Choosing the right Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software is crucial for accounting firms seeking to streamline operations and enhance client relationships. This guide delves into the intricacies of selecting the best CRM for accounting firms, addressing their unique needs and pain points. From optimizing client interactions to boosting reporting and analytics, we’ll explore essential features, integrations, and scalability considerations.
Accounting firms often grapple with managing client data, communication, and workflow efficiently. A robust CRM system can alleviate these challenges by centralizing client information, automating tasks, and providing insightful reporting. This detailed exploration will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions when selecting a CRM tailored to your firm’s specific requirements.
Introduction to CRM for Accounting Firms
A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system, tailored for accounting firms, is a software solution designed to manage and optimize interactions with clients. It goes beyond basic contact information, enabling firms to track client history, manage projects, and automate tasks, ultimately improving client service and firm profitability. Effective CRM use streamlines workflows, reduces errors, and fosters stronger client relationships, contributing to the overall success of the accounting practice.Accounting firms often face challenges in managing a large volume of client data, juggling multiple projects, and maintaining consistent communication.
These issues can lead to missed deadlines, inaccurate financial reporting, and strained client relationships. A well-implemented CRM system can address these pain points by providing a centralized platform for storing and accessing client information, scheduling appointments, and tracking project progress, ultimately improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the firm’s operations.
Typical Needs and Pain Points of Accounting Firms
Accounting firms frequently face issues managing large volumes of client data, which can lead to information silos and inconsistencies. Maintaining accurate client records, tracking project timelines, and ensuring timely communication across teams can be challenging. Often, manual processes for client interaction lead to errors, missed deadlines, and inefficient resource allocation. These challenges can be mitigated by implementing a CRM system, which provides a centralized platform for managing client information, streamlining communication, and automating tasks.
Common Features in Accounting Firm CRMs
CRMs designed for accounting practices typically include features for managing client accounts, including contact details, financial history, and communication logs. These systems also often offer project management tools to track progress, deadlines, and allocate resources. Key features include automated reminders, task management, and reporting tools to analyze performance. Integration with existing accounting software is another common feature, streamlining data flow and reducing manual entry.
Role of CRM in Streamlining Client Interactions and Processes
A CRM system plays a crucial role in streamlining client interactions. By centralizing client data, firms can improve communication, track interactions, and manage expectations. This centralized system allows for easier project management, including tracking progress, deadlines, and resource allocation. Automation of tasks like sending reminders and generating reports can free up staff time for more complex client engagements.
This overall efficiency improvement contributes to improved client satisfaction and increased profitability.
Key Benefits of Using a CRM for Accounting Firms
| Feature | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized Client Data | Stores all client information in one place, accessible to authorized staff. | Improved data accuracy, reduced data redundancy, enhanced collaboration, and easier access to client history. | Potential for data security concerns if not properly managed. |
| Automated Tasks | Automates routine tasks like sending reminders, generating reports, and scheduling appointments. | Increased efficiency, reduced workload for staff, minimized errors, and improved response time. | Initial setup and configuration may require significant time and resources. |
| Improved Communication | Facilitates communication among staff and with clients through centralized messaging and notifications. | Enhanced client satisfaction, improved collaboration, reduced misunderstandings, and better project management. | Requires training and adherence to communication protocols to ensure effectiveness. |
| Enhanced Reporting | Provides comprehensive reports on client interactions, project performance, and financial data. | Data-driven insights for better decision-making, improved forecasting, and enhanced strategic planning. | Reporting overload is possible if not managed properly; potential for misinterpretation of data. |
Key Features to Consider
Choosing the right CRM for an accounting firm is crucial for streamlining operations and enhancing client relationships. A well-selected system can significantly improve efficiency, allowing professionals to focus on strategic tasks rather than administrative burdens. A robust CRM should seamlessly integrate with existing accounting software and provide a comprehensive view of client interactions.Effective client management, comprehensive reporting, and seamless integration are vital for any accounting CRM.
These features enable firms to maintain accurate client records, track progress on projects, and generate insightful reports. By prioritizing these features, accounting firms can maximize the return on investment from their CRM.
Client Management Features
Client management is paramount in an accounting CRM. A strong system should allow for detailed client profiles, encompassing contact information, financial history, and project details. This centralized repository facilitates efficient communication and ensures that all relevant information is readily available to the team. Furthermore, features like task management and automated reminders are crucial for staying organized and on track with client deadlines.
