Zoho’s user management system is crucial for businesses looking to optimize security and productivity. This guide dives deep into the intricacies of Zoho user management, covering everything from creating and managing users to securing access and troubleshooting common issues. Understanding user roles and permissions is key to maximizing the potential of your Zoho applications.
From setting up new accounts to managing access controls, this guide walks you through the complete user management process within various Zoho applications. It provides a clear overview of how to effectively leverage user management features to enhance security and streamline your workflow. Discover practical strategies for ensuring efficient and secure user management practices in your Zoho environment.
Introduction to Zoho User Management
Zoho’s user management system provides a centralized platform for controlling access and permissions across various Zoho applications. This system is crucial for businesses seeking to manage their workforce efficiently and maintain a secure environment. Effective user management is essential for streamlined workflows, data protection, and adherence to compliance regulations.Zoho’s comprehensive approach to user management enables businesses to easily assign roles and permissions, tailor access to specific data and functionalities, and track user activity.
This robust system fosters a secure and compliant environment while boosting productivity and reducing administrative overhead.
Overview of Zoho User Management Features
Zoho’s user management features are designed to be flexible and scalable, adapting to the changing needs of a business. The system offers granular control over user accounts, roles, and permissions, ensuring that each user has access only to the resources necessary for their job functions. This approach helps to prevent unauthorized access and maintain data integrity.
User Roles and Permissions
Zoho applications employ a hierarchical system of user roles and permissions. Different roles grant varying levels of access to data and functionalities within an application. For instance, an administrator role might have full access, while a standard user role might be restricted to specific modules or data views. This tiered structure ensures that sensitive data remains protected while still allowing authorized users to perform their tasks effectively.
Understanding these roles and their corresponding permissions is vital for effective workforce management.
Importance of Robust User Management in a Business Context
Robust user management is paramount for a business’s operational efficiency and security. By defining clear roles and permissions, businesses can avoid security breaches, protect sensitive data, and maintain compliance with industry regulations. It also helps in streamlining workflows by ensuring that the right people have the right access to the right information at the right time. This ultimately leads to increased productivity and reduced administrative burden.
Impact of User Management on Security and Compliance
Effective user management directly impacts a business’s security posture and compliance efforts. By controlling user access, businesses can minimize the risk of data breaches and unauthorized activities. It also helps to ensure that the organization adheres to data privacy regulations and industry standards, thus mitigating potential legal and reputational risks. Implementing robust user management practices is essential for protecting a business’s assets and maintaining its credibility.
Comparison of User Management Across Zoho Applications
| Application | User Roles | Permission Granularity | Data Access | Security Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zoho CRM | Administrator, Sales Representative, Marketing Manager, etc. | Highly granular, allowing specific access to records, modules, and functionalities. | Users can access customer data, sales opportunities, and marketing campaigns based on their roles. | Role-based access control (RBAC), audit logs, multi-factor authentication (MFA) options. |
| Zoho Mail | Administrator, User, Delegate | Granular, allowing control over mailbox access, sending restrictions, and delegated permissions. | Users can access emails, manage contacts, and collaborate on projects via email. | Strong spam filters, email encryption, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) options. |
This table provides a basic comparison of user management in Zoho CRM and Zoho Mail. Other Zoho applications, such as Zoho Projects or Zoho Books, have their own unique user management features that may differ in specific aspects.
