future of CRM for small businesses hinges on its ability to integrate seamlessly with existing operations and provide actionable insights.
Innovative features are crucial to enhancing efficiency and effectiveness, enabling small businesses to compete effectively in a dynamic market. The trend is towards more user-friendly, intuitive systems that reduce the learning curve and minimize the need for extensive technical support.
Emerging CRM Technology Trends
Small businesses are increasingly seeking CRM solutions that address their specific needs, often involving integrations with existing accounting software, inventory management systems, and e-commerce platforms. This trend highlights the importance of adaptable and flexible CRM systems. Furthermore, the rise of cloud-based solutions offers enhanced accessibility and scalability, enabling businesses to adapt to fluctuating needs without significant infrastructure investments.
Innovative CRM Features
Several innovative features are likely to emerge in CRM software for small businesses. These include AI-powered lead scoring and qualification, automated appointment scheduling, and advanced customer segmentation based on real-time data analysis. Additionally, predictive analytics features will help anticipate customer needs and tailor marketing strategies for optimal results.
AI’s Role in Small Business CRM
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to play an increasingly important role in CRM systems for small businesses. AI-driven chatbots can provide instant customer support, handle routine inquiries, and free up human agents for more complex issues. AI can also analyze customer interactions to identify patterns and predict future behavior, enabling businesses to proactively address potential problems and enhance customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the adoption of these trends offers significant opportunities, potential challenges exist. Data privacy concerns, security vulnerabilities, and the need for skilled personnel to manage and interpret AI-driven insights are key considerations. The ability to effectively leverage these new tools will depend on a business’s capacity to adapt, invest in training, and prioritize data security.
Example of Future CRM Capabilities
Consider a scenario where a small e-commerce business utilizes AI-powered CRM to automatically categorize customer interactions based on product interest. This allows the business to personalize marketing campaigns, recommend relevant products, and proactively address potential customer issues before they escalate. This tailored approach improves customer experience and significantly boosts sales conversions. Further advancements may involve the integration of augmented reality (AR) for virtual product demonstrations or personalized experiences within the CRM platform.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, CRM for small businesses is no longer a luxury but a necessity. This guide has provided a roadmap for navigating the complexities of CRM implementation, offering insights into choosing the right software, maximizing its features, and effectively measuring its success. By understanding and applying the strategies Artikeld, small businesses can enhance customer relationships, optimize processes, and propel their growth trajectory.
Common Queries
What are the common challenges small businesses face when implementing CRM systems?
Small businesses often struggle with budget constraints, limited resources, and a lack of technical expertise. Training employees to use the new system and integrating it with existing software can also pose difficulties. Data migration and maintaining data security are also crucial factors.
What are some free or freemium CRM options available?
Several reputable CRM providers offer free or freemium plans with essential features. Research is crucial to identify suitable options that align with the specific needs and scale of your business. Explore reviews and comparisons to determine the best fit.
How can I track the success of my CRM implementation?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) like sales efficiency, customer satisfaction, and conversion rates can be monitored to assess CRM effectiveness. Utilize CRM dashboards to visualize these metrics and identify areas for improvement.
How do I integrate my CRM with existing business software?
Careful planning and research are essential when integrating a CRM with existing software. Seek guidance from CRM providers and explore options for seamless data transfer and synchronization. Thorough testing and troubleshooting are crucial to ensure smooth operation.