This level of organization translates into enhanced client satisfaction and improved project outcomes.
Reporting and Analytics Capabilities
Comprehensive reporting and analytics are essential for data-driven decision-making in accounting. A CRM should provide various reporting options, ranging from simple summaries to detailed breakdowns of client interactions. These reports should be customizable to address specific firm needs and readily exportable to facilitate analysis and strategic planning. Key metrics, such as client profitability and project timelines, should be readily available for review and adjustment.
This data-driven approach allows firms to identify trends, improve efficiency, and ultimately, optimize profitability.
Comparison of Reporting Features
Different CRM systems offer varying reporting capabilities. Some may excel at generating simple dashboards for overview data, while others may provide in-depth, customizable reports. Consider whether the CRM offers pre-built reports tailored to accounting functions, or if it allows for advanced customization to suit specific reporting needs. A crucial consideration is the system’s ability to export data into various formats for further analysis with external tools.
Example Accounting CRM Systems
| System Name | Client Management | Reporting | Integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| System A | Detailed client profiles, task management, automated reminders, secure document storage. | Pre-built reports for financial performance, customizable dashboards, data export options. | Integrates with major accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero). |
| System B | Comprehensive client history, advanced search filters, customizable contact management. | In-depth reporting features, real-time data visualization, interactive charts. | Integrates with various accounting platforms and other business tools. |
| System C | Extensive client data storage, robust security features, automated data entry. | Customizable reports, advanced filtering options, drill-down capabilities. | Limited integration options compared to others. |
Integration and Compatibility
Choosing the right CRM for an accounting firm hinges significantly on its ability to seamlessly integrate with existing systems. Effective integration streamlines workflows, minimizes data duplication, and enhances overall efficiency. This is crucial for firms needing to maintain client data, track financial transactions, and manage projects across various platforms.A well-integrated CRM system can automatically populate client information from accounting software, reducing manual data entry and the risk of errors.
This also allows for real-time data updates, ensuring everyone has access to the most current information. This efficiency translates into better client service and potentially higher profitability.
Essential Integrations for Accounting CRMs
A robust accounting CRM should integrate with core accounting software, such as QuickBooks, Xero, or Sage. Beyond this, crucial integrations encompass email marketing platforms (e.g., Mailchimp, Constant Contact), project management tools (e.g., Asana, Trello), and potentially time-tracking software. These integrations can significantly streamline client communication, project management, and time billing processes.
Accounting Software Integrations (e.g., QuickBooks)
Many CRMs offer integrations with popular accounting software like QuickBooks. These integrations typically involve transferring client data, automating invoice generation, and synchronizing financial transactions. The specific functionalities of these integrations vary between CRM platforms, so thorough research and testing are recommended before implementation. For example, a CRM might allow users to automatically import client contact information from QuickBooks into the CRM database, while another might allow for two-way synchronization of transaction data.
This enables seamless data flow between the CRM and accounting software, minimizing manual data entry and enhancing overall efficiency.
Integrating Existing Systems with a CRM
Accounting firms can integrate their existing systems with a CRM in several ways. A direct API connection allows for real-time data transfer between systems. File import/export functionalities provide a method for transferring data in bulk. Some CRMs offer custom integrations or third-party apps that bridge the gap between disparate systems. Careful consideration of data format compatibility is crucial for successful implementation.
Furthermore, the chosen method should align with the firm’s specific technological infrastructure and data management policies.
Data Security and Privacy in CRM Integrations
Data security and privacy are paramount when integrating accounting software with a CRM. Strict adherence to industry standards (like GDPR) is essential. Secure data transfer protocols and robust encryption mechanisms are vital. Accounting firms should thoroughly vet potential CRM vendors for their security practices. Ensuring data encryption during transfer and storage is critical.
Regular security audits and data breach response plans are crucial for protecting sensitive financial information.
Examples of Successful CRM Integrations with Accounting Software
Several accounting firms have successfully integrated their existing accounting software with CRMs. For instance, a firm using QuickBooks might integrate with a CRM to automate the process of creating invoices based on client data and project details, saving valuable time and minimizing errors. Another firm using Xero might integrate their CRM with their time-tracking software to automatically record time spent on client projects, leading to accurate billing and enhanced project management.