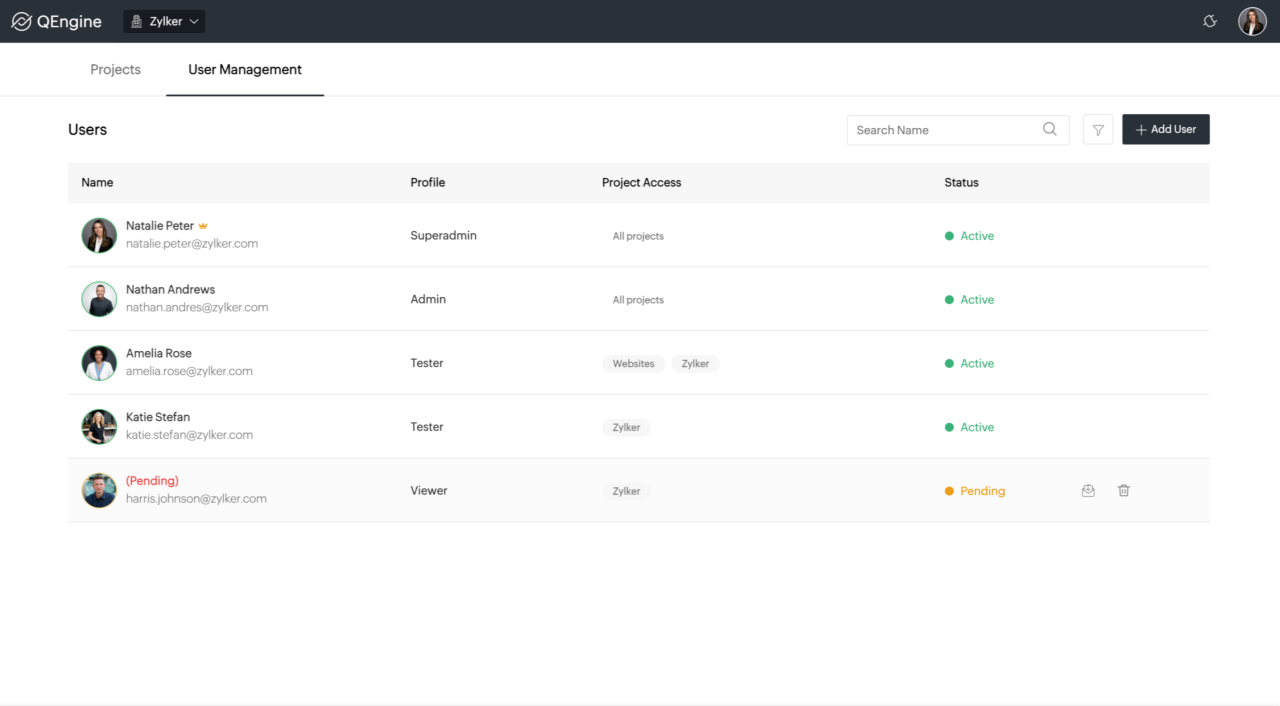
User Creation and Management
Zoho applications offer robust user management capabilities, enabling administrators to effectively create, manage, and assign roles to users. This empowers organizations to control access to sensitive data and resources while maintaining a well-organized user base. Proper management ensures compliance and optimized productivity.
Creating New Users
Creating new users within Zoho applications typically involves accessing the user management section of the application. The specific steps may vary slightly depending on the application. However, a common process includes providing necessary information, such as the user’s name, email address, and desired password. Administrators often need to specify the user’s role and department, further tailoring access permissions.
Verification and approval steps may also be included, depending on the application’s security settings.
Assigning Roles and Permissions
Zoho applications typically employ a role-based access control system. Roles define a set of permissions, granting users specific access levels to data and functionalities. Administrators can assign these roles to users, controlling what they can see and do within the application. This granular control enhances security and maintains data integrity. For instance, a “Sales Representative” role might grant access to sales data but not financial reports.
Managing User Profiles and Details
Managing user profiles and details is crucial for maintaining accurate records and facilitating efficient communication. Administrators can update user information, such as contact details, roles, or access levels. This ensures that the application’s records are current and reliable. Regular review and updates help maintain compliance and organizational efficiency.
Adding or Removing Users from Groups
Users can be organized into groups for collaborative projects or shared access. Adding or removing users from these groups is a straightforward process. Group membership directly impacts access permissions and resource allocation. For instance, adding a user to a project team automatically grants them access to the relevant files and functionalities within that team.
Bulk User Creation and Management
Bulk user creation and management is a time-saving feature. Administrators can import user data from external sources or create multiple users with similar attributes using templates or spreadsheets. This significantly speeds up the process for large organizations or onboarding new employees. Data validation and error handling are often included to ensure data accuracy.