Compatibility Issues and Solutions for Accounting CRMs
| Software | CRM | Issue | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| QuickBooks Online | Salesforce | Limited two-way data synchronization | Utilize a third-party integration app to bridge the gap |
| Xero | Zoho CRM | Difficulties with custom fields | Adjust CRM settings or seek customization options |
| Sage 50 | Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Lack of direct API integration | Employ file import/export functionality for data transfer |
| QuickBooks Desktop | HubSpot CRM | Issues with data format compatibility | Employ data mapping tools to resolve format discrepancies |
Client Relationship Management

A robust CRM system is crucial for accounting firms to effectively manage client relationships. It streamlines communication, enhances service delivery, and ultimately contributes to increased client retention. By centralizing client data and automating key tasks, CRMs empower accounting professionals to focus on building stronger, more profitable client partnerships.Client relationship management is a cornerstone of success in the accounting industry.
Modern CRMs facilitate sophisticated strategies for building and maintaining strong client connections, leading to greater client satisfaction and, consequently, increased profitability.
Client Relationship Strategies
Effective client relationship management involves proactive strategies that go beyond simply managing client data. CRMs facilitate the implementation of these strategies by providing tools for targeted outreach, personalized communication, and proactive service. These tools help accounting firms anticipate client needs and provide timely, relevant solutions.
Improved Client Communication and Service
A CRM system empowers accounting firms to enhance client communication and service through various features. Automated reminders for appointments, email templates for common inquiries, and personalized communication based on client history are all possibilities. These features ensure consistent and timely communication, which directly contributes to improved client satisfaction. For example, a CRM might automatically send a follow-up email to a client after a meeting, summarizing key takeaways and next steps.
Client Interaction and History Management
Managing client interactions and tracking client history is a critical aspect of CRM implementation. CRMs allow for the meticulous documentation of all interactions, from initial consultations to ongoing support. This comprehensive history is readily accessible to all relevant team members, fostering a cohesive and consistent experience for the client. A detailed client history enables accounting firms to understand client preferences, identify potential issues early, and provide proactive solutions.
Client Retention Improvement
Client retention is paramount for sustained growth in any accounting firm. CRMs provide valuable tools to improve client retention by enabling proactive outreach, targeted communication, and personalized service. For instance, a CRM can be configured to automatically send birthday greetings or anniversary messages to clients, demonstrating appreciation and strengthening the relationship. Regular follow-ups and proactive identification of potential issues also contribute to increased client retention.
Client Data Security
Robust client data security is paramount within a CRM system for accounting firms. Accounting firms are entrusted with sensitive financial information, making data security a top priority. CRMs must incorporate advanced security protocols to safeguard client data from unauthorized access, breaches, and data loss. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. The implementation of multi-factor authentication and data encryption adds an additional layer of protection.
Scalability and Growth
A robust CRM system is crucial for accounting firms aiming for sustained growth. It provides a framework for managing expanding client bases and complex workflows, enabling firms to adapt effectively to increasing demands. The right CRM solution will not only handle the current workload but also anticipate future needs, allowing the firm to scale operations smoothly.
Adapting to Expanding Client Base
A CRM system must be capable of handling an increasing number of clients and associated data. This involves features that facilitate efficient client record management, regardless of the volume. Effective solutions should include automated data entry and robust search capabilities, ensuring that vital client information remains accessible and up-to-date. The CRM system should also provide comprehensive reporting features to monitor key metrics, facilitating proactive identification of client needs and potential issues.
Scalability also includes the ability to add new users and roles as the firm expands, ensuring everyone has access to the information they need.
Scaling to Meet Growing Needs
Accounting firms often experience rapid growth, requiring their CRM to adapt. For example, a small firm with a few dozen clients might initially use a simpler CRM. As the firm grows and acquires more clients, a more sophisticated solution with advanced features, such as automated reporting, custom dashboards, and advanced analytics, becomes necessary. Successful implementations of CRM solutions for growing practices demonstrate that choosing a scalable platform allows the firm to handle the increased complexity and volume of client interactions without significant disruptions to workflows.
A well-structured CRM system facilitates the addition of new services or departments, ensuring seamless transitions.