User Attributes and Fields
The following table Artikels common user attributes and their corresponding fields, providing a comprehensive overview of the information typically stored within Zoho applications’ user management systems.
| Attribute | Field Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| First Name | Text | User’s first name |
| Last Name | Text | User’s last name |
| Email Address | User’s primary email address | |
| Password | Password | User’s password |
| Role | Dropdown/Selection | Assigned role defining permissions |
| Department | Text/Dropdown | User’s department or team |
| Contact Number | Phone Number | User’s contact number |
| Address | Text | User’s address |
| Status | Dropdown/Selection | Active/Inactive status of the user |
User Authentication and Security
Zoho’s user management system prioritizes security to protect sensitive data and maintain a secure environment for all users. Robust authentication methods and comprehensive security measures are critical components of this system. Understanding these aspects is essential for maintaining data integrity and preventing unauthorized access.Zoho employs various authentication methods to verify user identities and control access to resources. These methods are designed to balance user convenience with stringent security protocols.
Security measures extend beyond authentication, encompassing policies and procedures to safeguard user accounts from potential threats.
Authentication Methods Supported by Zoho
Zoho offers a range of authentication methods, each tailored to specific security needs and user preferences. These methods include username/password combinations, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and single sign-on (SSO) integrations. These options are designed to cater to a broad spectrum of security requirements.
Security Measures for User Accounts
Zoho implements several security measures to protect user accounts. These include robust password policies, regular security audits, and data encryption protocols. These measures are critical to safeguard user data and prevent unauthorized access. Regular security audits help identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
Password Management Best Practices
Strong password management is crucial for safeguarding user accounts. Users should follow best practices to create and maintain strong passwords. This includes using unique passwords for each account, employing a password manager, and enabling multi-factor authentication. These practices significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Utilizing a password manager can assist in generating and storing strong, unique passwords.
Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a critical security measure that adds an extra layer of protection beyond a simple username and password. By requiring multiple verification steps, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised. It’s a crucial security component for enhancing account protection.
Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
| Security Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Phishing Attacks | Implement robust email filtering and security awareness training for users. Use strong spam filters and educate users on identifying phishing attempts. |
| Malware Infections | Regularly update software and operating systems. Use antivirus and anti-malware software. Educate users about safe browsing habits and avoid suspicious websites. |
| Brute-Force Attacks | Implement account lockout policies and rate limiting measures to prevent automated attempts at gaining access. Utilize robust account lockout protocols. |
| Data Breaches | Employ strong encryption protocols for sensitive data. Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities. |
| Social Engineering | Provide comprehensive security awareness training to users, covering techniques like phishing and impersonation. Establish clear communication protocols for sensitive information. |
User Access Control and Permissions
Zoho’s user access control system is a crucial element for maintaining data security and operational efficiency. Properly configured permissions ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive information and applications, mitigating risks of unauthorized data breaches and misuse. This section details the hierarchical structure of permissions, granting and revoking access, and controlling sensitive information.User permissions in Zoho are organized in a hierarchical structure, enabling granular control over access to data and applications.
This structure allows administrators to assign varying levels of access, from basic viewing to complete control, ensuring that users only interact with the data and features relevant to their roles.
Permission Hierarchy in Zoho
Zoho’s permission structure is tiered, allowing for a range of access levels. This tiered system enables a fine-grained approach to managing access, where administrators can control who has access to which data and applications. Different roles can have different permissions, allowing for greater flexibility and control.
Granting and Revoking Access
Granting and revoking access to specific data or applications is a straightforward process within Zoho. Administrators can modify user roles and permissions to adjust access levels based on user responsibilities and organizational needs. This dynamic approach to access control allows for adaptation to evolving business requirements.
Controlling Access to Sensitive Information
Controlling access to sensitive information is a critical aspect of data security. Administrators can restrict access to confidential data by assigning appropriate permissions. By using role-based access control, Zoho ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized disclosure.
Creating Custom Permission Sets
Custom permission sets in Zoho provide the flexibility to tailor access rights to specific user needs. Administrators can create custom roles with tailored permissions for specific teams or departments, adapting the system to unique organizational requirements. This customizability allows for a highly granular control over user access.
Security Implications of Different Access Control Models
Various access control models exist, each with its own set of security implications. The choice of model depends on the specific security needs of the organization. Role-based access control (RBAC), a common model in Zoho, offers a structured approach, allowing for granular control over access. This approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access compared to less structured models.
Different Permission Levels and Corresponding Access Rights
| Permission Level | Access Rights |
|---|---|
| Viewer | Can view data but cannot modify or delete it. |
| Editor | Can view, modify, and delete data within their designated scope. |
| Administrator | Can perform all actions on all data within the system. |
This table provides a concise overview of the different permission levels and their corresponding access rights. This structured approach simplifies the management of user access, allowing for efficient and effective control over data and applications.
User Management Tools and Integrations
Zoho’s user management system offers a robust platform for controlling access and managing user accounts. However, its power is amplified when integrated with other tools and services. This section explores how to leverage third-party integrations, automate processes, monitor user activity, and integrate with other business applications for a streamlined and efficient user management experience.
Third-Party Integrations
Zoho integrates with numerous third-party applications. This allows for seamless data flow and unified management across different platforms. Integration possibilities can be beneficial in scenarios where users need to be managed and synchronized across multiple platforms.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) Providers: Integrating with SSO providers like Okta, OneLogin, or Azure Active Directory allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials. This enhances security and simplifies user authentication.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Platforms: Integrating with IAM platforms can provide advanced user lifecycle management, such as automated user provisioning, deprovisioning, and access controls. This reduces manual effort and ensures consistency across the organization.
- Directory Services: Zoho can be configured to sync with directory services like Active Directory. This simplifies user management by leveraging existing infrastructure.
User Provisioning and Deprovisioning Automation
Automating user provisioning and deprovisioning streamlines administrative tasks and reduces the risk of human error. This automation process ensures new hires are automatically added to relevant systems and terminated users are removed promptly.
- Automated User Creation: Integrate with HR systems to automatically create user accounts when new employees are hired. This ensures access to necessary resources is granted immediately, eliminating delays and improving onboarding efficiency.
- Automated User Deletion: Configure the system to automatically remove user accounts when employees leave the company. This ensures that sensitive data is protected and access to resources is revoked promptly.
User Activity Monitoring and Auditing
Monitoring user activity and auditing access controls provides insights into user behavior and helps maintain security. This functionality helps identify unusual activity and ensure compliance with security policies.
- Activity Logging: Zoho’s user management system logs user actions, such as login attempts, access to specific resources, and data modifications. This detailed record provides a historical view of user activity and can be used for troubleshooting and auditing purposes.
- Security Alerts: Set up alerts for unusual login patterns or unauthorized access attempts. This helps quickly identify and respond to potential security threats.
Integration with Other Business Applications
Integration with other business applications creates a unified platform for managing user access and activities. This unified view simplifies user administration and provides a centralized location for managing user permissions across different systems.
- CRM Systems: Integrate with CRM systems to link user accounts with customer interactions and sales data. This allows for granular control over access to customer information based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Project Management Tools: Integrate with project management tools to associate user accounts with project assignments and access levels. This improves team management and ensures users have appropriate permissions for their tasks.
Reporting Capabilities
Zoho’s user management system provides reporting capabilities to track user activity and access patterns. This allows for insights into user behavior, identifying trends and potential issues.
- Access Reports: Generate reports detailing who accessed which resources, when, and for how long. These reports can be crucial for compliance and security auditing.
- User Activity Reports: Generate reports on user logins, account creations, and other key user activities. These reports can provide valuable insights into user behavior and system usage.
Integration Table
| Integration | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Single Sign-On (SSO) | Enhanced security, simplified authentication |
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Automated user lifecycle management, consistent access controls |
| Directory Services (e.g., Active Directory) | Leveraging existing infrastructure, simplified user management |
| HR Systems | Automated user creation, improved onboarding |
| CRM Systems | Linked user accounts with customer interactions, granular access control |
| Project Management Tools | Associated user accounts with projects, improved team management |
Troubleshooting User Management Issues
Managing user accounts effectively often involves resolving issues that arise. This section details common problems encountered during user management within Zoho and provides practical solutions. Efficient troubleshooting ensures smooth operations and maintains a secure environment for all users.
Common User Management Issues and Solutions
Troubleshooting user management issues often involves understanding the root cause of the problem. Here’s a breakdown of common issues and their solutions:
- Password Reset Requests: The process for handling password reset requests is crucial. Users can initiate a password reset via a self-service portal or through administrative intervention. The system should validate the user’s identity before granting a reset, preventing unauthorized access. A strong password policy is essential for maintaining account security.
- Lost or Forgotten Accounts: Losing access to a Zoho account can be frustrating. Recovery procedures should be clearly defined and easy to follow. These procedures often involve verifying the user’s identity through various means, like email confirmation or security questions. A well-defined process for account recovery is critical for minimizing disruptions and maintaining user trust.