Efficient Workflow Management for Future Expansion
A CRM system empowers accounting firms to streamline their workflows, which is essential for future expansion. By automating tasks like data entry, communication, and reporting, a CRM frees up valuable staff time for higher-level strategic activities. This automation leads to improved efficiency, allowing the firm to handle increased workloads and take on new clients without overburdening staff. The efficient flow of information within the CRM supports better decision-making, facilitating strategic growth plans.
Strategies for Scaling CRM Implementation
Implementing a CRM effectively for an accounting firm requires careful planning and execution. This involves:
- Phased Rollout: Implementing the CRM in phases, starting with a pilot group and gradually expanding to other departments or teams. This allows for testing and adjustments before a full-scale launch. This approach reduces the risk of widespread disruption and allows for feedback incorporation.
- Comprehensive Training: Providing thorough training to all staff members using the CRM. Clear guidelines and practical demonstrations of the CRM’s features are crucial to ensure efficient use and maximize its benefits. This will guarantee effective utilization of the system across the firm.
- Regular System Updates: Staying current with the latest system updates and features is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and security. This proactive approach ensures that the CRM remains aligned with evolving business needs and best practices.
- Regular Review and Evaluation: Periodically reviewing and evaluating the CRM’s performance, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments. This continuous process allows for adapting to changing needs and maximizing the benefits of the CRM solution.
Choosing the Right CRM
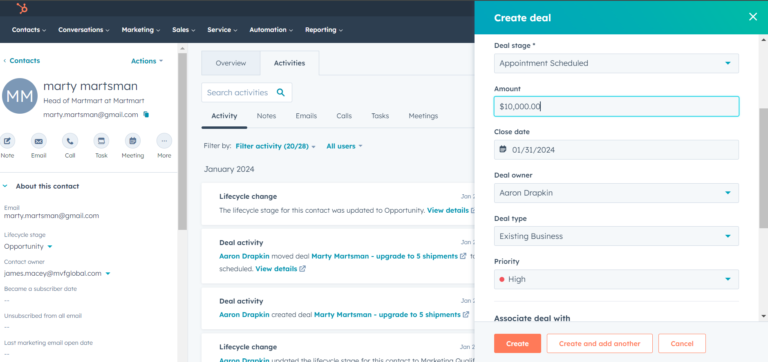
Selecting the appropriate Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is crucial for accounting firms to streamline operations, enhance client relationships, and boost profitability. A well-chosen CRM can automate tasks, improve communication, and provide valuable insights into client interactions, ultimately leading to a more efficient and client-centric practice.Careful consideration of various factors, from pricing models to user interface, is essential in making an informed decision.
A tailored CRM solution will directly impact the firm’s ability to manage client data, track engagements, and deliver exceptional service.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a CRM
Choosing a CRM system requires careful evaluation of several factors. These factors should align with the firm’s specific needs and growth trajectory. Consideration of these factors helps ensure the chosen CRM system is a good fit and effectively supports the firm’s objectives.
- Budget: Pricing models for CRM systems vary significantly. Some offer tiered pricing structures, while others may charge based on the number of users or features utilized. Budget constraints should influence the selection process, ensuring the chosen system aligns with the firm’s financial resources.
- Scalability: The chosen CRM should accommodate future growth. An accounting firm’s needs may evolve as it expands its services or client base. A system’s ability to adapt to these changes is vital for long-term success.
- Integration: Integration with existing accounting software and other business applications is critical for seamless data flow. A CRM system that can easily connect with other tools within the firm’s infrastructure is essential for maximizing efficiency.
- User Interface (UI) and Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is essential for efficient adoption and utilization by staff members. A CRM system that is intuitive and easy to navigate will minimize training time and enhance overall user satisfaction.
- Support and Training: The provider’s level of support and training resources is critical for effective implementation and ongoing use. Reliable support and comprehensive training materials ensure a smooth transition and enable staff to fully leverage the CRM’s capabilities.
Pricing Models and Features Comparison
Different CRM systems offer varying pricing models and features. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting a system that best meets the firm’s specific needs and budget.
- Subscription-based models: These models often involve monthly or annual fees, typically based on the number of users, features, or storage capacity. This model provides predictable costs and allows firms to adjust their spending as needed.