- User Account Lockouts: Account lockouts are a security measure, but they can be problematic if a user is locked out unintentionally. The system should have clear guidelines for lockout duration and the process for unlocking accounts. This involves confirming the user’s identity to prevent unauthorized access while ensuring quick restoration of access for legitimate users.
- Access Denied Errors: Access denied errors can stem from various causes, such as incorrect credentials, insufficient permissions, or issues with the network connection. Troubleshooting these errors requires a systematic approach. Checking user roles and permissions, validating credentials, and verifying network connectivity are key steps in resolving access denied errors.
Password Reset Request Resolution Process
Initiating a password reset often involves a multi-step process. The user typically needs to provide verification details to ensure their identity. The system then generates a temporary password and sends it to the registered email address. This temporary password allows the user to log in and change it to a more secure password.
Lost or Forgotten Account Recovery Procedure
Recovering a lost or forgotten account involves several stages. First, the user should try to remember their account credentials. If unsuccessful, a recovery form is often available on the platform. The user may need to provide details such as the email address associated with the account, answer security questions, or provide additional verification. A robust recovery procedure is essential to prevent account loss while adhering to security protocols.
Managing User Account Lockouts
User account lockouts are a security feature. The system often locks an account after a predefined number of failed login attempts. Unlocking a locked account usually involves providing the correct credentials or contacting an administrator. A configurable lockout policy is often implemented, allowing administrators to customize the lockout settings based on their security requirements.
Resolving Access Denied Errors
Troubleshooting access denied errors often involves checking multiple factors. The system might deny access if the user’s credentials are incorrect, if their permissions are insufficient for the requested action, or if there’s a network issue. Reviewing user roles and permissions, verifying network connectivity, and validating credentials are critical steps in addressing access denied errors.
Table of Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Password Reset Request Issues | Verify user identity; generate a temporary password; guide user through password change. |
| Lost or Forgotten Account | Use account recovery form; provide required verification; restore access. |
| Account Lockout | Contact administrator; provide valid credentials; review lockout policy. |
| Access Denied Error | Check credentials; verify permissions; ensure network connectivity. |
Best Practices for Zoho User Management
Effective Zoho user management is crucial for maintaining a secure and productive work environment. A well-structured approach to user creation, access control, and regular reviews is essential for optimal system performance and data protection. Implementing best practices minimizes security risks and maximizes user efficiency.
Strategies for Efficient User Management
A robust user management strategy involves streamlining processes for creating, updating, and removing user accounts. This proactive approach ensures that user access aligns with their roles and responsibilities, reducing potential security vulnerabilities and simplifying administrative tasks. Establishing clear guidelines for user account creation, including required information and approval workflows, will significantly improve the overall efficiency of the user management process.
Implementing Secure User Management Practices
Security is paramount in user management. Implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regular security audits is critical. These measures mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Furthermore, regularly reviewing and updating security protocols ensures that the system remains aligned with evolving security threats.
Improving User Productivity Through Effective Access Control
Appropriate access control is key to user productivity. Granting users only the permissions they need to perform their job tasks will minimize the risk of accidental data breaches and improve overall system performance. This targeted approach reduces the potential for errors and enhances the user experience by avoiding unnecessary complications.
Importance of Regular User Audits and Reviews
Regular user audits and reviews are vital for maintaining system integrity and compliance. Audits help identify any unauthorized access attempts or potential security gaps. These reviews also allow for the modification of access permissions as roles and responsibilities evolve within the organization. Such reviews help ensure compliance with regulations and minimize the risks associated with outdated access rights.
Summary of Best Practices for User Management
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Streamlined User Creation | Establish clear guidelines and approval workflows for user account creation to maintain accuracy and security. |
| Robust Password Policies | Implement strong password policies, including length, complexity, and expiration requirements, to enhance account security. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Enable MFA to add an extra layer of security, requiring multiple verification steps for login access. |
| Regular Security Audits | Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance with regulations. |
| Targeted Access Control | Grant users only the necessary permissions to perform their job tasks, minimizing the risk of data breaches and improving efficiency. |
| Regular User Reviews | Conduct periodic reviews of user accounts and access privileges to ensure alignment with evolving roles and responsibilities. |
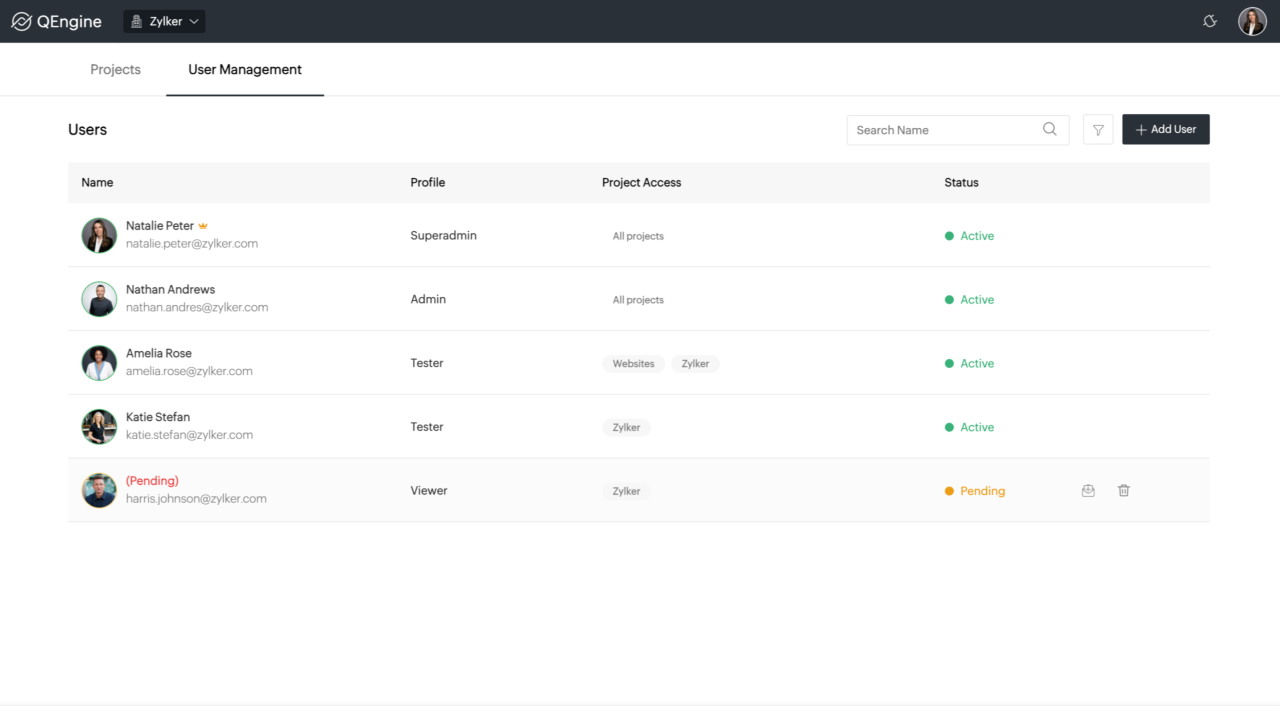
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering Zoho user management empowers businesses to effectively utilize their Zoho applications. This guide has explored the essential aspects of user creation, authentication, access control, and troubleshooting, offering practical insights for optimizing your Zoho environment. Implementing the best practices Artikeld will lead to a more secure, productive, and compliant system.
Essential FAQs
What are some common user management issues in Zoho?
Common issues include password resets, lost accounts, access denied errors, and issues with user role assignments. Our guide provides solutions to these problems.
How do I create a new user in Zoho CRM?
The process for creating a new user in Zoho CRM involves navigating to the user management section, entering the required details, and assigning appropriate roles and permissions.
What are the different user roles in Zoho Mail?
Zoho Mail offers various user roles, each with specific permissions. These roles define the level of access granted to different users.
Can I automate user provisioning and deprovisioning in Zoho?
Yes, Zoho integrates with various third-party tools to automate these processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing manual effort.
What security measures are in place to protect Zoho user accounts?
Zoho employs robust security measures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), secure password policies, and regular security audits to safeguard user accounts.

![The Best Google Sheets CRM Free Template [+ How To Use] The Best Google Sheets CRM Free Template [+ How To Use]](https://budget.novel.or.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/6415b6903669f805050b1621_7b7ec1b9-a062-4ba8-a099-25fbe4e15274-2-1-60x60.png)