- Per-user pricing: Some CRMs charge a fee for each user accessing the system, making it essential to consider the projected user base. This model allows for flexibility in scaling the number of users according to the firm’s growth.
- Custom pricing: Certain systems offer customized pricing packages based on the specific requirements of the accounting firm. This approach provides a degree of flexibility for firms with unique needs or extensive feature requirements.
Key Metrics for CRM Performance Evaluation
Evaluating a CRM system’s performance involves considering various key metrics relevant to accounting firms. Metrics should be chosen to align with the firm’s specific objectives and priorities.
- Client Satisfaction: Measuring client satisfaction through surveys or feedback mechanisms is crucial. Positive client experiences directly impact the firm’s reputation and long-term success.
- Lead Conversion Rates: Tracking the percentage of leads that convert into paying clients helps assess the CRM’s effectiveness in generating business.
- Sales Cycle Efficiency: Monitoring the time it takes to close deals helps evaluate the CRM’s impact on sales productivity.
- Data Accuracy and Accessibility: Ensuring accurate and readily accessible client data is essential for efficient operations. A CRM system should facilitate easy retrieval and management of crucial client information.
Importance of User Interface and Ease of Use
A user-friendly CRM interface is crucial for seamless adoption and ongoing use. The system’s intuitiveness directly impacts staff productivity and satisfaction.A CRM system should be designed with an intuitive interface that minimizes training time and allows staff to quickly learn and use the system’s features. This contributes to a more productive workflow.
Popular CRM Systems Comparison
Evaluating different CRM systems is crucial for selecting the most suitable option for an accounting firm. This comparison provides a starting point for evaluating different systems based on their strengths and weaknesses.
| System | Pros | Cons | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce | Extensive features, robust integration capabilities, strong customer support, scalable platform. | Steep learning curve, high initial investment, complex interface for some users. | Variable, typically starts at a few hundred dollars per user per month. |
| Zoho CRM | Comprehensive features, affordable pricing, user-friendly interface, excellent integration options. | Limited customization options compared to some competitors, potential performance issues with high user volumes. | Variable, typically starts at a few dollars per user per month. |
| HubSpot CRM | Free tier available, user-friendly interface, excellent marketing automation tools, good integration options. | Limited advanced features, may not be suitable for firms with highly specialized needs. | Variable, typically starts at a free tier with paid tiers based on features and user count. |
Implementation and Training
Implementing a CRM system in an accounting firm requires careful planning and execution to ensure smooth adoption and maximize its benefits. A well-structured implementation process, coupled with comprehensive training, is crucial for successful CRM integration. This involves not just technical setup but also fostering a culture of understanding and usage among accounting staff.Effective CRM implementation is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process of adaptation and refinement.
Success hinges on the ability of the firm’s staff to embrace the system and use it effectively to streamline their workflow. A well-defined implementation plan and dedicated training sessions are critical to achieving this goal.
Steps in Implementing a CRM System
A phased approach to implementation is recommended. This minimizes disruption and allows for adjustments along the way. This process ensures a gradual integration and avoids overwhelming the team.
A phased approach to CRM implementation minimizes disruption and allows for adjustments along the way.
- Assessment and Planning: Thorough analysis of current workflows, identifying areas needing improvement and how the CRM can address them. This includes mapping out processes that will be integrated into the CRM system, identifying key users, and outlining realistic goals for the system’s implementation. Determining the resources required (staff time, budget) is also a crucial part of this phase.
- Data Migration: Carefully transferring existing client data into the CRM system. This step necessitates careful planning to avoid data loss or errors. Data validation checks are essential. Mapping existing data fields to CRM fields is a vital task. For example, a firm might need to convert paper-based client files to a digital format.
This could involve scanning documents and entering information into the system.
- System Configuration: Customizing the CRM system to meet the specific needs of the accounting firm. This may include setting up different user roles, defining access permissions, and configuring workflows. This step often involves collaboration between IT staff and accounting personnel to ensure optimal configuration.
- Testing and Validation: Rigorous testing of the system with real-world scenarios and user input to identify and fix potential issues. This ensures that the CRM system functions correctly and efficiently within the accounting firm’s operational context. Test cases should cover different scenarios and user roles to validate the system’s functionality.
- Pilot Launch and Feedback: A limited group of users starts using the system, providing feedback and identifying any necessary improvements. This allows the firm to fine-tune the system and identify potential pain points before full implementation. The feedback loop is crucial for the long-term success of the CRM.
- Full System Launch: The CRM system is rolled out to all relevant staff members. Clear communication about the system and its benefits is essential for a smooth transition. Training should be provided to help users adapt to the new system.
Importance of Training
Proper training ensures that accounting staff members understand how to effectively utilize the CRM system. This translates to improved efficiency, better client service, and increased profitability.
Proper training ensures that accounting staff members understand how to effectively utilize the CRM system.
Training not only imparts technical skills but also fosters a positive attitude toward using the CRM, maximizing its potential benefits. This will enhance the team’s ability to manage client interactions, track financial data, and collaborate efficiently.
Methods for Effective CRM Training
A multi-faceted approach to training is crucial.
- Hands-on Workshops: Practical sessions that allow staff to use the CRM system in real-world scenarios. This provides a chance to answer questions and build confidence in the system’s capabilities.
- Interactive Tutorials: Step-by-step guides and videos demonstrating the various functions of the CRM. These are beneficial for self-paced learning and can be reviewed later. This can be augmented by online video tutorials, readily available for different features and functionalities.
- Role-Playing Exercises: Simulated client interactions and accounting tasks to familiarize staff with CRM usage in different contexts. This enhances understanding of the CRM’s application in practical situations.
- Regular Follow-up Sessions: Ongoing support and mentorship to address any issues and questions that arise after the initial training. This ensures continued support for the team’s growth and efficiency in utilizing the system.
Measuring CRM Implementation Success
Key performance indicators (KPIs) can gauge the effectiveness of the CRM system.
- Increased Efficiency: Quantify time saved in completing tasks using the CRM compared to previous methods. This could be measured in terms of time saved per task or overall time reduction in completing key accounting procedures.
- Improved Client Satisfaction: Measure client feedback through surveys or feedback forms. This helps to assess how well the CRM system supports client interactions and service.
- Reduced Errors: Track the number of errors or discrepancies before and after implementing the CRM. This could involve examining the reduction in data entry mistakes or a decrease in client account discrepancies.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Assess how effectively the CRM facilitates communication and collaboration among team members. This involves examining the frequency of internal communication and feedback through the CRM system.
Step-by-Step Guide for Implementing a CRM
A well-defined implementation plan is crucial for a successful CRM rollout.
- Conduct a comprehensive needs assessment: Analyze current workflows, identify pain points, and determine CRM requirements.
- Select a suitable CRM system: Choose a system that aligns with the firm’s specific needs and budget.
- Plan data migration: Develop a strategy for transferring existing client data into the CRM system.
- Configure the CRM system: Customize the system to match the firm’s specific workflows and user roles.
- Implement thorough training: Provide hands-on training and ongoing support to staff.
- Pilot the system: Introduce the system to a small group of users for feedback and refinement.
- Launch the CRM system: Roll out the CRM system to all relevant staff.
- Monitor and evaluate performance: Track KPIs and gather feedback to ensure the system’s effectiveness.
Last Word

In conclusion, implementing the right CRM for accounting firms is a strategic investment that pays dividends in enhanced client relationships, improved operational efficiency, and ultimately, greater profitability. By understanding the crucial features, integrations, and scalability aspects, accounting professionals can select a CRM that effectively supports their firm’s growth and success. This guide has provided a roadmap to navigate the complexities of CRM selection, empowering accounting firms to make informed choices and maximize their return on investment.
FAQ
What are some common integrations for accounting CRMs?
Many accounting CRMs integrate with popular accounting software like QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage, enabling seamless data flow between systems. Some also integrate with email platforms, marketing automation tools, and project management software.
How does a CRM improve client communication and service?
CRMs facilitate better client communication by centralizing contact information, enabling automated communication sequences, and providing a centralized record of interactions. This enhances responsiveness and allows for personalized service.
What are the key metrics to evaluate a CRM’s performance?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for evaluating a CRM include client retention rates, response times to client inquiries, data accuracy, user adoption rates, and overall efficiency improvements.
How can I ensure data security and privacy in a CRM?
Choose a CRM provider with robust security measures, including data encryption and access controls. Implementing strong passwords and adhering to data privacy regulations (like GDPR) are also crucial.